Social norms information for alcohol misuse in university and college students
- PMID: 26711838
- PMCID: PMC8750744
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006748.pub4
Social norms information for alcohol misuse in university and college students
Abstract
Background: Drinking is influenced by youth perceptions of how their peers drink. These perceptions are often incorrect, overestimating peer drinking norms. If inaccurate perceptions can be corrected, young people may drink less.
Objectives: To determine whether social norms interventions reduce alcohol-related negative consequences, alcohol misuse or alcohol consumption when compared with a control (ranging from assessment only/no intervention to other educational or psychosocial interventions) among university and college students.
Search methods: The following electronic databases were searched up to July 2015: the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library), MEDLINE, EMBASE, PsycINFO. The Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) only to March 2008. Reference lists of included studies and review articles were manually searched. No restriction based on language or date was applied.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials or cluster-randomised controlled trials that compared a social normative intervention versus no intervention, alcohol education leaflet or other 'non-normative feedback' alcohol intervention and reported on alcohol consumption or alcohol-related problems in university or college students.
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures as expected by Cochrane. Each outcome was analysed by mode of delivery: mailed normative feedback (MF); web/computer normative feedback (WF); individual face-to-face normative feedback (IFF); group face-to-face normative feedback (GFF); and normative marketing campaign (MC).
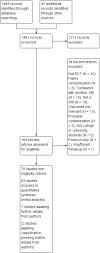
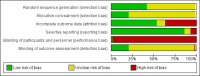
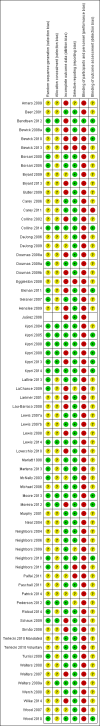
Main results: A total of 70 studies (44,958 participants) were included in the review, and 63 studies (42,784 participants) in the meta-analyses. Overall, the risk of bias assessment showed that these studies provided moderate or low quality evidence.Outcomes at four or more months post-intervention were of particular interest to assess when effects were sustained beyond the immediate short term. We have reported pooled effects across delivery modes only for those analyses for which heterogeneity across delivery modes is not substantial (I(2) < 50%).Alcohol-related problems at four or more months: IFF standardised mean difference (SMD) -0.14, 95% confidence interval (CI) -0.24 to -0.04 (participants = 2327; studies = 11; moderate quality evidence), equivalent to a decrease of 1.28 points in the 69-point alcohol problems scale score. No effects were found for WF or MF.Binge drinking at four or more months: results pooled across delivery modes: SMD -0.06, 95% CI -0.11 to -0.02 (participants = 11,292; studies = 16; moderate quality evidence), equivalent to 2.7% fewer binge drinkers if 30-day prevalence is 43.9%.Drinking quantity at four or more months: results pooled across delivery modes: SMD -0.08, 95% CI -0.12 to -0.04 (participants = 21,169; studies = 32; moderate quality evidence), equivalent to a reduction of 0.9 drinks consumed each week, from a baseline of 13.7 drinks per week.Drinking frequency at four or more months: WF SMD -0.11, 95% CI -0.17 to -0.04 (participants = 9929; studies = 10; moderate quality evidence), equivalent to a decrease of 0.17 drinking days/wk, from a baseline of 2.74 days/wk; IFF SMD -0.21, 95% CI -0.31 to -0.10 (participants = 1464; studies = 8; moderate quality evidence), equivalent to a decrease of 0.32 drinking days/wk, from a baseline of 2.74 days/wk. No effects were found for GFF or MC.Estimated blood alcohol concentration (BAC) at four or more months: peak BAC results pooled across delivery modes: SMD -0.08, 95% CI -0.17 to 0.00 (participants = 7198; studies = 11; low quality evidence), equivalent to a reduction in peak BAC from an average of 0.144% to 0.135%. No effects were found for typical BAC with IFF.
Authors' conclusions: The results of this review indicate that no substantive meaningful benefits are associated with social norms interventions for prevention of alcohol misuse among college/university students. Although some significant effects were found, we interpret the effect sizes as too small, given the measurement scales used in the studies included in this review, to be of relevance for policy or practice. Moreover, the significant effects are not consistent for all misuse measures, heterogeneity was a problem in some analyses and bias cannot be discounted as a potential cause of these findings.
