Thoracic Vertebral Body Irradiation Contributes to Acute Hematologic Toxicity During Chemoradiation Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 26700708
- PMCID: PMC5767469
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.09.022
Thoracic Vertebral Body Irradiation Contributes to Acute Hematologic Toxicity During Chemoradiation Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To determine the relationships between radiation doses to the thoracic bone marrow and declines in blood cell counts in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with chemoradiation therapy (CRT).
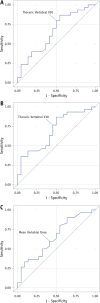
Methods and materials: We included 52 patients with NSCLC treated with definitive concurrent carboplatin-paclitaxel and RT. Dose-volume histogram (DVH) parameters for the thoracic vertebrae (TV), sternum, scapulae, clavicles, and ribs were assessed for associations with changes in blood counts during the course of CRT. Linear and logistic regression analyses were performed to identify associations between hematologic nadirs and DVH parameters. A DVH parameter of Vx was the percentage of the total organ volume exceeding x radiation dose.
Results: Grade ≥ 3 hematologic toxicity including neutropenia developed in 21% (n=11), leukopenia in 42% (n=22), anemia in 6% (n=3), and throbocytopenia in 2% (n=1) of patients. Greater RT dose to the TV was associated with higher risk of grade ≥ 3 leukopenia across multiple DVH parameters, including TV V20 (TVV) (odds ratio [OR] 1.06; P=.025), TVV30 (OR 1.07; P=.013), and mean vertebral dose (MVD) (OR 1.13; P=.026). On multiple regression analysis, TVV30 (β = -0.004; P=.018) and TVV20 (β = -0.003; P=.048) were associated with white blood cell nadir. Additional bone marrow sites (scapulae, clavicles, and ribs) did not affect hematologic toxicity. A 20% chance of grade ≥ 3 leukopenia was associated with a MVD of 13.5 Gy and a TTV30 of 28%. Cutoff values to avoid grade ≥ 3 leukopenia were MVD ≤ 23.9 Gy, TVV20 ≤ 56.0%, and TVV30 ≤ 52.1%.
Conclusions: Hematologic toxicity is associated with greater RT doses to the TV during CRT for NSCLC. Sparing of the TV using advanced radiation techniques may improve tolerance of CRT and result in improved tolerance of concurrent chemotherapy.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiation Dose to the Thoracic Vertebral Bodies Is Associated With Acute Hematologic Toxicities in Patients Receiving Concurrent Chemoradiation for Lung Cancer: Results of a Single-Center Retrospective Analysis.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018 Mar 1;100(3):748-755. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.11.025. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018. PMID: 29413286 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric predictors of acute haematological toxicity in oesophageal cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.Br J Radiol. 2016 Oct;89(1066):20160350. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20160350. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Br J Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27556422 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chemotherapy Regimen and Radiation Modality on Hematologic Toxicities in Patients Receiving Definitive Platinum-based Doublet Chemoradiation for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Am J Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;40(6):625-630. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000206. Am J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 26165417
-
Non-small cell lung cancer treatment-related bone marrow toxicities.Semin Oncol. 2005 Apr;32(2 Suppl 3):S81-5. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.03.014. Semin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16015540 Review.
-
Radiotherapy-associated neutropenia and thrombocytopenia: analysis of risk factors and development of a predictive model.Blood. 1997 Apr 1;89(7):2303-10. Blood. 1997. PMID: 9116273 Review.
Cited by
-
Vertebral body irradiation during chemoradiation therapy for esophageal cancer contributes to acute bone marrow toxicity.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Jun;10(3):513-522. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2019.01.20. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31183202 Free PMC article.
-
Redefine the Role of Proton Beam Therapy for the Locally-Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Assisting the Reduction of Acute Hematologic Toxicity.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 30;12:812031. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.812031. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847952 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric analysis of lymphopenia during chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer.J Thorac Dis. 2020 May;12(5):2395-2405. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2020.03.93. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32642145 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy-related lymphopenia in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving palliative radiotherapy.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020 Feb 19;22:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2020.02.005. eCollection 2020 May. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32181373 Free PMC article.
-
The p53 R72P polymorphism does not affect the physiological response to ionizing radiation in a mouse model.Cell Cycle. 2017 Jun 18;16(12):1153-1163. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1312234. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28594296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sause W, Kolesar P, Taylor SI, et al. Final results of phase III trial in regionally advanced unresectable non-small cell lung cancer: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group, and Southwest Oncology Group. Chest. 2000;117:358–364. - PubMed
-
- Furuse K, Fukuoka M, Kawahara M, et al. Phase III study of concurrent versus sequential thoracic radiotherapy in combination with mitomycin, vindesine, and cisplatin in unresectable stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2692–2699. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials