A hyperbranched dopamine-containing PEG-based polymer for the inhibition of α-synuclein fibrillation
- PMID: 26707645
- PMCID: PMC4727786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.12.060
A hyperbranched dopamine-containing PEG-based polymer for the inhibition of α-synuclein fibrillation
Abstract
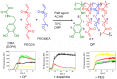
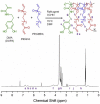
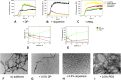
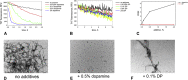
Aggregation of α-synuclein is believed to play an important role in Parkinson's disease and in other neurodegenerative maladies. Small molecule inhibitors of this process are among the most promising drug candidates for neurodegenerative diseases. Dendrimers have also been studied for anti-fibrillation applications but they can be difficult and expensive to synthetize. Here we show that RAFT polymerization can be used to produce a hyperbranched polyethylene glycol structure via a one-pot reaction. This polymer included a dopamine moiety, a known inhibitor of α-synuclein fibril formation. Dopamine within the polymer structure was capable of aggregation inhibition, although not to the same degree as free dopamine. This result opens up new avenues for the use of controlled radical polymerizations as a means of preparing hyperbranched polymers for anti-fibrillation activity, but shows that the incorporation of functional groups from known small molecules within polymers may alter their biological activity.
Keywords: Dopamine; Hyperbranched polymers; Macromolecular crowding; Parkinson's disease; Protein aggregation; RAFT polymerization; α-synuclein.
Copyright © 2016 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zarranz J.J., Alegre J., Gomez-Esteban J.C., Lezcano E., Ros R., Ampuero I., Vidal L., Hoenicka J., Rodriguez O., Atares B., Llorens V., Gomez Tortosa E., del Ser T., Munoz D.G., de Yebenes J.G. The new mutation, E46K, of alpha-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann. Neurol. 2004;55:164–173. - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos M.H., Lavedan C., Leroy E., Ide S.E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., Pike B., Root H., Rubenstein J., Boyer R., Stenroos E.S., Chandrasekharappa S., Athanassiadou A., Papapetropoulos T., Johnson W.G., Lazzarini A.M., Duvoisin R.C., Di Iorio G., Golbe L.I., Nussbaum R.L. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science. 1997;276:2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Kruger R., Kuhn W., Muller T., Woitalla D., Graeber M., Kosel S., Przuntek H., Epplen J.T., Schols L., Riess O. Ala30Pro mutation in the gene encoding alpha-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat. Genet. 1998;18:106–108. - PubMed
-
- Petrucci S., Ginevrino M., Valente E.M. Phenotypic spectrum of alpha-synuclein mutations: new insights from patients and cellular models. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016;22:S16–S20. - PubMed
-
- Singleton A., Gwinn-Hardy K., Sharabi Y., Li S.T., Holmes C., Dendi R., Hardy J., Crawley A., Goldstein D.S. Association between cardiac denervation and parkinsonism caused by alpha-synuclein gene triplication. Brain. 2004;127:768–772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

