Development of a candidate reference material for adventitious virus detection in vaccine and biologicals manufacturing by deep sequencing
- PMID: 26709640
- PMCID: PMC4823300
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.12.020
Development of a candidate reference material for adventitious virus detection in vaccine and biologicals manufacturing by deep sequencing
Abstract
Background: Unbiased deep sequencing offers the potential for improved adventitious virus screening in vaccines and biotherapeutics. Successful implementation of such assays will require appropriate control materials to confirm assay performance and sensitivity.
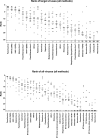
Methods: A common reference material containing 25 target viruses was produced and 16 laboratories were invited to process it using their preferred adventitious virus detection assay.
Results: Fifteen laboratories returned results, obtained using a wide range of wet-lab and informatics methods. Six of 25 target viruses were detected by all laboratories, with the remaining viruses detected by 4-14 laboratories. Six non-target viruses were detected by three or more laboratories.
Conclusion: The study demonstrated that a wide range of methods are currently used for adventitious virus detection screening in biological products by deep sequencing and that they can yield significantly different results. This underscores the need for common reference materials to ensure satisfactory assay performance and enable comparisons between laboratories.
Keywords: Adventitious virus; Collaborative study; Deep sequencing; Reference material; Vaccine.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Cutrone R., Lednicky J., Dunn G., Rizzo P., Bocchetta M., Chumakov K. Some oral poliovirus vaccines were contaminated with infectious SV40 after 1961. Cancer Res. 2005;65(Nov (22)):10273–10279. pii:65/22/10273. - PubMed
-
- Gombold J., Karakasidis S., Niksa P., Podczasy J., Neumann K., Richardson J. Systematic evaluation of in vitro and in vivo adventitious virus assays for the detection of viral contamination of cell banks and biological products. Vaccine. 2014;32(May (24)):2916–2926. pii:S0264-410X(14)00194-7. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dubin G., Toussaint J.F., Cassart J.P., Howe B., Boyce D., Friedland L. Investigation of a regulatory agency enquiry into potential porcine circovirus type 1 contamination of the human rotavirus vaccine. Rotarix: approach and outcome. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2013;9(Nov (11)):2398–2408. pii:25973. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gilliland S.M., Forrest L., Carre H., Jenkins A., Berry N., Martin J. Investigation of porcine circovirus contamination in human vaccines. Biologicals. 2012;40(Jul (4)):270–277. pii:S1045-1056(12)00026-7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