Conflict of interest statement
Oxford Brookes University has received funding from the alcohol industry for prevention programme development and training. No conflict of interest has been perceived between the funding provided and this Cochrane review.
David R Foxcroft: none
Maria Teresa Moreira: none
Nerissa ML Almeida Santimano: none
Lesley A Smith: none
Figures



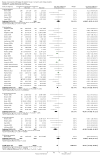
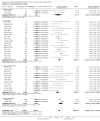
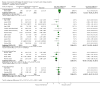
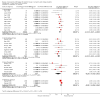






Update of
-
Social norms information for alcohol misuse in university and college students.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 26;1:CD006748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006748.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Dec 29;(12):CD006748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006748.pub4. PMID: 25622306 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Amaro 2009 {published data only}
Baer 2001 {published data only}
Bendtsen 2012 {published data only}
-
- Bendtsen P, McCambridge J, Bendtsen M, Karlsson N, Nilsen P. Effectiveness of a proactive mail‐based alcohol Internet intervention for university students: dismantling the assessment and feedback components in a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Medical Internet Research 2012;14(5):e142. - PMC - PubMed
Bewick 2008a {published data only}
-
- Bewick BM, Trusler K, Mulhern B, Barkham M, Hill AJ. The feasibility and effectiveness of a web‐based personalised feedback and social norms alcohol intervention in UK university students: a randomised control trial. Addictive Behaviors 2008;33(9):1192‐8. - PubMed
Bewick 2010 {published data only}
Bewick 2013 {published data only}
Borsari 2000 {published data only}
-
- Borsari B, Carey KB. Effects of a brief motivational intervention with college student drinkers. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2000;68:728‐33. - PubMed
Borsari 2005 {published data only}
Bryant 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bryant ZE. Testing the effectiveness of e‐mailed BASICS feedback with college students. Unpublished dissertation, Auburn U, USA,. Bryant, Zachary Earl: Auburn U , US,, 2009.
Bryant 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bryant ZE, Henslee AM, Correia CJ. Testing the effects of e‐mailed personalized feedback on risky alcohol use among college students. Addictive Behaviors 2013;38(10):2563‐7. - PubMed
Butler 2009 {published data only}
-
- Butler LH, Correia CJ. Brief alcohol intervention with college student drinkers: face‐to‐face versus computerized feedback. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2009;23(1):163‐7. - PubMed
Carey 2006 {published data only}
Carey 2011 {published data only}
Collins 2002 {published data only}
-
- Collins SE, Carey KB, Sliwinski MJ. Mailed personalized normative feedback as a brief intervention for at‐risk college drinkers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2002;63(5):559‐67. - PubMed
Collins 2014 {published data only}
DeJong 2006 {published data only}
-
- DeJong W, Schneider SK, Towvim LG, Murphy MJ, Doerr EE, Simonsen NR, et al. A multisite randomized trial of social norms marketing campaigns to reduce college student drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2006;67(6):868‐79. - PubMed
DeJong 2009 {published data only}
-
- DeJong W, Scheider SK, Towvim LG, Murphy MJ, Doerr EE, Simonsen NR, et al. A multi‐site randomized trial of social norms marketing campaigns to reduce college student drinking: a replication failure. Substance Abuse 2009;30(2):127‐40. - PubMed
Doumas 2008a {published data only}
-
- Doumas DM, Haustveit T. Reducing heavy drinking in intercollegiate athletes: evaluation of a web‐based personalized feedback program. The Sport Psychologist 2008;22(2):212‐28.
Doumas 2009a {published data only}
-
- Doumas DM, McKinley LL, Book P. Evaluation of two Web‐based alcohol interventions for mandated college students. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2009;36:65‐74. - PubMed
Doumas 2009b {published data only}
-
- Doumas DM, Andersen LL. Reducing alcohol use in first‐year university students: evaluation of a Web‐based personalized feedback program. Journal of College Counseling 2009;12(1):18–32.
