Lignocellulose conversion for biofuel: a new pretreatment greatly improves downstream biocatalytic hydrolysis of various lignocellulosic materials
- PMID: 26705422
- PMCID: PMC4690250
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-015-0419-4
Lignocellulose conversion for biofuel: a new pretreatment greatly improves downstream biocatalytic hydrolysis of various lignocellulosic materials
Abstract
Background: Lignocellulosic biomass is an attractive renewable resource for future liquid transport fuel. Efficient and cost-effective production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic biomass depends on the development of a suitable pretreatment system. The aim of this study is to investigate a new pretreatment method that is highly efficient and effective for downstream biocatalytic hydrolysis of various lignocellulosic biomass materials, which can accelerate bioethanol commercialization.
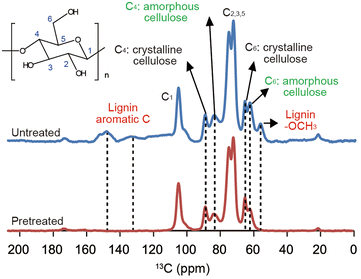
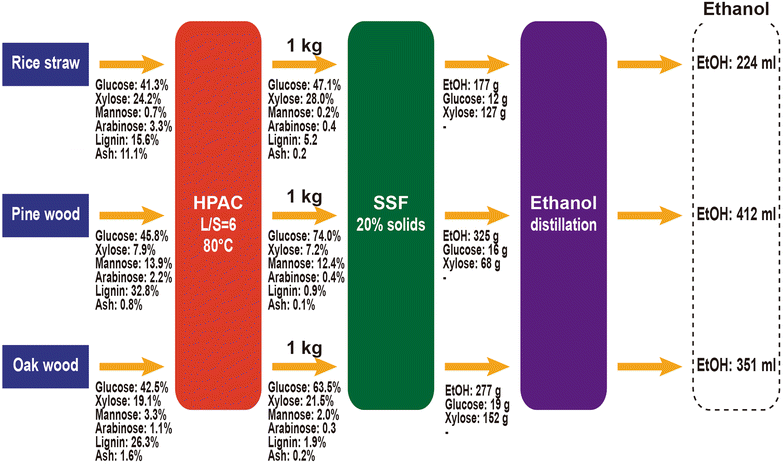
Results: The optimal conditions for the hydrogen peroxide-acetic acid (HPAC) pretreatment were 80 °C, 2 h, and an equal volume mixture of H2O2 and CH3COOH. Compared to organo-solvent pretreatment under the same conditions, the HPAC pretreatment was more effective at increasing enzymatic digestibility. After HPAC treatment, the composition of the recovered solid was 74.0 % cellulose, 20.0 % hemicelluloses, and 0.9 % lignin. Notably, 97.2 % of the lignin was removed with HPAC pretreatment. Fermentation of the hydrolyzates by S. cerevisiae resulted in 412 mL ethanol kg(-1) of biomass after 24 h, which was equivalent to 85.0 % of the maximum theoretical yield (based on the amount of glucose in the raw material).
Conclusion: The newly developed HPAC pretreatment was highly effective for removing lignin from lignocellulosic cell walls, resulting in enhanced enzymatic accessibility of the substrate and more efficient cellulose hydrolysis. This pretreatment produced less amounts of fermentative inhibitory compounds. In addition, HPAC pretreatment enables year-round operations, maximizing utilization of lignocellulosic biomass from various plant sources.
Keywords: Bioethanol; Energy efficiency; Lignocellulosic biomass; Pretreatment.
Figures




Similar articles
-
An overview of key pretreatment processes for biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol.3 Biotech. 2015 Oct;5(5):597-609. doi: 10.1007/s13205-015-0279-4. Epub 2015 Feb 3. 3 Biotech. 2015. PMID: 28324530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lignocellulosic Biomass: A Sustainable Bioenergy Source for the Future.Protein Pept Lett. 2018;25(2):148-163. doi: 10.2174/0929866525666180122144504. Protein Pept Lett. 2018. PMID: 29359659 Review.
-
Investigation of hydrogen peroxide-acetic acid pretreatment to enhance the enzymatic digestibility of bamboo residues.Bioresour Technol. 2022 Jan;344(Pt A):126162. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126162. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Bioresour Technol. 2022. PMID: 34678451
-
Pretreatment technologies for an efficient bioethanol production process based on enzymatic hydrolysis: A review.Bioresour Technol. 2010 Jul;101(13):4851-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.093. Epub 2009 Dec 29. Bioresour Technol. 2010. PMID: 20042329
-
Organic solvent pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and biochemicals: A review.Bioresour Technol. 2016 Jan;199:21-33. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.102. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Bioresour Technol. 2016. PMID: 26343573 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of novel lignocellulose-degrading enzymes from the porcupine microbiome using synthetic metagenomics.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 2;14(1):e0209221. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209221. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30601862 Free PMC article.
-
Lignocellulosic Materials for the Production of Biofuels, Biochemicals and Biomaterials and Applications of Lignocellulose-Based Polyurethanes: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;14(5):881. doi: 10.3390/polym14050881. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35267704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of various delignification/desilication pre-treatments and indigenous fungal cellulase for improved hydrolysis of paddy straw.3 Biotech. 2022 Jul;12(7):150. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03211-5. Epub 2022 Jun 20. 3 Biotech. 2022. PMID: 35747505 Free PMC article.
-
A novel cell factory for efficient production of ethanol from dairy waste.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016 Feb 26;9:33. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0448-7. eCollection 2016. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2016. PMID: 26925162 Free PMC article.
-
Xylanase production from Penicillium citrinum isolate HZN13 using response surface methodology and characterization of immobilized xylanase on glutaraldehyde-activated calcium-alginate beads.3 Biotech. 2016 Dec;6(2):164. doi: 10.1007/s13205-016-0484-9. Epub 2016 Aug 11. 3 Biotech. 2016. PMID: 28330236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barakat A, Monlau F, Solhy A, Carrere H. Mechanical dissociation and fragmentation of lignocellulosic biomass: effect of initial moisture, biochemical and structural properties on energy requirement. Appl Energ. 2015;142:240–246. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.076. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

