Neural coding in barrel cortex during whisker-guided locomotion
- PMID: 26701910
- PMCID: PMC4764557
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.12559
Neural coding in barrel cortex during whisker-guided locomotion
Abstract
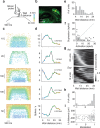
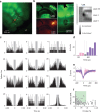
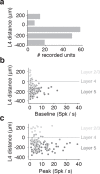
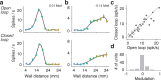
Animals seek out relevant information by moving through a dynamic world, but sensory systems are usually studied under highly constrained and passive conditions that may not probe important dimensions of the neural code. Here, we explored neural coding in the barrel cortex of head-fixed mice that tracked walls with their whiskers in tactile virtual reality. Optogenetic manipulations revealed that barrel cortex plays a role in wall-tracking. Closed-loop optogenetic control of layer 4 neurons can substitute for whisker-object contact to guide behavior resembling wall tracking. We measured neural activity using two-photon calcium imaging and extracellular recordings. Neurons were tuned to the distance between the animal snout and the contralateral wall, with monotonic, unimodal, and multimodal tuning curves. This rich representation of object location in the barrel cortex could not be predicted based on simple stimulus-response relationships involving individual whiskers and likely emerges within cortical circuits.
Keywords: barrel cortex; calcium imaging; electrophysiologygy; head-fixed; mouse; navigation; neuroscience; whiskers.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that no competing interests exist.
Figures
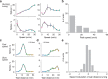
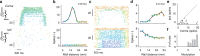

Similar articles
-
Layer-specific integration of locomotion and sensory information in mouse barrel cortex.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 13;10(1):2585. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10564-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31197148 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse, reliable, and long-term stable representation of periodic whisker deflections in the mouse barrel cortex.Neuroimage. 2015 Jul 15;115:52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.045. Epub 2015 Apr 28. Neuroimage. 2015. PMID: 25934471
-
Representation of tactile scenes in the rodent barrel cortex.Neuroscience. 2018 Jan 1;368:81-94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.08.039. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 28843997 Review.
-
Feedforward motor information enhances somatosensory responses and sharpens angular tuning of rat S1 barrel cortex neurons.Elife. 2017 Jan 6;6:e21843. doi: 10.7554/eLife.21843. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28059699 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Circuits in Barrel Cortex for Whisker Sensory Perception.Physiol Rev. 2021 Jan 1;101(1):353-415. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00019.2019. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Physiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 32816652 Review.
Cited by
-
Commentary: Spatial Olfactory Learning Contributes to Place Field Formation in the Hippocampus.Front Syst Neurosci. 2018 Apr 10;12:8. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2018.00008. eCollection 2018. Front Syst Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29692712 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Biology and bioinspiration of soft robotics: Actuation, sensing, and system integration.iScience. 2021 Sep 1;24(9):103075. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103075. eCollection 2021 Sep 24. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34568796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Layer 6 ensembles can selectively regulate the behavioral impact and layer-specific representation of sensory deviants.Elife. 2020 Dec 2;9:e48957. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48957. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33263283 Free PMC article.
-
Layer 6 corticothalamic neurons induce high gamma oscillations through cortico-cortical and cortico-thalamo-cortical pathways.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 14:2024.10.05.616808. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.05.616808. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39868278 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Sensorimotor processing in the rodent barrel cortex.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019 Sep;20(9):533-546. doi: 10.1038/s41583-019-0200-y. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31367018 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Armstrong-James M, Fox K, Das-Gupta A. Flow of excitation within rat barrel cortex on striking a single vibrissa. Journal of Neurophysiology. 1992;68:1345–1358. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

