Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse neural stem cells and small intestinal epithelial cells by small molecule compounds
- PMID: 26704449
- PMCID: PMC4816130
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2015.142
Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse neural stem cells and small intestinal epithelial cells by small molecule compounds
Abstract
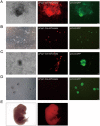
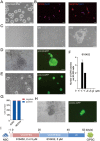
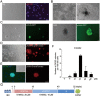
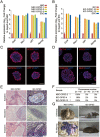
Recently, we reported a chemical approach to generate pluripotent stem cells from mouse fibroblasts. However, whether chemically induced pluripotent stem cells (CiPSCs) can be derived from other cell types remains to be demonstrated. Here, using lineage tracing, we first verify the generation of CiPSCs from fibroblasts. Next, we demonstrate that neural stem cells (NSCs) from the ectoderm and small intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) from the endoderm can be chemically reprogrammed into pluripotent stem cells. CiPSCs derived from NSCs and IECs resemble mouse embryonic stem cells in proliferation rate, global gene expression profile, epigenetic status, self-renewal and differentiation capacity, and germline transmission competency. Interestingly, the pluripotency gene Sall4 is expressed at the initial stage in the chemical reprogramming process from different cell types, and the same core small molecules are required for the reprogramming, suggesting conservation in the molecular mechanism underlying chemical reprogramming from these diverse cell types. Our analysis also shows that the use of these small molecules should be fine-tuned to meet the requirement of reprogramming from different cell types. Together, these findings demonstrate that full chemical reprogramming approach can be applied in cells of different tissue origins and suggest that chemical reprogramming is a promising strategy with the potential to be extended to more initial types.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A combination of small molecules directly reprograms mouse fibroblasts into neural stem cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jul 15;476(1):42-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.080. Epub 2016 May 17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27207831
-
Chemically Induced Reprogramming of Somatic Cells to Pluripotent Stem Cells and Neural Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Feb 6;17(2):226. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020226. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26861316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds.Science. 2013 Aug 9;341(6146):651-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1239278. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Science. 2013. PMID: 23868920
-
Derivation of Neural Stem Cells from Mouse Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1357:329-38. doi: 10.1007/7651_2015_227. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 25863785
-
Chemical compound-based direct reprogramming for future clinical applications.Biosci Rep. 2018 May 8;38(3):BSR20171650. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171650. Print 2018 Jun 29. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29739872 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Homogeneity of XEN Cells Is Critical for Generation of Chemically Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Mol Cells. 2023 Apr 30;46(4):209-218. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2023.2127. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Mol Cells. 2023. PMID: 36852435 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating cell fate through reprogramming: approaches and applications.Development. 2024 Oct 1;151(19):dev203090. doi: 10.1242/dev.203090. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Development. 2024. PMID: 39348466 Review.
-
Impelling force and current challenges by chemicals in somatic cell reprogramming and expansion beyond hepatocytes.World J Stem Cells. 2019 Sep 26;11(9):650-665. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v11.i9.650. World J Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 31616541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Small Molecules in the Central Nervous System Direct Neuronal Reprogramming.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jul 7;10:799152. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.799152. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35875485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From unipotency to pluripotency: deciphering protein networks and signaling pathways in the generation of embryonic stem-like cells from murine spermatogonial stem cells.BMC Genomics. 2025 Apr 30;26(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11612-y. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40307702 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006; 126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell 2007; 131:861–872. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science 2007; 318:1917–1920. - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka S. Elite and stochastic models for induced pluripotent stem cell generation. Nature 2009; 460:49–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

