Standardizing chromatin research: a simple and universal method for ChIP-seq
- PMID: 26704968
- PMCID: PMC4838356
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1495
Standardizing chromatin research: a simple and universal method for ChIP-seq
Abstract
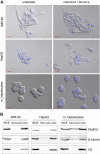
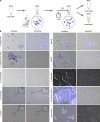
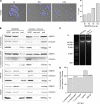
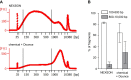
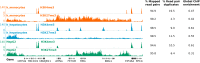
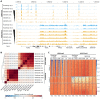
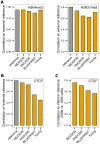
Chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by next generation sequencing (ChIP-seq) is a key technique in chromatin research. Although heavily applied, existing ChIP-seq protocols are often highly fine-tuned workflows, optimized for specific experimental requirements. Especially the initial steps of ChIP-seq, particularly chromatin shearing, are deemed to be exceedingly cell-type-specific, thus impeding any protocol standardization efforts. Here we demonstrate that harmonization of ChIP-seq workflows across cell types and conditions is possible when obtaining chromatin from properly isolated nuclei. We established an ultrasound-based nuclei extraction method (NEXSON: Nuclei EXtraction by SONication) that is highly effective across various organisms, cell types and cell numbers. The described method has the potential to replace complex cell-type-specific, but largely ineffective, nuclei isolation protocols. By including NEXSON in ChIP-seq workflows, we completely eliminate the need for extensive optimization and sample-dependent adjustments. Apart from this significant simplification, our approach also provides the basis for a fully standardized ChIP-seq and yields highly reproducible transcription factor and histone modifications maps for a wide range of different cell types. Even small cell numbers (∼10,000 cells per ChIP) can be easily processed without application of modified chromatin or library preparation protocols.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Barski A., Cuddapah S., Cui K., Roh T.-Y., Schones D.E., Wang Z., Wei G., Chepelev I., Zhao K. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell. 2007;129:823–837. - PubMed
-
- Johnson D.S., Mortazavi A., Myers R.M., Wold B. Genome-wide mapping of in vivo protein-DNA interactions. Science. 2007;316:1497–1502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