Eggleston 2008 {published data only}
-
- Eggleston AM. Components analysis of a brief intervention for college drinkers. Ohio State University PhD dissertation, USA. Eggleston, Angela Meade: The Ohio State U , US,, 2008.
Ekman 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ekman DS, Andersson A, Nilsen P, Stahlbrandt H, Johansson AL, Bendtsen P. Electronic screening and brief intervention for risky drinking in Swedish university students—a randomized controlled trial. Addictive Behaviors 2011;36(6):654‐9. - PubMed
Geisner 2007 {published data only}
-
- Geisner IM, Neighbors C, Larimer ME. A randomized clinical trial of a brief, mailed intervention for symptoms of depression. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2006;74(2):393‐9. - PubMed
Henslee 2009 {published data only}
-
- Henslee AM, Correia CJ. The use of freshmen seminar programs to deliver personalized feedback. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education 2009;53(3):39‐52.
Juárez 2006 {published data only}
-
- Juarez P, Walters ST, Daugherty M, Radi C. A randomized trial of motivational interviewing and feedback with heavy drinking college students. Journal of Drug Education 2006;36(3):233‐46. - PubMed
Kypri 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kypri K, Saunders J, Williams S, McGee RO, Langley JD, Cashell‐Smith ML, et al. Web‐based screening and brief intervention for hazardous drinking: a double‐blind randomised controlled trial. Addiction 2004;99:1410‐7. - PubMed
Kypri 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kypri K, McAnally HM. Randomized controlled trial of a web‐based primary care intervention for multiple health risk behaviors. Preventive Medicine 2005;41(3‐4):761‐6. - PubMed
Kypri 2008 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Kypri K, Langley JD, Saunders JB, Cashell‐Smith ML, Herbison P. Randomized controlled trial of web‐based alcohol screening and brief intervention in primary care. Archives of Internal Medicine 2008;168(5):530‐6. - PubMed
Kypri 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kypri K, Hallett J, Howat P, McManus A, Maycock B, Bowe S, et al. Randomized controlled trial of proactive web‐based alcohol screening and brief intervention for university students. Archives of Internal Medicine 2009;169(16):1508‐14. - PubMed
Kypri 2013 {published and unpublished data}
Kypri 2014 {published and unpublished data}
LaBrie 2013 {published data only}
LaChance 2009 {published data only}
Larimer 2001 {published data only}
-
- Larimer ME, Turner AP, Anderson BK, Foder JS, Kilmer JR, Palmer RS, et al. Evaluating a brief alcohol intervention with fraternities. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2001;62:370‐80. - PubMed
Lau‐Barraco 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lau‐Barraco C, Dunn ME. Evaluation of a single‐session expectancy challenge intervention to reduce alcohol use among college students. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2008;22(2):168‐75. - PubMed
Lewis 2007a {published data only}
Lewis 2007b {published data only}
Lewis 2008 {published data only}
Lewis 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lewis MA, Patrick ME, Litt DM, Atkins DC, Kim T, Blayney JA, et al. Randomized controlled trial of a web‐delivered personalized normative feedback intervention to reduce alcohol‐related risky sexual behavior among college students. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2014;82(3):429‐40. - PMC - PubMed
Lovecchio 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lovecchio CP, Wyatt TM, DeJong W. Reductions in drinking and alcohol‐related harms reported by first‐year college students taking an online alcohol education course: a randomized trial. Journal of Health Communication 2010;15(7):805‐19. - PubMed
Marlatt 1998 {published data only}
-
- Marlatt GA, Baer JS, Kivlahan DR, Dimeff LA, Larimer ME, Quigley LA, et al. Screening and brief intervention for high‐risk college student drinkers: results from a 2‐year follow‐up assessment. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1998;66(4):604‐7. - PubMed
Martens 2013 {published data only}
McNally 2003 {published data only}
-
- McNally AM, Palfai TP. Brief group alcohol interventions with college students: examining motivational components. Journal of Drug Education 2003;33(2):159‐76. - PubMed
Michael 2006 {published data only}
-
- Michael KD, Curtin L, Kirkley DE, Jones DL, Harris R. Group‐based motivational interviewing for alcohol use among college students: an exploratory study. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice 2006;37(6):629‐34.
