TM4SF1 Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 26709920
- PMCID: PMC4692438
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144969
TM4SF1 Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
Background: TM4SF1 is overexpressed in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and affects the development of this cancer. Also, multidrug resistance (MDR) is generally associated with tumor chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. However, the correlation between TM4SF1 and MDR remains unknown. This research aims to investigate the effect of TM4SF1 on gemcitabine resistance in PDAC and explore the possible molecular mechanism between TM4SF1 and MDR.
Methods: The expression of TM4SF1 was evaluated in pancreatic cancer cell lines and human pancreatic duct epithelial (HPDE) cell lines by quantitative RT-PCR. TM4SF1 siRNA transfection was carried out using Hiperfect transfection reagent to knock down TM4SF1. The transcripts were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR, RT-PCR and western blotting for further study. The cell proliferation and apoptosis were obtained to investigate the sensitivity to gemcitabine of pancreatic cancer cells after silencing TM4SF1 in vitro. We demonstrated that cell signaling of TM4SF1 mediated chemoresistance in cancer cells by assessing the expression of multidrug resistance (MDR) genes using quantitative RT-PCR. In vivo, we used orthotopic pancreatic tumor models to investigate the effect of proliferation after silencing TM4SF1 by a lentivirus-mediated shRNA in MIA PaCa-2 cell lines.
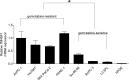
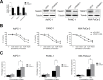
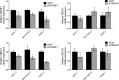
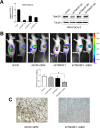
Results: The mRNA expression of TM4SF1 was higher in seven pancreatic cancer cell lines than in HPDE cell lines. In three gemcitabine-sensitive cell lines (L3.6pl, BxPC-3, SU86.86), the expression of TM4SF1 was lower than that in four gemcitabine-resistant cell lines (MIA PaCa-2, PANC-1, Hs766T, AsPC-1). We evaluated that TM4SF1 was a putative target for gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Using AsPC-1, MIA PaCa-2 and PANC-1, we investigated that TM4SF1 silencing affected cell proliferation and increased the percentages of cell apoptosis mediated by treatment with gemcitabine compared with cells which were treated with negative control. This resistance was associated with the expression of multidrug resistance genes including ABCB1 and ABCC1. In vivo, silencing of TM4SF1 in MIA PaCa-2 cell lines increased the effectiveness of gemcitabine-based treatment in orthotopic pancreatic tumor models evaluated using noninvasive bioluminescent imaging.
Conclusion: These findings suggest that TM4SF1 is a surface membrane antigen that is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer cells and increases the chemoresistance to gemcitabine. Thus, TM4SF1 may be a promising target to overcome the chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
BRD4 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell proliferation and enhances gemcitabine resistance.Oncol Rep. 2015 Apr;33(4):1699-706. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3774. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25647019
-
TIMP1 down-regulation enhances gemcitabine sensitivity and reverses chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Jul;189:114085. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114085. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32522594
-
Cyclopamine reverts acquired chemoresistance and down-regulates cancer stem cell markers in pancreatic cancer cell lines.Swiss Med Wkly. 2011 May 31;141:w13208. doi: 10.4414/smw.2011.13208. eCollection 2011. Swiss Med Wkly. 2011. PMID: 21630164
-
Gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Drug Resist Updat. 2015 Nov;23:55-68. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2015.10.002. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Drug Resist Updat. 2015. PMID: 26690340 Review.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters in progression and clinical outcome of pancreatic cancer: What is the way forward?World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug 7;24(29):3222-3238. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i29.3222. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30090003 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lost miR-141 and upregulated TM4SF1 expressions associate with poor prognosis of pancreatic cancer: regulation of EMT and angiogenesis by miR-141 and TM4SF1 via AKT.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Apr 2;21(4):354-363. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1702401. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31906774 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Chemoresistance-Associated ABC Proteins in Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic and Gastrointestinal Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 20;14(14):3524. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143524. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current research of the Notch pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Eur J Med Res. 2025 May 20;30(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02626-z. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40394648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Three Members of Transmembrane-4-Superfamily, TM4SF1, TM4SF4, and TM4SF5, as Emerging Anticancer Molecular Targets against Cancer Phenotypes and Chemoresistance.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;16(1):110. doi: 10.3390/ph16010110. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The challenge of drug resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a current overview.Cancer Biol Med. 2019 Nov;16(4):688-699. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2019.0252. Cancer Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31908888 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

