A hyperbranched dopamine-containing PEG-based polymer for the inhibition of α-synuclein fibrillation
- PMID: 26707645
- PMCID: PMC4727786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.060
A hyperbranched dopamine-containing PEG-based polymer for the inhibition of α-synuclein fibrillation
Abstract
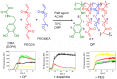
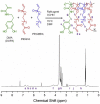
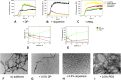
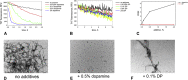
Aggregation of α-synuclein is believed to play an important role in Parkinson's disease and in other neurodegenerative maladies. Small molecule inhibitors of this process are among the most promising drug candidates for neurodegenerative diseases. Dendrimers have also been studied for anti-fibrillation applications but they can be difficult and expensive to synthetize. Here we show that RAFT polymerization can be used to produce a hyperbranched polyethylene glycol structure via a one-pot reaction. This polymer included a dopamine moiety, a known inhibitor of α-synuclein fibril formation. Dopamine within the polymer structure was capable of aggregation inhibition, although not to the same degree as free dopamine. This result opens up new avenues for the use of controlled radical polymerizations as a means of preparing hyperbranched polymers for anti-fibrillation activity, but shows that the incorporation of functional groups from known small molecules within polymers may alter their biological activity.
Keywords: Dopamine; Hyperbranched polymers; Macromolecular crowding; Parkinson's disease; Protein aggregation; RAFT polymerization; α-synuclein.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of macromolecular crowding on protein aggregation and amyloid fibril formation.J Mol Recognit. 2004 Sep-Oct;17(5):456-64. doi: 10.1002/jmr.699. J Mol Recognit. 2004. PMID: 15362105
-
Molecular crowding accelerates aggregation of α-synuclein by altering its folding pathway.Eur Biophys J. 2021 Jan;50(1):59-67. doi: 10.1007/s00249-020-01486-1. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Eur Biophys J. 2021. PMID: 33386904
-
Accelerated alpha-synuclein fibrillation in crowded milieu.FEBS Lett. 2002 Mar 27;515(1-3):99-103. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(02)02446-8. FEBS Lett. 2002. PMID: 11943202
-
Research Progress of α-Synuclein Aggregation Inhibitors for Potential Parkinson's Disease Treatment.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(20):1959-1974. doi: 10.2174/1389557523666230517163501. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37198991 Review.
-
Biophysics of Parkinson's disease: structure and aggregation of alpha-synuclein.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009 Oct;10(5):483-99. doi: 10.2174/138920309789351921. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19538146 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A health concern regarding the protein corona, aggregation and disaggregation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019 May;1863(5):971-991. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.02.012. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2019. PMID: 30802594 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitigation of Amyloidosis with Nanomaterials.Adv Mater. 2020 May;32(18):e1901690. doi: 10.1002/adma.201901690. Epub 2019 Jun 11. Adv Mater. 2020. PMID: 31183916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perspective Insights to Bio-Nanomaterials for the Treatment of Neurological Disorders.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Oct 12;9:724158. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.724158. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34712651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advanced Bioactive Polymers and Materials for Nerve Repair: Strategies and Mechanistic Insights.J Funct Biomater. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):255. doi: 10.3390/jfb16070255. J Funct Biomater. 2025. PMID: 40710469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Star Polymers Reduce Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Toxicity via Accelerated Amyloid Aggregation.Biomacromolecules. 2017 Dec 11;18(12):4249-4260. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b01301. Epub 2017 Oct 31. Biomacromolecules. 2017. PMID: 29035554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zarranz J.J., Alegre J., Gomez-Esteban J.C., Lezcano E., Ros R., Ampuero I., Vidal L., Hoenicka J., Rodriguez O., Atares B., Llorens V., Gomez Tortosa E., del Ser T., Munoz D.G., de Yebenes J.G. The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann. Neurol. 2004;55:164–173. - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos M.H., Lavedan C., Leroy E., Ide S.E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., Pike B., Root H., Rubenstein J., Boyer R., Stenroos E.S., Chandrasekharappa S., Athanassiadou A., Papapetropoulos T., Johnson W.G., Lazzarini A.M., Duvoisin R.C., Di Iorio G., Golbe L.I., Nussbaum R.L. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R., Kuhn W., Muller T., Woitalla D., Graeber M., Kosel S., Przuntek H., Epplen J.T., Schols L., Riess O. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat. Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
-
- Petrucci S., Ginevrino M., Valente E.M. Phenotypic spectrum of alpha-synuclein mutations: new insights from patients and cellular models. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016;22:S16–S20. - PubMed
-
- Singleton A., Gwinn-Hardy K., Sharabi Y., Li S.T., Holmes C., Dendi R., Hardy J., Crawley A., Goldstein D.S. Association between cardiac denervation and parkinsonism caused by alpha-synuclein gene triplication. Brain. 2004;127:768–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

