Natural killer (NK) cells inhibit systemic metastasis of glioblastoma cells and have therapeutic effects against glioblastomas in the brain
- PMID: 26704632
- PMCID: PMC4690248
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-2034-y
Natural killer (NK) cells inhibit systemic metastasis of glioblastoma cells and have therapeutic effects against glioblastomas in the brain
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is characterized by extensive local invasion, which is in contrast with extremely rare systemic metastasis of GBM. Molecular mechanisms inhibiting systemic metastasis of GBM would be a novel therapeutic candidate for GBM in the brain.
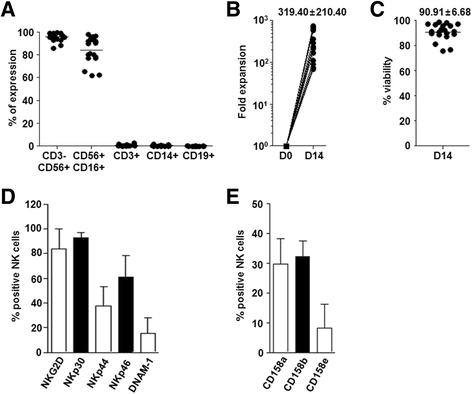
Methods: Patient-derived GBM cells were primarily cultured from surgical samples of GBM patients and were inoculated into the brains of immune deficient BALB/c-nude or NOD-SCID IL2Rgamma(null) (NSG) mice. Human NK cells were isolated from peripheral blood mononucleated cells and expanded in vitro.
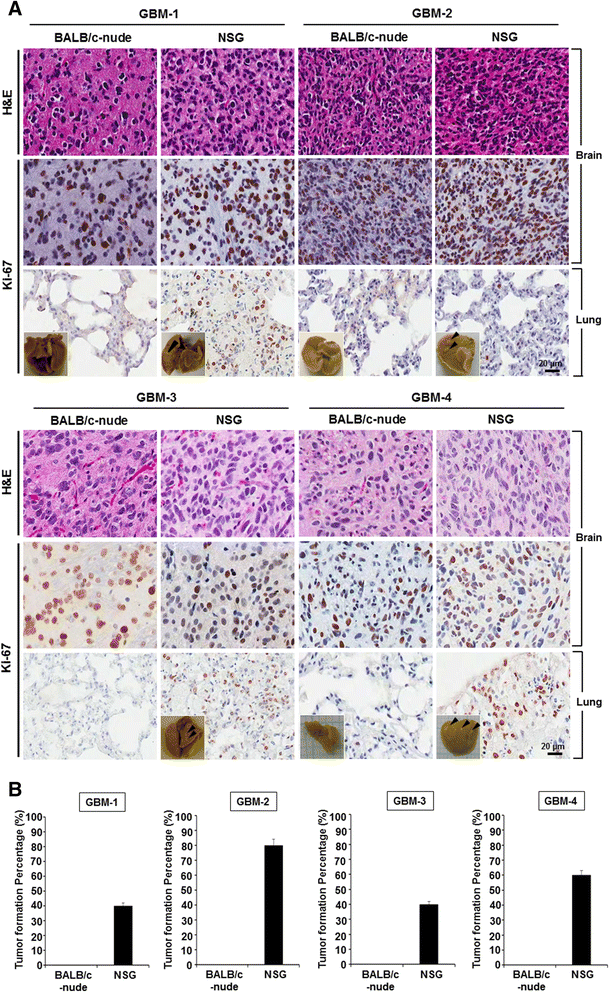
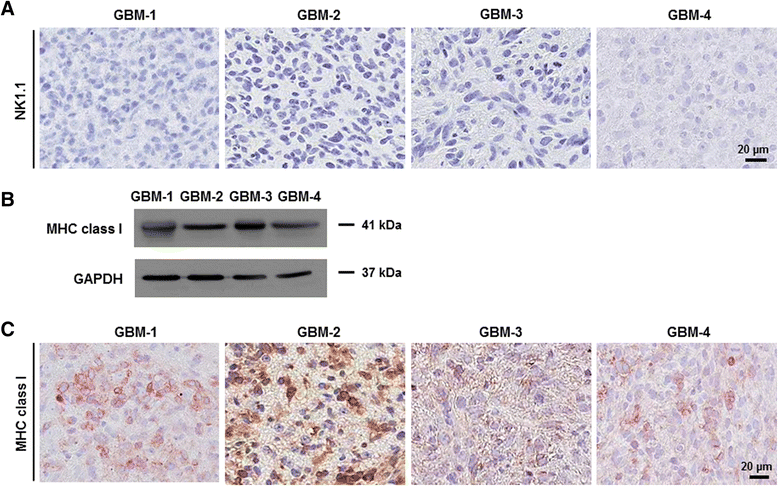
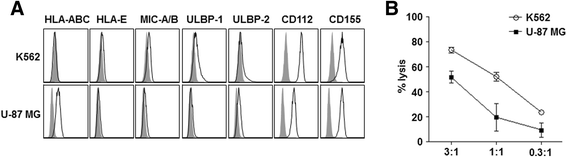
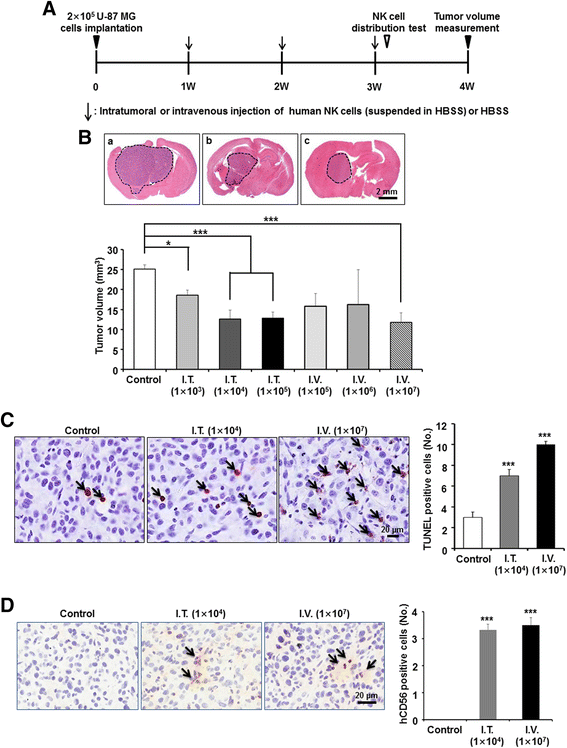
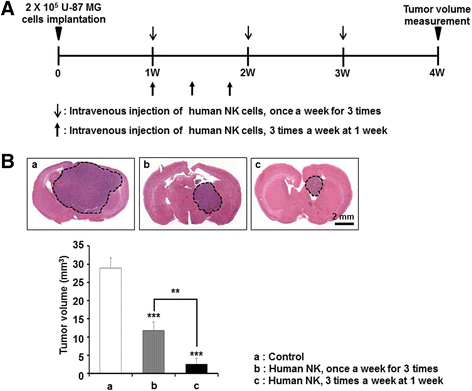
Results: Patient-derived GBM cells in the brains of NSG mice unexpectedly induced spontaneous lung metastasis although no metastasis was detected in BALB/c-nude mice. Based on the difference of the innate immunity between two mouse strains, NK cell activities of orthotopic GBM xenograft models based on BALB/c-nude mice were inhibited. NK cell inactivation induced spontaneous lung metastasis of GBM cells, which indicated that NK cells inhibit the systemic metastasis. In vitro cytotoxic activities of human NK cells against GBM cells indicated that cytotoxic activity of NK cells against GBM cells prevents systemic metastasis of GBM and that NK cells could be effective cell therapeutics against GBM. Accordingly, NK cells transplanted into orthotopic GBM xenograft models intravenously or intratumorally induced apoptosis of GBM cells in the brain and showed significant therapeutic effects.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that innate NK immunity is responsible for rare systemic metastasis of GBM and that sufficient supplementation of NK cells could be a promising immunotherapeutic strategy for GBM in the brain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
ErbB2/HER2-Specific NK Cells for Targeted Therapy of Glioblastoma.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015 Dec 6;108(5). doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv375. Print 2016 May. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2015. PMID: 26640245
-
