Development and clinical evaluation of a simple optical method to detect and measure patient external motion
- PMID: 26699313
- PMCID: PMC5690156
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i5.5524
Development and clinical evaluation of a simple optical method to detect and measure patient external motion
Abstract
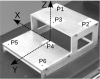
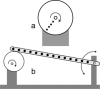
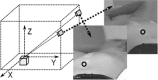
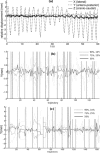
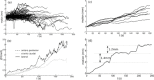
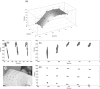
A simple and independent system to detect and measure the position of a number of points in space was devised and implemented. Its application aimed to detect patient motion during radiotherapy treatments, alert of out-of-tolerances motion, and record the trajectories for subsequent studies. The system obtains the 3D position of points in space, through its projections in 2D images recorded by two cameras. It tracks black dots on a white sticker placed on the surface of the moving object. The system was tested with linear displacements of a phantom, circular trajectories of a rotating disk, oscillations of an in-house phantom, and oscillations of a 4D phantom. It was also used to track 461 trajectories of points on the surface of patients during their radiotherapy treatments. Trajectories of several points were reproduced with accuracy better than 0.3 mm in the three spatial directions. The system was able to follow periodic motion with amplitudes lower than 0.5 mm, to follow trajectories of rotating points at speeds up to 11.5 cm/s, and to track accurately the motion of a respiratory phantom. The technique has been used to track the motion of patients during radiotherapy and to analyze that motion. The method is flexible. Its installation and calibration are simple and quick. It is easy to use and can be implemented at a very affordable price. Data collection does not involve any discomfort to the patient and does not delay the treatment, so the system can be used routinely in all treatments. It has an accuracy similar to that of other, more sophisticated, commercially available systems. It is suitable to implement a gating system or any other application requiring motion detection, such as 4D CT, MRI or PET.
Figures



References
-
- Langen K and Jones D. Organ motion and its management. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2001;50(1):265–78. - PubMed
-
- ICRU. Determination of absorbed dose in a patient irradiated by beams of X or gamma rays in radiotherapy procedures. ICRU Report 24. Bethesda, MD: ICRU; 1976.
-
- IAEA. Absorbed dose determination in external beam radiotherapy: an international code of practice for dosimetry based on standards of absorbed dose to water. IAEA Technical Report Series no. 398. Vienna: IAEA; 2000.
-
- Bortfeld T, Jiang SB, Rietzel E. Effects of motion on the total dose distribution. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2004;14(1):41–51. - PubMed
-
- Dutreix A. When and how can we improve precision in radiotherapy? Radiother Oncol. 1984;2(4):275–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