Moore 2013 {published data only}
Moreira 2012 {unpublished data only}
Murphy 2001 {published data only}
-
- Murphy JG, Duchnick JJ, Vuchinich RE, Davison JW, Karg R, Olson AM, et al. Relative efficacy of a brief motivational intervention for college student drinkers. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors 2001;15:373‐9. - PubMed
Neal 2004 {published data only}
-
- Neal DJ, Carey KB. Developing discrepancy within self‐regulation theory: use of personalized normative feedback and personal strivings with heavy‐drinking college students. Addictive Behaviors 2004;29(2):281‐97. - PubMed
Neighbors 2004 {published data only}
-
- Neighbors C, Larimer ME, Lewis MA. Targeting misperceptions of descriptive drinking norms: efficacy of a computer‐delivered personalized normative feedback intervention. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 2004;72(3):434‐47. - PubMed
Neighbors 2006 {published data only}
Neighbors 2009 {published data only}
Neighbors 2010 {published and unpublished data}
Neighbors 2011 {published data only}
Palfai 2011 {published data only}
-
- Palfai TP, Zisserson R, Saitz R. Using personalized feedback to reduce alcohol use among hazardous drinking college students: the moderating effect of alcohol‐related negative consequences. Addictive Behaviors 2011;36(5):539‐42. - PubMed
Paschall 2011 {published and unpublished data}
Patrick 2014 {published data only}
Pederson 2012 {published data only}
Ridout 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ridout B, Campbell A. Using Facebook to deliver a social norm intervention to reduce problem drinking at university. Drug and Alcohol Review 2014;33:667‐673. - PubMed
Schaus 2009 {published data only}
Simão 2008 {published data only}
-
- Simão MO, Kerr‐Corrêa F, Smaira SI, Trinca LA, Floripes TM, Dalben I, et al. Prevention of "risky" drinking among students at a Brazilian university. Alcohol and Alcoholism (Oxford, Oxfordshire) 2008;43(4):470‐6. - PubMed
Terlecki 2010 Mandated {published data only}
-
- Terlecki MA, Larimer ME, Copeland AL. Clinical outcomes of a brief motivational intervention for heavy drinking mandated college students: a pilot study. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2010;71(1):54‐60. - PubMed
Terlecki 2010 Voluntary {published data only}
-
- Terlecki MA, Larimer ME, Copeland AL. Clinical outcomes of a brief motivational intervention for heavy drinking mandated college students: a pilot study. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2010;71(1):54‐60. - PubMed
Turrisi 2009 {published data only}
Walters 2000 {published data only}
-
- Walters ST, Bennett ME, Miller JE. Reducing alcohol use in college students: a controlled trial of two brief interventions. Journal of Drug Education 2000;30(3):361‐72. - PubMed
Walters 2007 {published data only}
-
- Walters ST, Vader AM, Harris TR. A controlled trial of web‐based feedback for heavy drinking college students. Prevention Science 2007;8(1):83‐8. - PubMed
Walters 2009a {published data only}
Werch 2000 {published data only}
-
- Werch CE, Pappas DM, Carlson JM, DiClemente CC, Chally PS, Sinder JA. Results of a social norm intervention to prevent binge drinking among first‐year residential college students. Journal of American College Health 2000;49(2):85‐92. - PubMed
Wilke 2014 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wilke DJ, Mennicke A, Howell RL, Magnuson AB. A peer‐facilitated intervention to reduce risky drinking among fraternity and sorority members. Journal of Social Work Practice in the Addictions 2014;14(1):42‐63.
