Kv7.5 Potassium Channel Subunits Are the Primary Targets for PKA-Dependent Enhancement of Vascular Smooth Muscle Kv7 Currents
- PMID: 26700561
- PMCID: PMC4767407
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.115.101758
Kv7.5 Potassium Channel Subunits Are the Primary Targets for PKA-Dependent Enhancement of Vascular Smooth Muscle Kv7 Currents
Abstract
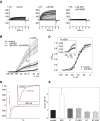
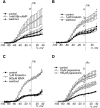
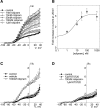
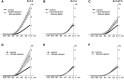
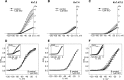
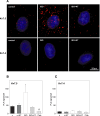
Kv7 (KCNQ) channels, formed as homo- or heterotetramers of Kv7.4 and Kv7.5 α-subunits, are important regulators of vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) membrane voltage. Recent studies demonstrate that direct pharmacological modulation of VSMC Kv7 channel activity can influence blood vessel contractility and diameter. However, the physiologic regulation of Kv7 channel activity is still poorly understood. Here, we study the effect of cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) activation on whole cell K(+) currents through endogenous Kv7.5 channels in A7r5 rat aortic smooth muscle cells or through Kv7.4/Kv7.5 heteromeric channels natively expressed in rat mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells. The contributions of specific α-subunits are further dissected using exogenously expressed human Kv7.4 and Kv7.5 homo- or heterotetrameric channels in A7r5 cells. Stimulation of Gαs-coupled β-adrenergic receptors with isoproterenol induced PKA-dependent activation of endogenous Kv7.5 currents in A7r5 cells. The receptor-mediated enhancement of Kv7.5 currents was mimicked by pharmacological agents that increase [cAMP] (forskolin, rolipram, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine, and papaverine) or mimic cAMP (8-bromo-cAMP); the 2- to 4-fold PKA-dependent enhancement of currents was also observed with exogenously expressed Kv7.5 channels. In contrast, exogenously-expressed heterotetrameric Kv7.4/7.5 channels in A7r5 cells or native mesenteric artery smooth muscle Kv7.4/7.5 channels were only modestly enhanced, and homo-tetrameric Kv7.4 channels were insensitive to this regulatory pathway. Correspondingly, proximity ligation assays indicated that isoproterenol induced PKA-dependent phosphorylation of exogenously expressed Kv7.5 channel subunits, but not of Kv7.4 subunits. These results suggest that signal transduction-mediated responsiveness of vascular smooth muscle Kv7 channel subunits to cAMP/PKA activation follows the order of Kv7.5 >> Kv7.4/Kv7.5 > Kv7.4.
Copyright © 2016 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential protein kinase C-dependent modulation of Kv7.4 and Kv7.5 subunits of vascular Kv7 channels.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):2099-111. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.527820. Epub 2013 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24297175 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of PKA-Dependent Potentiation of Kv7.5 Channel Activity in Human Airway Smooth Muscle Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 30;19(8):2223. doi: 10.3390/ijms19082223. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30061510 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Determinants of Kv7.5 Potassium Channels That Confer Changes in Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate (PIP2) Affinity and Signaling Sensitivities in Smooth Muscle Cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Mar;97(3):145-158. doi: 10.1124/mol.119.117192. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31871302
-
Novel treatment strategies for smooth muscle disorders: Targeting Kv7 potassium channels.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Sep;165:14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 11. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27179745 Review.
-
Kv7 channel trafficking by the microtubule network in vascular smooth muscle.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021 Jul;232(3):e13692. doi: 10.1111/apha.13692. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2021. PMID: 34021973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kv7 Channels and Excitability Disorders.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;267:185-230. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_457. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33860384
-
Pirfenidone Is a Vasodilator: Involvement of KV7 Channels in the Effect on Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilatation in Type-2 Diabetic Mice.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 12;11:619152. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.619152. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33643042 Free PMC article.
-
Heteromeric Channels Formed From Alternating Kv7.4 and Kv7.5 α-Subunits Display Biophysical, Regulatory, and Pharmacological Characteristics of Smooth Muscle M-Currents.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 12;11:992. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00992. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32903335 Free PMC article.
-
Kcne4 Deletion Sex-Dependently Alters Vascular Reactivity.J Vasc Res. 2016;53(3-4):138-148. doi: 10.1159/000449060. Epub 2016 Oct 7. J Vasc Res. 2016. PMID: 27710966 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and functional roles of KCNQ-encoded voltage-gated potassium (Kv7) channels in human corpus cavernosum smooth muscle.Pflugers Arch. 2020 Jan;472(1):89-102. doi: 10.1007/s00424-019-02343-7. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Pflugers Arch. 2020. PMID: 31919767
References
-
- Barhanin J, Lesage F, Guillemare E, Fink M, Lazdunski M, Romey G. (1996) KVLQT1 and lsK (minK) proteins associate to form the IKS cardiac potassium current. Nature 384:78–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

