Evaluation of Intracellular Signaling Downstream Chimeric Antigen Receptors
- PMID: 26700307
- PMCID: PMC4689545
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144787
Evaluation of Intracellular Signaling Downstream Chimeric Antigen Receptors
Abstract
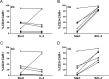
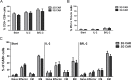
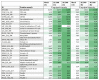
CD19-targeting CAR T cells have shown potency in clinical trials targeting B cell leukemia. Although mainly second generation (2G) CARs carrying CD28 or 4-1BB have been investigated in patients, preclinical studies suggest that third generation (3G) CARs with both CD28 and 4-1BB have enhanced capacity. However, little is known about the intracellular signaling pathways downstream of CARs. In the present work, we have analyzed the signaling capacity post antigen stimulation in both 2G and 3G CARs. 3G CAR T cells expanded better than 2G CAR T cells upon repeated stimulation with IL-2 and autologous B cells. An antigen-driven accumulation of CAR+ cells was evident post antigen stimulation. The cytotoxicity of both 2G and 3G CAR T cells was maintained by repeated stimulation. The phosphorylation status of intracellular signaling proteins post antigen stimulation showed that 3G CAR T cells had a higher activation status than 2G. Several proteins involved in signaling downstream the TCR were activated, as were proteins involved in the cell cycle, cell adhesion and exocytosis. In conclusion, 3G CAR T cells had a higher degree of intracellular signaling activity than 2G CARs which may explain the increased proliferative capacity seen in 3G CAR T cells. The study also indicates that there may be other signaling pathways to consider when designing or evaluating new generations of CARs.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

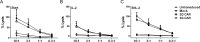



Similar articles
-
In Vivo Fate and Activity of Second- versus Third-Generation CD19-Specific CAR-T Cells in B Cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphomas.Mol Ther. 2018 Dec 5;26(12):2727-2737. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 13. Mol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30309819 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Design of Engineered Costimulation Determines Tumor Rejection Kinetics and Persistence of CAR T Cells.Cancer Cell. 2015 Oct 12;28(4):415-428. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.004. Cancer Cell. 2015. PMID: 26461090 Free PMC article.
-
Target antigen density governs the efficacy of anti-CD20-CD28-CD3 ζ chimeric antigen receptor-modified effector CD8+ T cells.J Immunol. 2015 Feb 1;194(3):911-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402346. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25520398
-
4-1BB chimeric antigen receptors.Cancer J. 2014 Mar-Apr;20(2):134-40. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000028. Cancer J. 2014. PMID: 24667959 Review.
-
Deciphering CD137 (4-1BB) signaling in T-cell costimulation for translation into successful cancer immunotherapy.Eur J Immunol. 2016 Mar;46(3):513-22. doi: 10.1002/eji.201445388. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Eur J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26773716 Review.
Cited by
-
How Can We Engineer CAR T Cells to Overcome Resistance?Biologics. 2021 May 19;15:175-198. doi: 10.2147/BTT.S252568. eCollection 2021. Biologics. 2021. PMID: 34040345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CAR-T design: Elements and their synergistic function.EBioMedicine. 2020 Aug;58:102931. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102931. Epub 2020 Jul 30. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32739874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeric Antigen Receptor Library Screening Using a Novel NF-κB/NFAT Reporter Cell Platform.Mol Ther. 2019 Feb 6;27(2):287-299. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.11.015. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Mol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30573301 Free PMC article.
-
Toward high-throughput engineering techniques for improving CAR intracellular signaling domains.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Mar 27;11:1101122. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1101122. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37051270 Free PMC article.
-
Learning from TCR Signaling and Immunological Synapse Assembly to Build New Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 17;23(22):14255. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214255. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brentjens RJ, Davila ML, Riviere I, Park J, Wang X, Cowell LG, et al. CD19-targeted T cells rapidly induce molecular remissions in adults with chemotherapy-refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(177):177ra38 Epub 2013/03/22. 10.1126/scitranslmed.30059305/177/177ra38 [pii]. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kalos M, Levine BL, Porter DL, Katz S, Grupp SA, Bagg A, et al. T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3(95):95ra73. Epub 2011/08/13. doi: 3/95/95ra73 [pii] 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002842 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kochenderfer JN, Dudley ME, Kassim SH, Somerville RP, Carpenter RO, Stetler-Stevenson M, et al. Chemotherapy-refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and indolent B-cell malignancies can be effectively treated with autologous T cells expressing an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(6):540–9. 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.2025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

