Long-term effects of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy in Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
- PMID: 26700861
- PMCID: PMC4690279
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-015-0453-7
Long-term effects of peginterferon alfa-2a therapy in Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection
Abstract
Background: There is no information on the long-term effects of peginterferon (PEG-IFN) alfa-2a therapy for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) in Japan. This double-blind, randomized trial investigated the efficacy of PEG-IFN therapy.
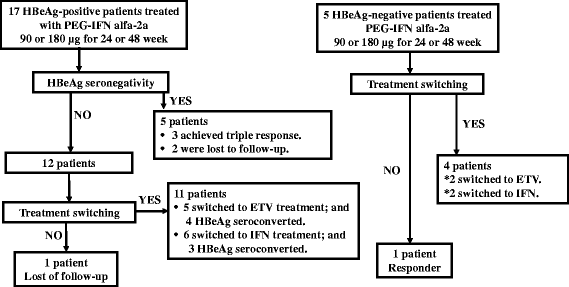
Methods: We analyzed 22 Japanese patients with CHB (hepatitis B e antigen [HBeAg]-positive: 17, HBeAg-negative: 5) treated with PEG-IFN alfa-2a and followed-up posttreatment for 5 years. Responders represented patients who showed persistent normalization of alanine transferase (ALT) levels, HBeAg clearance, and low hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA levels (HBeAg-positive patient; <5 log copies/mL, HBeAg-negative patient; <4.3 log copies/mL) at end of treatment, and at 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 years posttreatment. In addition, baseline HBeAg-positive patients who showed sustained normalization of ALT level, HBeAg clearance, and low HBV DNA level for more than 6 months until at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years after completion of PEG-IFN were also classified as "triple responders" and the proportion of triple responders relative to all patients was termed the "triple response rate".
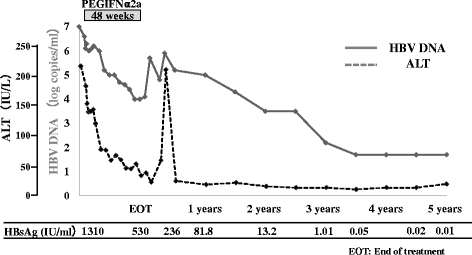
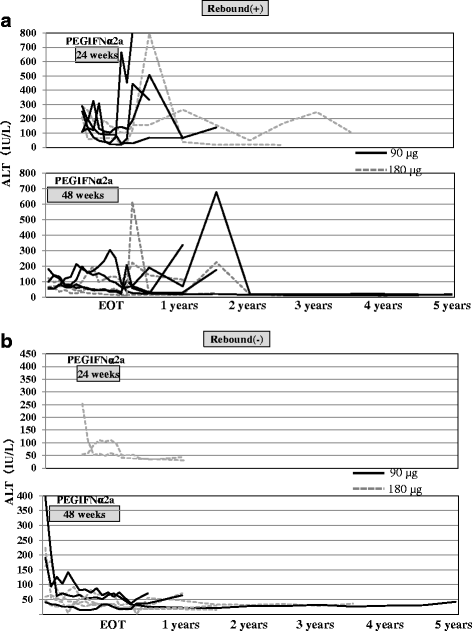
Results: The response rates among HBeAg-positive patients were 13%, 25%, 14%, 21% and 21% at end of treatment, and at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years, respectively. The response rate tended to be higher in patients treated for 48 than 24 weeks. The respective response rates among HBeAg-negative patients were 0%, 20%, 20%, 20% and 25%. During the treatment period, hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) clearance at 3.5 years was noted in one patient, who was 37-year-old, male, had genotype C and received PEG-IFN alfa-2a at 90 μg for 48 weeks.
Conclusion: At 5 years after completion of PEG-IFN, the triple response rate in HBeAg-positive patients and combined response rate in HBeAg-negative patients were 21% (3/14) and 25% (1/4), respectively. The triple response was seen in three patients who had all been treated with PEG-IFN for 48 weeks.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase IV randomized clinical study: Peginterferon alfa-2a with adefovir or entecavir pre-therapy for HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B.J Formos Med Assoc. 2018 Jul;117(7):588-597. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2017.12.007. Epub 2018 Feb 16. J Formos Med Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29456079 Clinical Trial.
-
Peginterferon-α2a combined with response-guided short-term lamivudine improves response rate in hepatitis B e antigen-positive hepatitis B patients: a pilot study.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 Oct;25(10):1165-9. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e3283612e95. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23571612 Clinical Trial.
-
Durable hepatitis B surface antigen decline in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B patients treated with pegylated interferon-α2b: relation to response and HBV genotype.Antivir Ther. 2012;17(1):9-17. doi: 10.3851/IMP1887. Antivir Ther. 2012. PMID: 22267464 Clinical Trial.
-
Peginterferon alfa-2a (40 kD) stopping rules in chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data.Antivir Ther. 2019;24(2):133-140. doi: 10.3851/IMP3304. Antivir Ther. 2019. PMID: 30865588
-
Why do I treat HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B patients with pegylated interferon?Liver Int. 2013 Feb;33 Suppl 1:157-63. doi: 10.1111/liv.12064. Liver Int. 2013. PMID: 23286860 Review.
Cited by
-
Sustained serological and complete responses in HBeAg-positive patients treated with Peginterferon alfa-2b: a 6-year long-term follow-up of a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial in China.BMC Gastroenterol. 2019 May 2;19(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-0981-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31046700 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
HBV DNA and HBsAg: Early Prediction of Response to Peginterferon α-2a in HBeAg-Negative Chronic Hepatitis B.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Feb 4;17(3):383-389. doi: 10.7150/ijms.39775. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32132873 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated with Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Kinetics and Responses in Pegylated Interferon Alpha-2a Monotherapy for Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B.Intern Med. 2021;60(4):507-516. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5432-20. Epub 2021 Feb 15. Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33583931 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Functional Cure in Chinese HBeAg-negative Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Treated with Peg-interferon Alpha-2a.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2019 Sep 28;7(3):249-257. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2019.00016. Epub 2019 Aug 20. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31608217 Free PMC article.
-
CONSORT: Effects of adding adefovirdipivoxil to peginterferon alfa-2a at different time points on HBeAg-positivepatients: A prospective, randomized study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Aug;95(31):e4471. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004471. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27495085 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