Targeting and Therapy of Glioblastoma in a Mouse Model Using Exosomes Derived From Natural Killer Cells.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 23;9:824. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00824. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. Retraction in: Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 16;10:1770. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01770. PMID: 29740437 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Antitumor effects of intracranial injection of B7-H3-targeted Car-T and Car-Nk cells in a patient-derived glioblastoma xenograft model.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024 Oct 5;73(12):256. doi: 10.1007/s00262-024-03808-0. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39367952 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Molecular Targets for Natural Killer Cell Immunotherapy against Glioblastoma Multiforme.Cells. 2024 Sep 17;13(18):1567. doi: 10.3390/cells13181567. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural killer cells in breast cancer cell growth and metastasis in SCID mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2005 Oct;59 Suppl 2:S375-9. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(05)80082-4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 16507413 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Role of Interleukin-15 Stimulated Natural Killer Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Carboplatin in Osimertinib-Resistant H1975 Lung Cancer Cells with EGFR Mutations.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 8;16(1):83. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16010083. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38258094 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cell-related gene signature predicts malignancy of glioma and the survival of patients.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 2;22(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09230-y. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35236310 Free PMC article.
-
The War Is on: The Immune System against Glioblastoma-How Can NK Cells Drive This Battle?Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 8;10(2):400. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020400. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Advantages and Challenges of Anticancer Dendritic Cell Vaccines and NK Cells in Adoptive Cell Immunotherapy.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;9(11):1363. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9111363. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NK cell-based cancer immunotherapy: from basic biology to clinical development.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jan 6;14(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01014-w. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33407739 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Avril T, Vauleon E, Hamlat A, Saikali S, Etcheverry A, Delmas C, et al. Human glioblastoma stem-like cells are more sensitive to allogeneic NK and T cell-mediated killing compared with serum-cultured glioblastoma cells. Brain Pathol. 2012;22(2):159–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00515.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

