Pseudoepitheliomatous Hyperplasia in a Red Pigment Tattoo: A Separate Entity or Hypertrophic Lichen Planus-like Reaction?
- PMID: 26705448
- PMCID: PMC4689511
Pseudoepitheliomatous Hyperplasia in a Red Pigment Tattoo: A Separate Entity or Hypertrophic Lichen Planus-like Reaction?
Abstract
Red pigment tattoos are known to cause pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in the skin, frequently simulating squamous cell carcinoma or keratoacanthoma. Herein, the authors present two additional cases of red pigment tattoo pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in which they noted a lichenoid tissue reaction. They reviewed the previously published cases and observed a lichenoid reaction in the histopathological images similar to hypertrophic lichen planus. The authors suggest that these reactions might best be referred to as "lichenoid reaction with pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia" or "hypertrophic lichen planus-like reaction." Accordingly, recognition of an inflammatory component may allow additional treatment options.
Figures





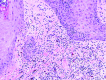


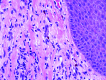
References
-
- Thum CK, Biswas A. Inflammatory complications related to tattooing: a histopathological approach based on pattern analysis. Am J Dermatopathol. 2015 Jan;37(1):54–66. - PubMed
-
- Balfour E, Olhoffer I, Leffell D, Handerson T. Massive pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia: an unusual reaction to a tattoo. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:338–340. - PubMed
-
- Cui W, McGregor DH, Stark SP, et al. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia—an unusual reaction following tattoo: report of a case and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:743–745. - PubMed
-
- Kluger N, Durand L, Minier-Thoumin C, et al. Pseudoepitheliomatous epidermal hyperplasia in tattoos: report of three cases. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2008;9:337–340. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
