Enhancement of dissolution rate of class II drugs (Hydrochlorothiazide); a comparative study of the two novel approaches; solid dispersion and liqui-solid techniques
- PMID: 26702260
- PMCID: PMC4669426
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsps.2015.01.025
Enhancement of dissolution rate of class II drugs (Hydrochlorothiazide); a comparative study of the two novel approaches; solid dispersion and liqui-solid techniques
Abstract
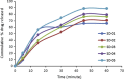
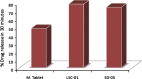
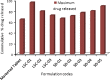
Liqui-solid technique and solid dispersion formation are two novel approaches for enhancement of dissolution rate of BCS class II drugs. Liqui-solid compact converts a liquid drug or drug solution into a free flowing powder with enhanced dissolution rate. In case of solid dispersion drug is molecularly dispersed in a hydrophilic polymer in solid state. In the present study, Liqui-solid and solid dispersion techniques were applied to enhance the dissolution of the Hydrochlorothiazide. Three formulations of Hydrochlorothiazide were prepared by liqui-solid technique using micro crystalline cellulose as carrier material and colloidal silicon dioxide as coating material. Water, poly ethylene glycol-400 and Tween-60 were used as solvent system. Solid dispersions of Hydrochlorothiazide were prepared by solvent fusion method using PEG-4000 as carrier polymer. Tablets were subjected to evaluation of various physical and chemical characteristics. Dissolution profiles of tablets prepared by the novel techniques were compared with marketed conventional tablets. Model independent techniques including similarity factor, dissimilarity factor and dissolution efficiency were applied for comparison of dissolution profiles. The results obtained indicated that liqui-solid compact formulations were more effective in enhancing the dissolution rate compared with solid dispersion technique. The liqui-solid compacts improved the dissolution rate up to 95% while the solid dispersion increased it to 88%.
Keywords: Dissolution efficiency; Hydrochlorothiazide; Liqui-solid compacts; PEG-4000; Similarity factor; Solid dispersion.
Figures


References
-
- Ali N. The effect of type and concentration of vehicles on dissolution rate of poorly soluble drugs (indomethacin) from liquisolid compacts. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2005;8(1):18–25. - PubMed
-
- Appa R.B., Shivalingam M.R., Kishore R.Y.V., Somesekhara Rao, Rajesh K., Sunitha N. Formulation and evaluation of aceclofenac solid dispersions for dissolution rate enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Drug Res. 2010;2:146–150.
-
- Ashok A.H., Prabhakar R.J. Improvement of solubility and dissolution rate of indomethacin by solid dispersion in polyvinyl pyrrolidone K30 and poloxomer 188. Asian J. Pharm. Technol. 2012;2(3):116–122.
-
- Bashar A.A., Hatim S.A., Ayman A.K. Comparative dissolution of diltiazem immediate and extended release products using conventional USP and innovative dissolution paddles. Open Drug Delivery J. 2010;4:48–54.
-
- Cherukuri S., Chappidi S.R., Anilkumar Dindigala, Amrutha Wadla, Anusha Arepalli Leela. Liquisolid technique: a novel approach to enhance solubility and bioavailability of BCS-2 drugs. Int. Res. J. Pharm. 2012;3(7)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

