PSMA-specific theranostic nanoplex for combination of TRAIL gene and 5-FC prodrug therapy of prostate cancer
- PMID: 26706476
- PMCID: PMC4706473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.11.048
PSMA-specific theranostic nanoplex for combination of TRAIL gene and 5-FC prodrug therapy of prostate cancer
Abstract
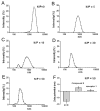
Metastatic prostate cancer causes significant morbidity and mortality and there is a critical unmet need for effective treatments. We have developed a theranostic nanoplex platform for combined imaging and therapy of prostate cancer. Our prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) targeted nanoplex is designed to deliver plasmid DNA encoding tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), together with bacterial cytosine deaminase (bCD) as a prodrug enzyme. Nanoplex specificity was tested using two variants of human PC3 prostate cancer cells in culture and in tumor xenografts, one with high PSMA expression and the other with negligible expression levels. The expression of EGFP-TRAIL was demonstrated by fluorescence optical imaging and real-time PCR. Noninvasive (19)F MR spectroscopy detected the conversion of the nontoxic prodrug 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC) to cytotoxic 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) by bCD. The combination strategy of TRAIL gene and 5-FC/bCD therapy showed significant inhibition of the growth of prostate cancer cells and tumors. These data demonstrate that the PSMA-specific theranostic nanoplex can deliver gene therapy and prodrug enzyme therapy concurrently for precision medicine in metastatic prostate cancer.
Keywords: Gene therapy; PSMA; Prodrug enzyme therapy; Prostate cancer; TRAIL; Theranostic imaging.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Koo H, Huh MS, Sun IC, Yuk SH, Choi K, Kim K, Kwon IC. In vivo targeted delivery of nanoparticles for theranosis. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44:1018–1028. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

