Alectinib in ALK-positive, crizotinib-resistant, non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial
- PMID: 26708155
- PMCID: PMC4752892
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00488-X
Alectinib in ALK-positive, crizotinib-resistant, non-small-cell lung cancer: a single-group, multicentre, phase 2 trial
Erratum in
-
Correction to Lancet Oncol 2016; 17: 234-42.Lancet Oncol. 2017 Mar;18(3):e134. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30077-3. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Lancet Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28271868 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Alectinib--a highly selective, CNS-active, ALK inhibitor-showed promising clinical activity in crizotinib-naive and crizotinib-resistant patients with ALK-rearranged (ALK-positive) non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). We aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of alectinib in patients with ALK-positive NSCLC who progressed on previous crizotinib.
Methods: We did a phase 2 study at 27 centres in the USA and Canada. We enrolled patients aged 18 years or older with stage IIIB-IV, ALK-positive NSCLC who had progressed after crizotinib. Patients were treated with oral alectinib 600 mg twice daily until progression, death, or withdrawal. The primary endpoint was the proportion of patients achieving an objective response by an independent review committee using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors, version 1.1. Response endpoints were assessed in the response-evaluable population (ie, patients with measurable disease at baseline who received at least one dose of study drug), and efficacy and safety analyses were done in the intention-to-treat population (all enrolled patients). This study is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01871805. The study is ongoing and patients are still receiving treatment.
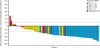
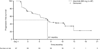
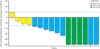
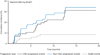
Findings: Between Sept 4, 2013, and Aug 4, 2014, 87 patients were enrolled into the study (intention-to-treat population). At the time of the primary analysis (median follow-up 4·8 months [IQR 3·3-7·1]), 33 of 69 patients with measurable disease at baseline had a confirmed partial response; thus, the proportion of patients achieving an objective response by the independent review committee was 48% (95% CI 36-60). Adverse events were predominantly grade 1 or 2, most commonly constipation (31 [36%]), fatigue (29 [33%]), myalgia 21 [24%]), and peripheral oedema 20 [23%]). The most common grade 3 and 4 adverse events were changes in laboratory values, including increased blood creatine phosphokinase (seven [8%]), increased alanine aminotransferase (five [6%]), and increased aspartate aminotransferase (four [5%]). Two patients died: one had a haemorrhage (judged related to study treatment), and one had disease progression and a history of stroke (judged unrelated to treatment).
Interpretation: Alectinib showed clinical activity and was well tolerated in patients with ALK-positive NSCLC who had progressed on crizotinib. Therefore, alectinib could be a suitable treatment for patients with ALK-positive disease who have progressed on crizotinib.
Funding: F Hoffmann-La Roche.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Alectinib in crizotinib-resistant, ALK-positive NSCLC.Lancet Oncol. 2016 Feb;17(2):134-135. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00555-0. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26708154 No abstract available.
-
Alectinib-a new chapter in the management of ALK-positive lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016 Jun;5(3):343-6. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2016.03.05. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27411885 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Current evidence in support of the second-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) tyrosine kinase inhibitor alectinib for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer positive for ALK translocation.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Oct;8(10):E1311-E1316. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.10.82. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27867615 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sequencing ALK inhibitors: alectinib in crizotinib-resistant patients, a phase 2 trial by Shaw et al.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Nov;8(11):2997-3002. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.11.76. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 28066567 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Shaw AT, Kim DW, Nakagawa K, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2385–2394. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2167–2177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