Wood 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wood MD, Capone C, Laforge R, Erickson DJ, Brand NH. Brief motivational intervention and alcohol expectancy challenge with heavy drinking college students: a randomized factorial study. Addictive Behaviors 2007;32(11):2509‐28. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbey 2009 {published data only}
Agostinelli 1995 {published data only}
-
- Agostinelli G, Brown J, Miller WR. Effects of normative feedback on consumption among heavy drinking college students. Journal of Drug Education 1995;25(1):31‐40. - PubMed
Andersson 2009 {published data only}
Baer 1992 {published data only}
-
- Baer JS, Marlatt GA, Kivlahan DR, Fromme K, Larimer ME, Williams E. An experimental test of three methods of alcohol risk reduction with young adults. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1992;60(6):974‐9. - PubMed
Barnett 1996 {published data only}
-
- Barnett LA, Far JM, Mauss AL, Miller JA. Changing perceptions of peer norms as a drinking reduction program for college students. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education 1996;41(2):39‐62.
Barnett 2007 {published data only}
Bendtsen 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bendtsen P, Johansson K, Akerlind I. Feasibility of an email‐based electronic screening and brief intervention (e‐SBI) to college students in Sweden. Addictive Behaviors 2006;31(5):777‐87. - PubMed
Bertholet 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bertholet N, Gaume J, Faouzi M, Daeppen JB, Gmel G. Perception of the amount of drinking by others in a sample of 20‐year‐old men: the more I think you drink, the more I drink. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2011;46(1):83‐7. - PubMed
Borsari 2009 {published data only}
Bush 2013 {published data only}
-
- Bush JA. The effectiveness of computer delivered personalised normative feedback on alcohol consumption and related problems among college students: a comparison of descriptive and injunctive norms. Dissertation Abstracts International Vol 73(10‐B9E)):2013.
Bustamante 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bustamante IV, Carvalho AMP, Oliveira EB, Oliveira HP, Figueroa SDS, Montoya Vasquez EM, et al. University students' perceived norms of peers and drug use: a multicentric study in five Latin American countries.. Revista Latino‐Americana de Enfermagem [online] (URL: http://www.scielo.br/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0104‐1169200... ; accessed December 2015) 2009;17:838‐43. - PubMed
Capone 2009 {published data only}
Carey 2009 {published data only}
Cimini 2009 {published data only}
Collins 2005 {published data only}
-
- Collins SE, Carey KB, Smyth J. Relationships of linguistic and motivation variables with drinking outcomes following two mailed brief interventions. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2005;66(4):526‐35. - PubMed
Collins 2009 {published data only}
Collins 2010 {published data only}
Coronges 2009 {published data only}
-
- Coronges K. Social selection and influence of alcohol & marijuana implicit cognitions and behaviors: a longitudinal investigation of peer social network dynamics. Doctoral dissertation, U Southern California, USA,. U Southern California, US,, 2009.
Cronce 2010 {published data only}
Cunningham 2008 {published data only}
Cunningham 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cunningham JA, Wong HTA. Assessing the immediate impact of normative drinking information using an immediate post‐test randomized controlled design: implications for normative feedback interventions?. Addictive Behaviors 2013;38:2252‐6. - PubMed
Curtin 2001 {published data only}
-
- Curtin L, Stephens RS, Bonenberger JL. Goal setting and feedback in the reduction of heavy drinking in female college students. Journal of College Student Psychotherapy 2001;15(3):17‐37.
Dimeff 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dimeff LA, McNeely M. Computer‐enhanced primary care practitioner advice for high‐risk college drinkers in a student primary health‐care setting. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice 2000;7(1):82‐100.
Doumas 2008b {published data only}
-
- Doumas DM, Hannah E. Preventing high‐risk drinking in youth in the workplace: a web‐based normative feedback program. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2008;34(3):263‐71. - PubMed
Doumas 2011 {published data only}
-
- Doumas DM, Workman C, Smith D, Navarro A. Reducing high‐risk drinking in mandated college students: evaluation of two personalized normative feedback interventions. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2011;40(4):376‐85. - PubMed
Ehlert 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ehlert JJ. SNAAKS: student nutrition attitudes, action, knowledge, and skills: a nutrition program tailored to the needs of predominantly Black and Hispanic college freshmen. Doctoral dissertation, Teachers College, Columbia U, USA,. Teachers Coll, Columbia U , US, 2010.
