Mononuclear Phagocyte-Derived Microparticulate Caspase-1 Induces Pulmonary Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury
- PMID: 26710067
- PMCID: PMC4692444
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145607
Mononuclear Phagocyte-Derived Microparticulate Caspase-1 Induces Pulmonary Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury
Abstract
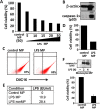
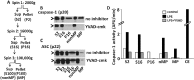
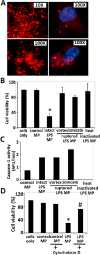
Lung endothelial cell apoptosis and injury occurs throughout all stages of acute lung injury (ALI/ARDS) and impacts disease progression. Lung endothelial injury has traditionally been focused on the role of neutrophil trafficking to lung vascular integrin receptors induced by proinflammatory cytokine expression. Although much is known about the pathogenesis of cell injury and death in ALI/ARDS, gaps remain in our knowledge; as a result of which there is currently no effective pharmacologic therapy. Enzymes known as caspases are essential for completion of the apoptotic program and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. We hypothesized that caspase-1 may serve as a key regulator of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell (HPMVEC) apoptosis in ALI/ARDS. Our recent experiments confirm that microparticles released from stimulated monocytic cells (THP1) induce lung endothelial cell apoptosis. Microparticles pretreated with the caspase-1 inhibitor, YVAD, or pan-caspase inhibitor, ZVAD, were unable to induce cell death of HPMVEC, suggesting the role of caspase-1 or its substrate in the induction of HPMVEC cell death. Neither un-induced microparticles (control) nor direct treatment with LPS induced apoptosis of HPMVEC. Further experiments showed that caspase-1 uptake into HPMVEC and the induction of HPMVEC apoptosis was facilitated by caspase-1 interactions with microparticulate vesicles. Altering vesicle integrity completely abrogated apoptosis of HPMVEC suggesting an encapsulation requirement for target cell uptake of active caspase-1. Taken together, we confirm that microparticle centered caspase-1 can play a regulator role in endothelial cell injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microparticulate Caspase 1 Regulates Gasdermin D and Pulmonary Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018 Jul;59(1):56-64. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0393OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29365280 Free PMC article.
-
Role of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in murine sepsis-induced lung injury in vivo.Respir Res. 2015 Sep 16;16(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0266-7. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26376777 Free PMC article.
-
The Src family tyrosine kinases src and yes have differential effects on inflammation-induced apoptosis in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 May 1;310(9):L880-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00306.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26919896 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary Endothelial Cell Apoptosis in Emphysema and Acute Lung Injury.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2018;228:63-86. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-68483-3_4. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29288386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A potential new pathway for heparin treatment of sepsis-induced lung injury: inhibition of pulmonary endothelial cell pyroptosis by blocking hMGB1-LPS-induced caspase-11 activation.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 15;12:984835. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.984835. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36189354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular and Extracellular Lipopolysaccharide Signaling in Sepsis: Avenues for Novel Therapeutic Strategies.J Innate Immun. 2021;13(6):323-332. doi: 10.1159/000515740. Epub 2021 May 18. J Innate Immun. 2021. PMID: 34004605 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in mesenchymal stromal cells: A novel therapeutic strategy for stroke.Exp Ther Med. 2018 May;15(5):4067-4079. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5993. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29725359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microparticle levels are reduced in patients with ARDS.Crit Care. 2017 May 25;21(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1700-7. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28545548 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles in coronary artery disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017 May;14(5):259-272. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.7. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28150804 Review.
-
The potential involvement of P2X7 receptor in COVID-19 pathogenesis: A new therapeutic target?Scand J Immunol. 2021 Feb;93(2):e12960. doi: 10.1111/sji.12960. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Scand J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32797724 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

