Acute and chronic ethanol exposure differentially regulate CB1 receptor function at glutamatergic synapses in the rat basolateral amygdala
- PMID: 26707595
- PMCID: PMC4912876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.12.005
Acute and chronic ethanol exposure differentially regulate CB1 receptor function at glutamatergic synapses in the rat basolateral amygdala
Abstract
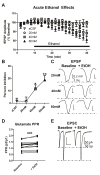
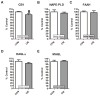
The endogenous cannabinoid (eCB) system has been suggested to play a key role in ethanol preference and intake, the acute effects of ethanol, and in the development of withdrawal symptoms following ethanol dependence. Ethanol-dependent alterations in glutamatergic signaling within the lateral/basolateral nucleus of the amygdala (BLA) are critical for the development and expression of withdrawal-induced anxiety. Notably, the eCB system significantly regulates both glutamatergic and GABAergic synaptic activity within the BLA. Chronic ethanol exposure significantly alters eCB system expression within regions critical to the expression of emotionality and anxiety-related behavior, including the BLA. Here, we investigated specific interactions between the BLA eCB system and its functional regulation of synaptic activity during acute and chronic ethanol exposure. In tissue from ethanol naïve-rats, a prolonged acute ethanol exposure caused a dose dependent inhibition of glutamatergic synaptic activity via a presynaptic mechanism that was occluded by CB1 antagonist/inverse agonists SR141716a and AM251. Importantly, this acute ethanol inhibition was attenuated following 10 day chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure (CIE). CIE exposure also significantly down-regulated CB1-mediated presynaptic inhibition at glutamatergic afferent terminals but spared CB1-inhibition of GABAergic synapses arising from local inhibitory-interneurons. CIE also significantly elevated BLA N-arachidonoylethanolamine (AEA or anandamide) levels and decreased CB1 receptor protein levels. Collectively, these data suggest a dynamic regulation of the BLA eCB system by acute and chronic ethanol.
Keywords: Anandamide; Basolateral amygdala; CB1; Dependence; Endogenous cannabinoid; Ethanol.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




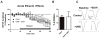
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

