Efficacy of TB-PCR using EBUS-TBNA samples in patients with intrathoracic granulomatous lymphadenopathy
- PMID: 26710846
- PMCID: PMC4693414
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-015-0162-4
Efficacy of TB-PCR using EBUS-TBNA samples in patients with intrathoracic granulomatous lymphadenopathy
Abstract
Background: Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) is widely used to perform mediastinal lymph node sampling. However, little information is available on polymerase chain reaction for Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB-PCR) using EBUS-TBNA samples in patients with intrathoracic granulomatous lymphadenopathy (IGL).
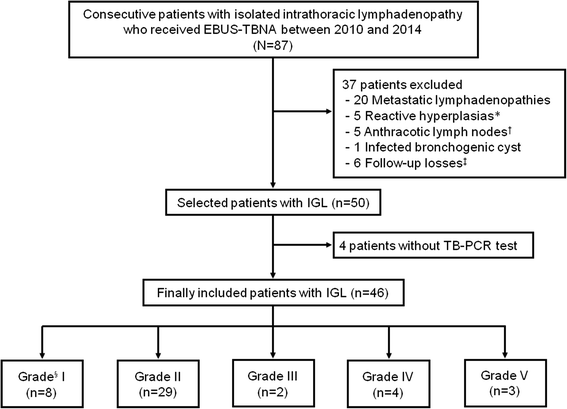
Methods: A retrospective study using a prospectively collected database was performed from January 2010 to December 2014 to evaluate the efficacy of the TB-PCR test using EBUS-TBNA samples in patients with IGL. During the study period, 87 consecutive patients with isolated intrathoracic lymphadenopathy who received EBUS-TBNA were registered and 46 patients with IGL were included.
Results: Of the 46 patients with IGL, tuberculous lymphadenitis and sarcoidosis were diagnosed in 16 and 30 patients, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of TB-PCR for tuberculous lymphadenitis were 56, 100, 100, and 81%, respectively. The overall diagnostic accuracy of TB-PCR for tuberculous lymphadenitis was 85%. In addition, seven (17%) patients had non-diagnostic results from a histological examination and all of them had non-diagnostic microbiological results of an acid-fast bacilli smear and culture. Four (57%) of the seven patients with non-diagnostic results had positive TB-PCR results, and anti-tuberculosis treatment led to clinical and radiological improvement in all of the patients.
Conclusions: TB-PCR using EBUS-TBNA samples is a useful laboratory test for diagnosing IGL. Moreover, this technique can prevent further invasive evaluation in patients whose histological and microbiological tests are non-diagnostic.
Figures
References
-
- Statement on sarcoidosis. Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, February 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:736–55. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

