Cell cycle-dependent resolution of DNA double-strand breaks
- PMID: 26700820
- PMCID: PMC4826256
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6644
Cell cycle-dependent resolution of DNA double-strand breaks
Abstract
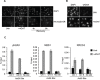
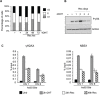
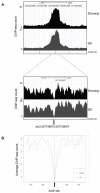
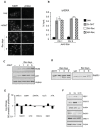
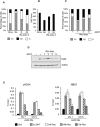
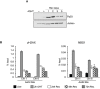
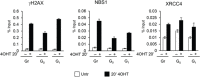
DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) elicit prompt activation of DNA damage response (DDR), which arrests cell-cycle either in G1/S or G2/M in order to avoid entering S and M phase with damaged DNAs. Since mammalian tissues contain both proliferating and quiescent cells, there might be fundamental difference in DDR between proliferating and quiescent cells (or G0-arrested). To investigate these differences, we studied recruitment of DSB repair factors and resolution of DNA lesions induced at site-specific DSBs in asynchronously proliferating, G0-, or G1-arrested cells. Strikingly, DSBs occurring in G0 quiescent cells are not repaired and maintain a sustained activation of the p53-pathway. Conversely, re-entry into cell cycle of damaged G0-arrested cells, occurs with a delayed clearance of DNA repair factors initially recruited to DSBs, indicating an inefficient repair when compared to DSBs induced in asynchronously proliferating or G1-synchronized cells. Moreover, we found that initial recognition of DSBs and assembly of DSB factors is largely similar in asynchronously proliferating, G0-, or G1-synchronized cells. Our study thereby demonstrates that repair and resolution of DSBs is strongly dependent on the cell-cycle state.
Keywords: AsiSI restriction enzyme; DSB repair; cell-cycle; site-specific DSBs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of nonhomologous DNA end joining, conservative homologous recombination, and single-strand annealing in the cell cycle-dependent repair of DNA double-strand breaks induced by H(2)O(2) in mammalian cells.Radiat Res. 2008 Dec;170(6):784-93. doi: 10.1667/RR1375.1. Radiat Res. 2008. PMID: 19138034
-
Homologous recombination protects mammalian cells from replication-associated DNA double-strand breaks arising in response to methyl methanesulfonate.DNA Repair (Amst). 2010 Oct 5;9(10):1050-63. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2010.07.005. Epub 2010 Aug 13. DNA Repair (Amst). 2010. PMID: 20708982
-
MYC impairs resolution of site-specific DNA double-strand breaks repair.Mutat Res. 2015 Apr;774:6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2015.02.005. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Mutat Res. 2015. PMID: 25770827
-
Cell cycle checkpoints and DNA repair preserve the stability of the human genome.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995 Mar;14(1):31-41. doi: 10.1007/BF00690209. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995. PMID: 7606819 Review.
-
Regulation of DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice.Cell Res. 2008 Jan;18(1):134-47. doi: 10.1038/cr.2007.111. Cell Res. 2008. PMID: 18157161 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA Damage Response in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Ageing.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun;14(3):147-154. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 May 21. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27221660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Damage Induces a Secretory Program in the Quiescent TME that Fosters Adverse Cancer Phenotypes.Mol Cancer Res. 2017 Jul;15(7):842-851. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0387. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Mol Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28356331 Free PMC article.
-
High turnover and rescue effect of XRCC1 in response to heavy charged particle radiation.Biophys J. 2022 Apr 19;121(8):1493-1501. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.03.011. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35276132 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide mapping of 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanosine reveals accumulation of oxidatively-generated damage at DNA replication origins within transcribed long genes of mammalian cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 10;47(1):221-236. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1152. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30462294 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 Suppresses Radiation-induced Neuroendocrine Differentiation and Sensitizes Prostate Cancer Cells to Radiation.Mol Cancer Ther. 2022 Mar 1;21(3):448-459. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-21-0103. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022. PMID: 35027481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berkovich E, Monnat RJ, Jr, Kastan MB. Roles of ATM and NBS1 in chromatin structure modulation and DNA double-strand break repair. Nature Cell Biology. 2007;9:683–690. - PubMed
-
- Matsuoka S, Ballif BA, Smogorzewska A, McDonald ER, 3rd, Hurov KE, Luo J, Bakalarski CE, Zhao Z, Solimini N, Lerenthal Y, Shiloh Y, Gygi SP, Elledge SJ. ATM and ATR substrate analysis reveals extensive protein networks responsive to DNA damage. Science. 2007;316:1160–1166. - PubMed
-
- Thompson LH. Recognition, signaling, and repair of DNA double-strand breaks produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: the molecular choreography. Mutation Research. 2012;751:158–246. - PubMed
-
- Rogakou EP, Pilch DR, Orr AH, Ivanova VS, Bonner WM. DNA double-stranded breaks induce histone H2AX phosphorylation on serine 139. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1998;273:5858–5868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

