The effects of voluntary exercise on oocyte quality in a diet-induced obese murine model
- PMID: 26700938
- PMCID: PMC4821597
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-15-0419
The effects of voluntary exercise on oocyte quality in a diet-induced obese murine model
Abstract
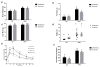
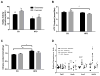
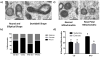
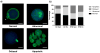
Obesity negatively affects many aspects of the human body including reproductive function. In females, the root of the decline in fertility is linked to problems in the oocyte. Problems seen in oocytes that positively correlate with increasing BMI include changes to the metabolism, lipid accumulation, meiosis, and metaphase II (MII) spindle structure. Studies in mice indicate that dietary interventions fail to reverse these problems. How exercise affects the oocytes has not been addressed. Therefore, we hypothesized an exercise intervention would improve oocyte quality. Here we show that in a mouse model of an exercise, intervention can improve lipid metabolism in germinal vesicle (GV) stage oocytes. Oocytes significantly increased activity and transcription of the β-oxidation enzyme hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase in response to exercise training only if the mice had been fed a high-fat diet (HFD). An exercise intervention also reversed the lipid accumulation seen in GV stage oocytes of HFD females. However, delays in meiosis and disorganized MII spindles remained present. Therefore, exercise is able to improve, but not reverse, damage imparted on oocytes as a result of an HFD and obesity. By utilizing an exercise intervention on an HFD, we determined only lipid content, and lipid metabolism is changed in GV oocytes. Moving forward, interventions to improve oocyte quality may need to be more targeted to the oocyte specifically. Because of the HFD-induced deficiency in β-oxidation, dietary supplementation with substrates to improve lipid utilization may be more beneficial.
© 2016 Society for Reproduction and Fertility.
Figures

References
-
- Arselin G, Giraud MF, Dautant A, Vaillier J, Brethes D, Coulary-Salin B, Schaeffer J, Velours J. The GxxxG motif of the transmembrane domain of subunit e is involved in the dimerization/oligomerization of the yeast ATP synthase complex in the mitochondrial membrane. European journal of biochemistry / FEBS. 2003;270:1875–1884. - PubMed
-
- Bachvarova R, De Leon V, Johnson A, Kaplan G, Paynton BV. Changes in total RNA, polyadenylated RNA, and actin mRNA during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Developmental biology. 1985;108:325–331. - PubMed
-
- Bellver J, Ayllon Y, Ferrando M, Melo M, Goyri E, Pellicer A, Remohi J, Meseguer M. Female obesity impairs in vitro fertilization outcome without affecting embryo quality. Fertil Steril. 2010;93:447–454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

