Small Molecule Modulators of Pre-mRNA Splicing in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 26700537
- PMCID: PMC4707101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2015.11.005
Small Molecule Modulators of Pre-mRNA Splicing in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
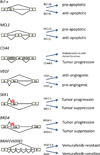
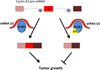
Pre-mRNA splicing is a fundamental process in mammalian gene expression and alternative RNA splicing plays a considerable role in generating protein diversity. RNA splicing events are also key to the pathology of numerous diseases, particularly cancers. Some tumors are molecularly addicted to specific RNA splicing isoforms making interference with pre-mRNA processing a viable therapeutic strategy. Several RNA splicing modulators have recently been characterized, some showing promise in preclinical studies. While the targets of most splicing modulators are constitutive RNA processing components, possibly leading to undesirable side effects, selectivity for individual splicing events has been observed. Given the high prevalence of splicing defects in cancer, small molecule modulators of RNA processing represent a potentially promising novel therapeutic strategy in cancer treatment. Here, we review their reported effects, mechanisms, and limitations.
Keywords: cancer therapy; splicing modulators.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Alternative RNA Splicing in Gastrointestinal Malignancies and Other Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 30;22(21):11790. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111790. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Function, clinical application, and strategies of Pre-mRNA splicing in cancer.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Jul;26(7):1181-1194. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0231-3. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30464224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts and mechanisms of alternative mRNA splicing in cancer metabolism, immune response, and therapeutics.Mol Ther. 2022 Mar 2;30(3):1018-1035. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.010. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Mol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34793975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule amiloride modulates oncogenic RNA alternative splicing to devitalize human cancer cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e18643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018643. Epub 2011 Jun 9. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21694768 Free PMC article.
-
[Pre-mRNA alternative splicing in cancer: functional impact, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives].Bull Cancer. 2006 Sep;93(9):909-19. Bull Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16980234 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Clusterization in acute myeloid leukemia based on prognostic alternative splicing signature to reveal the clinical characteristics in the bone marrow microenvironment.Cell Biosci. 2020 Oct 12;10:118. doi: 10.1186/s13578-020-00481-5. eCollection 2020. Cell Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33062256 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing modulation sensitizes chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to venetoclax by remodeling mitochondrial apoptotic dependencies.JCI Insight. 2018 Oct 4;3(19):e121438. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.121438. JCI Insight. 2018. PMID: 30282833 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant RNA Splicing in Cancer and Drug Resistance.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Nov 20;10(11):458. doi: 10.3390/cancers10110458. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30463359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Splicing modulation as novel therapeutic strategy against diffuse malignant peritoneal mesothelioma.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jan;39:215-225. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.12.025. Epub 2018 Dec 20. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30581150 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and functional significance of CHK1-S, an alternatively spliced isoform of the CHK1 gene, in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer. 2020 Jan 17;11(7):1792-1799. doi: 10.7150/jca.39443. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32194790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Venter JC, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291(5507):1304–1351. - PubMed
-
- Wahl MC, Will CL, Luhrmann R. The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell. 2009;136(4):701–718. - PubMed
-
- Graveley BR. Alternative splicing: increasing diversity in the proteomic world. Trends Genet. 2001;17(2):100–107. - PubMed
-
- Ge Y, Porse BT. The functional consequences of intron retention: alternative splicing coupled to NMD as a regulator of gene expression. Bioessays. 2014;36(3):236–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

