Comparison of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis patients--baseline characteristics, treatment adherence, and development of clinical variables during three years of anti-TNF therapy in clinical practice
- PMID: 26703005
- PMCID: PMC4718030
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-015-0897-6
Comparison of non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis and ankylosing spondylitis patients--baseline characteristics, treatment adherence, and development of clinical variables during three years of anti-TNF therapy in clinical practice
Abstract
Background: The relationship between non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is currently debated. Using observational data from the South Swedish Arthritis Treatment Group register, we thus aimed to compare clinical development and treatment adherence between nr-axSpA and AS patients during three years of anti-TNF (tumor necrosis factor) therapy in clinical practice, and to explore the impact of inflammatory activity measured by CRP (C-reactive protein) at treatment initiation.
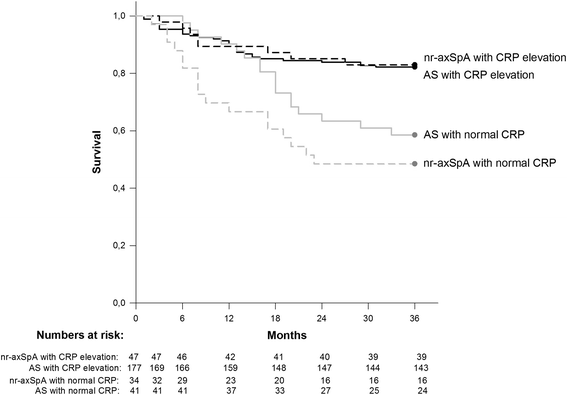
Methods: Nr-axSpA and AS patients (n = 86/238) in southern Sweden, commencing anti-TNF therapy 1999-2011, were followed during three years. Anti-TNF cessation was defined as stopping therapy, without restarting another anti-TNF agent within three months. Differences in the three year developments of patient's visual analogue scale (VAS) scores for global health and pain, EuroQol 5-Dimensions utility, evaluator's global disease activity assessment, CRP, and ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) were assessed by repeated ANOVA. Anti-TNF adherence was compared by Log rank test and Cox regression. In a subanalysis, the same outcomes were studied after splitting both groups into patients with/without baseline CRP elevation.
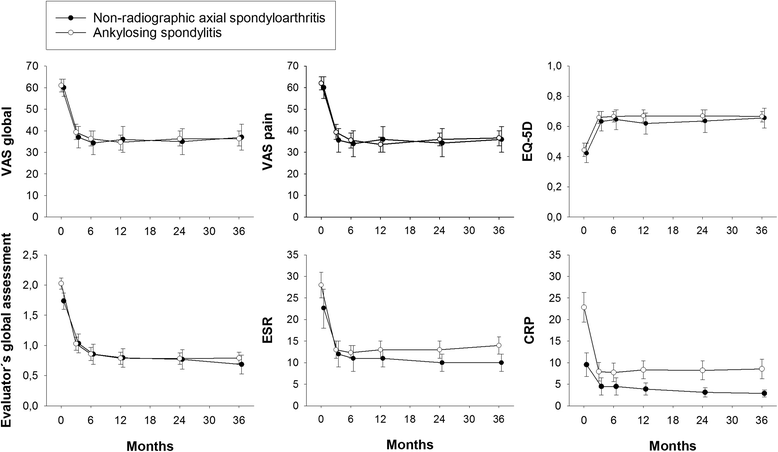
Results: Nr-axSpA patients were more often female and had lower acute phase reactants at baseline. Apart from CRP, which remained lower in the nr-axSpA group throughout follow-up (p = 0.004), no between-group differences were detected regarding clinical developments (p >0.1 for all comparisons) or anti-TNF adherence (hazard ratio: 1.1 (95% CI 0.7 to 1.8) for the nr-axSpA vs. AS group) during three years. Elevated baseline CRP was similarly associated with superior clinical outcomes and treatment adherence in both groups.
Conclusions: With the exception of constantly lower CRP levels in the nr-axSpA group, three years anti-TNF therapy resulted in similar clinical outcomes and treatment adherence in nr-axSpA and AS patients, thus strengthening the hypothesis that these diagnoses represent different aspects/phases of the same disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis versus Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Comparison of Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Effectiveness and Effect of HLA-B27 Status. An Observational Cohort Study from the Nationwide DANBIO Registry.J Rheumatol. 2017 Jan;44(1):59-69. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.160958. Epub 2016 Dec 1. J Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27909080
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibition in Ankylosing Spondylitis and Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: Treatment Response, Drug Survival, and Patient Outcome.J Rheumatol. 2015 Dec;42(12):2376-82. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150372. Epub 2015 Nov 15. J Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 26568593
-
Different drug survival of first line tumour necrosis factor inhibitors in radiographic and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a multicentre retrospective survey.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019 Sep-Oct;37(5):762-767. Epub 2019 Apr 16. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31025925
-
Efficacy of TNFα blockers in patients with ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: a meta-analysis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Jun;74(6):1241-8. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205322. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015. PMID: 24718959 Review.
-
Certolizumab pegol for treating axial spondyloarthritis.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016 Aug;16(8):1059-64. doi: 10.1080/14712598.2016.1205581. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27366922 Review.
Cited by
-
Unmet Needs in Axial Spondyloarthritis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Dec;55(3):332-339. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8637-0. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 28779298 Review.
-
Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Dec 22;19(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13075-017-1493-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 29273055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validity and reliability of EQ-5D-5L among patients with axial spondyloarthritis in Singapore.Eur J Rheumatol. 2020 Apr;7(2):71-78. doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2020.19043. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Eur J Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32644927 Free PMC article.
-
Not All Rashes Are Allergic: Keratoderma Blennorrhagicum-Like Rash Masquerading as Contact Dermatitis.Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2018 Dec 4;9:2152656718811566. doi: 10.1177/2152656718811566. eCollection 2018 Jan-Dec. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2018. PMID: 30546925 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Discontinuation, persistence and adherence to subcutaneous biologics delivered via a homecare route to Scottish adults with rheumatic diseases: a retrospective study.BMJ Open. 2019 Sep 4;9(9):e027059. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027059. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31488467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rudwaleit M, van der Heijde D, Landewe R, Listing J, Akkoc N, Brandt J, et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part II): validation and final selection. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:777–783. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.108233. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

