Catabolism of Branched Chain Amino Acids Contributes Significantly to Synthesis of Odd-Chain and Even-Chain Fatty Acids in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- PMID: 26710334
- PMCID: PMC4692509
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145850
Catabolism of Branched Chain Amino Acids Contributes Significantly to Synthesis of Odd-Chain and Even-Chain Fatty Acids in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Abstract
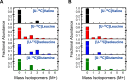
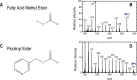
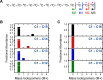
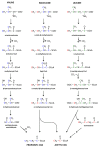
The branched chain amino acids (BCAA) valine, leucine and isoleucine have been implicated in a number of diseases including obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus, although the mechanisms are still poorly understood. Adipose tissue plays an important role in BCAA homeostasis by actively metabolizing circulating BCAA. In this work, we have investigated the link between BCAA catabolism and fatty acid synthesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes using parallel 13C-labeling experiments, mass spectrometry and model-based isotopomer data analysis. Specifically, we performed parallel labeling experiments with four fully 13C-labeled tracers, [U-13C]valine, [U-13C]leucine, [U-13C]isoleucine and [U-13C]glutamine. We measured mass isotopomer distributions of fatty acids and intracellular metabolites by GC-MS and analyzed the data using the isotopomer spectral analysis (ISA) framework. We demonstrate that 3T3-L1 adipocytes accumulate significant amounts of even chain length (C14:0, C16:0 and C18:0) and odd chain length (C15:0 and C17:0) fatty acids under standard cell culture conditions. Using a novel GC-MS method, we demonstrate that propionyl-CoA acts as the primer on fatty acid synthase for the production of odd chain fatty acids. BCAA contributed significantly to the production of all fatty acids. Leucine and isoleucine contributed at least 25% to lipogenic acetyl-CoA pool, and valine and isoleucine contributed 100% to lipogenic propionyl-CoA pool. Our results further suggest that low activity of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase and mass action kinetics of propionyl-CoA on fatty acid synthase result in high rates of odd chain fatty acid synthesis in 3T3-L1 cells. Overall, this work provides important new insights into the connection between BCAA catabolism and fatty acid synthesis in adipocytes and underscores the high capacity of adipocytes for metabolizing BCAA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Layman DK. The role of leucine in weight loss diets and glucose homeostasis. J Nutr. 2003; 133:261S–267S. - PubMed
-
- Suryawan A, Hawes JW, Harris RA, Shimomura Y, Jenkins AE, Hutson SM. A molecular model of human branched-chain amino acid metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998; 68:72–81. - PubMed
-
- Cota D, Proulx K, Smith KA, Kozma SC, Thomas G, Woods SC, et al. Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science. 2006; 312:927–930. - PubMed
-
- Hay N, Sonenberg N. Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 2004; 18:1926–1945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

