Boiogito, a Kampo medicine, improves hydrarthrosis in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis
- PMID: 26703073
- PMCID: PMC4691021
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-015-0979-7
Boiogito, a Kampo medicine, improves hydrarthrosis in a rat model of knee osteoarthritis
Abstract
Background: Hydrarthrosis, which is associated with knee pain and limited range of motion, decreases the quality of life (QOL) of patients with osteoarthritis (OA). The Kampo medicine boiogito is prescribed for the treatment of knee OA with hydrarthrosis; however, its precise mechanisms of action remain unknown. The purposes of this study were to assess the pharmacological effects of boiogito and its mechanisms of action on joint effusion in rats with surgically induced OA.
Methods: A rat OA model was produced by transecting the anterior (cranial) cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and medial meniscus in the right knee joints of 7-week-old female Wistar rats. The rats were given chow containing boiogito (1 or 2%) or indomethacin (0.002 %) for 4 weeks after surgical transection. Levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and hyaluronic acid (HA) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Knee joint pain was assessed using an incapacitance tester. Osmotic water permeability in cultured rabbit synovial cells was assessed using stopped-flow analysis.
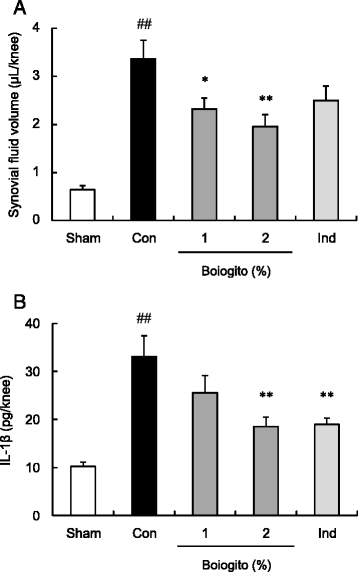
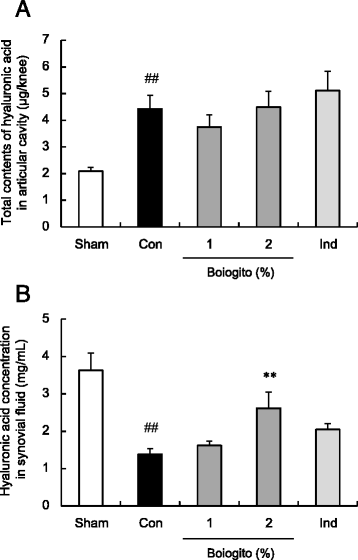
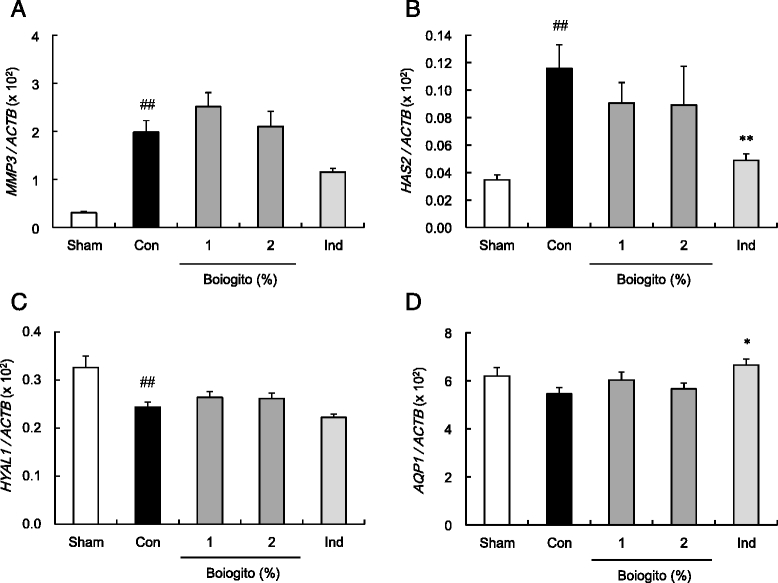
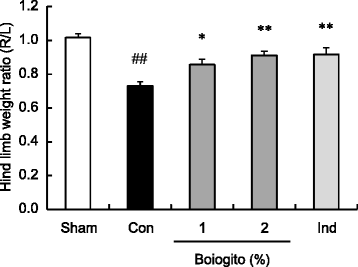
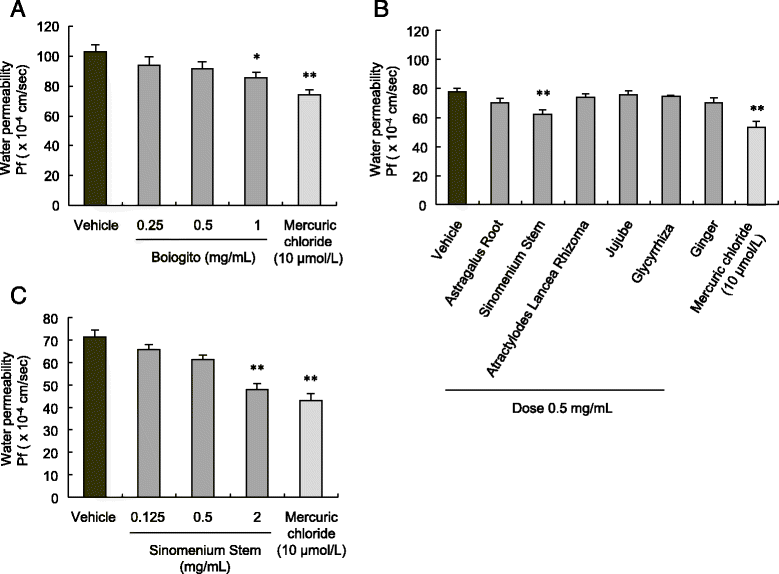
Results: Increased synovial fluid volume and knee joint pain were observed in rats with surgically induced OA. In rats with OA, levels of IL-1β and HA in the articular cavity were higher but concentration of HA in synovial fluid was lower than in sham-operated rats, suggesting excessive synovial fluid secretion. Administration of boiogito improved hydrarthrosis, IL-1β, and HA concentrations and alleviated knee joint pain in rats with OA. Indomethacin reduced IL-1β and knee joint pain but failed to improve hydrarthrosis or HA concentration in rats with OA. Osmotic water permeability in synovial cells, which is related to the function of the water channel aquaporin, was decreased by treatment with boiogito.
Conclusion: Boiogito ameliorates the increased knee joint effusion in rats with OA by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β production in the articular cavity and regulating function of water transport in the synovium. The improvement of hydrarthrosis by boiogito results in the increased HA concentration in synovial fluid, thus reducing joint pain. Boiogito may be a clinically useful treatment of QOL in patients with OA with hydrarthrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effects of sinomenine on synovial fluid and serum content of interleukin-1beta in rabbits with osteoarthritis].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008 Dec;6(12):1275-9. doi: 10.3736/jcim20081213. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 19063843 Chinese.
-
Rapid and sustained rise in the serum level of hyaluronan after anterior cruciate ligament transection in the dog knee joint.J Rheumatol. 1995 Feb;22(2):262-9. J Rheumatol. 1995. PMID: 7738949
-
