COPI selectively drives maturation of the early Golgi
- PMID: 26709839
- PMCID: PMC4758959
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.13232
COPI selectively drives maturation of the early Golgi
Abstract
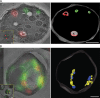
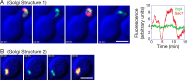
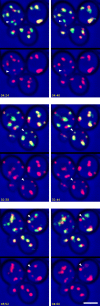
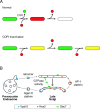
COPI coated vesicles carry material between Golgi compartments, but the role of COPI in the secretory pathway has been ambiguous. Previous studies of thermosensitive yeast COPI mutants yielded the surprising conclusion that COPI was dispensable both for the secretion of certain proteins and for Golgi cisternal maturation. To revisit these issues, we optimized the anchor-away method, which allows peripheral membrane proteins such as COPI to be sequestered rapidly by adding rapamycin. Video fluorescence microscopy revealed that COPI inactivation causes an early Golgi protein to remain in place while late Golgi proteins undergo cycles of arrival and departure. These dynamics generate partially functional hybrid Golgi structures that contain both early and late Golgi proteins, explaining how secretion can persist when COPI has been inactivated. Our findings suggest that cisternal maturation involves a COPI-dependent pathway that recycles early Golgi proteins, followed by multiple COPI-independent pathways that recycle late Golgi proteins.
Keywords: COPI; Golgi; Kex2; S. cerevisiae; Sec7; cell biology; cisternal maturation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
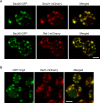
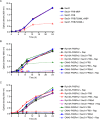
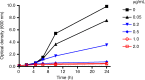
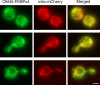




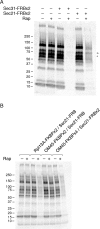


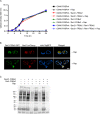




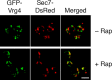
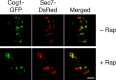




Similar articles
-
COPI is essential for Golgi cisternal maturation and dynamics.J Cell Sci. 2016 Sep 1;129(17):3251-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.193367. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Cell Sci. 2016. PMID: 27445311 Free PMC article.
-
The p24 Complex Contributes to Specify Arf1 for COPI Coat Selection.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 3;22(1):423. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010423. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33401608 Free PMC article.
-
Sec7p directs the transitions required for yeast Golgi biogenesis.Traffic. 2000 Feb;1(2):172-83. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010209.x. Traffic. 2000. PMID: 11208097
-
The COPI system: molecular mechanisms and function.FEBS Lett. 2009 Sep 3;583(17):2701-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.07.032. Epub 2009 Jul 22. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19631211 Review.
-
ER to Golgi-Dependent Protein Secretion: The Conventional Pathway.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1459:3-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3804-9_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27665548 Review.
Cited by
-
A microscopy-based kinetic analysis of yeast vacuolar protein sorting.Elife. 2020 Jun 25;9:e56844. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56844. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32584255 Free PMC article.
-
Ent3 and GGA adaptors facilitate diverse anterograde and retrograde trafficking events to and from the prevacuolar endosome.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 24;9(1):10747. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47035-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31341193 Free PMC article.
-
The Arf-GAP Age2 localizes to the late-Golgi via a conserved amphipathic helix.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Jul 24:2023.07.23.550229. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.23.550229. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Mol Biol Cell. 2023 Nov 1;34(12):ar119. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-07-0283. PMID: 37546741 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
RudLOV is an optically synchronized cargo transport method revealing unexpected effects of dynasore.EMBO Rep. 2025 Feb;26(3):613-634. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00342-z. Epub 2024 Dec 10. EMBO Rep. 2025. PMID: 39658747 Free PMC article.
-
A Kinetic View of Membrane Traffic Pathways Can Transcend the Classical View of Golgi Compartments.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Aug 6;7:153. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00153. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31448274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abazeed ME, Fuller RS. Yeast Golgi-localized, gamma-ear-containing, ADP-ribosylation factor-binding proteins are but adaptor protein-1 is not required for cell-free transport of membrane proteins from the trans-Golgi network to the prevacuolar compartment. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2008;19:4826–4836. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-05-0442. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