The effect of sodium hyaluronate treating knee osteoarthritis on synovial fluid interleukin -1β and clinical treatment mechanism.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015 Jan;28(1 Suppl):407-10. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25631505 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential mechanism of action of intra-articular hyaluronan therapy in osteoarthritis: are the effects molecular weight dependent?Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Aug;32(1):10-37. doi: 10.1053/sarh.2002.33720. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 12219318 Review.
-
Review of the Mechanism of Action for Supartz FX in Knee Osteoarthritis.Cartilage. 2018 Jan;9(1):11-20. doi: 10.1177/1947603516684588. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Cartilage. 2018. PMID: 29219021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of combination therapy with unkeito and boiogito for menopausal arthralgia: A retrospective observational study.J Family Med Prim Care. 2024 Jan;13(1):311-316. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1069_23. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Family Med Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 38482295 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressive Activity of Boiogito, a Japanese Traditional Kampo Medicine, on Periostin Secretion in Human Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes In Vitro.Cureus. 2024 Apr 5;16(4):e57690. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57690. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38711706 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive Effect of the Japanese Traditional Herbal Medicine Boiogito on Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis in Rats.Medicines (Basel). 2020 Dec 4;7(12):74. doi: 10.3390/medicines7120074. Medicines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33291715 Free PMC article.
-
Kampo for the Treatment of Pain in Japan: A Review.Pain Ther. 2020 Jun;9(1):161-170. doi: 10.1007/s40122-020-00160-w. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Pain Ther. 2020. PMID: 32157597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese medicine therapy reduces the risk of total knee replacement in patients with knee osteoarthritis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jun;98(23):e15964. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015964. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31169724 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang W, Nuki G, Moskowitz RW, Abramson S, Altman RD, Arden NK, et al. OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis: part III: Changes in evidence following systematic cumulative update of research published through January 2009. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(4):476–99. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2010.01.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ishijima M, Nakamura T, Shimizu K, Hayashi K, Kikuchi H, Soen S, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection versus oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a multi-center, randomized, open-label, non-inferiority trial. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R18. doi: 10.1186/ar4446. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