Epstein 2008 {published data only}
-
- Epstein JA, Griffin KW, Botvin GJ. A social influence model of alcohol use for inner‐city adolescents: family drinking, perceived drinking norms, and perceived social benefits of drinking. Journal of Studies on Alcohol & Drugs 2008;69(3):397‐405. - PubMed
Fleming 2010 {published data only}
Frone 2010 {published data only}
Genannt 2008 {published data only}
-
- Genannt Bonsmann SS, Walczyk T, Renggli S, Hurrell RF. Oxalic acid does not influence nonhaem iron absorption in humans: a comparison of kale and spinach meals. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;62(3):336‐41. - PubMed
Ghandour 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ghandour LA, Karam EG, Maalouf WE. Lifetime alcohol use, abuse and dependence among university students in Lebanon: exploring the role of religiosity in different religious faiths. Addiction 2009;104(6):940‐8. - PubMed
Graham 2004 {published data only}
-
- Graham JW, Tatterson JW, Roberts MM, Johnston SE. Preventing alcohol‐related harm in college students: alcohol‐related harm prevention program effects on hypothesized mediating variables. Health Education Research 2004;19(1):71‐84. - PubMed
Granfield 2002 {published data only}
-
- Granfield R. Believe it or not: examining the emergence of new drinking norms in college. Journal of Alcohol & Drug Education 2002;47(2):18‐33.
Granfield 2005 {published data only}
-
- Granfield R. Alcohol use in college: limitations on the transformation of social norms. Addiction Research and Theory 2005;13(3):281‐92.
Gregory 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gregory BM. College alcohol & life skills study with students athletes. Dissertation, Florida Atlantic University, USA, 2001.
Grossbard 2010 {published data only}
Hallett 2009 {published data only}
-
- Hallett J, Maycock B, Kypri K, Howat P, McManus A. Development of a Web‐based alcohol intervention for university students: processes and challenges. Drug & Alcohol Review 2009;28(1):31‐9. - PubMed
Hanewinkel 2005 {published data only}
-
- Hanewinkel R, Wiborg G. Brief alcohol screening and intervention for college students (BASICS): a German pilot study. SUCHT 2005;51(5):285–90.
Huchting 2008 {published data only}
Hustad 2009 {published data only}
Jacobs‐Priebe 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jacobs‐Priebe L. The social norms approach to preventing violence against women: the role of ambivalent sexism. Unpublished dissertation, Vanderbilt University, USA,. Jacobs‐Priebe, Lynette: Vanderbilt U , US,, 2008.
Kearney 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kearney B, Manley D, Mendoza R. The impact of an alcohol education program using social norming. Kentucky Nurse 2013;April/May/June:6‐7. - PubMed
Kerksiek 2008 {published data only}
-
- Kerksiek KA, Bell NJ, Harris KS. Exploring meanings of adolescent and young adult alcohol/other drug use: perspectives of students in recovery. Alcoholism Treatment Quarterly 2008;26(3):295‐311.
Kwan 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kwan PP. Contextualizing social network influences on substance use among high risk adolescents. Doctoral dissertation, U Southern California, USA,. U Southern California, US, 2010.
Kypri 2003 {published data only}
-
- Kypri K, Saunders JB, Gallagher SJ. Acceptability of various brief intervention approaches for hazardous drinking among university students. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2003;38(6):626‐8. - PubMed
Kypri 2007 {published data only}
-
- Kypri K, Langley JD, Saunders JB, Cashell‐Smith ML. Assessment may conceal therapeutic benefit: findings from a randomized controlled trial for hazardous drinking. Addiction 2007;102(1):71‐80. - PubMed
LaBrie 2007 {published data only}
-
- LaBrie JW, Pedersen ER, Lamb TF, Quinlan T. A campus‐based motivational enhancement group intervention reduces problematic drinking in freshmen male college students. Addictive Behaviors 2007;32(5):889‐901. - PubMed
LaBrie 2008 {published data only}
LaBrie 2009 {published data only}
LaBrie 2010a {published data only}
LaBrie 2010b {published data only}
Larimer 2007 {published data only}
Larimer 2009 {published data only}
Lysaught 2004 {published data only}
-
- Lysaught EM, Wodarski JS, Parris H. A comparison of an assessment/information‐based group versus an assessment‐only group: an investigation of drinking reduction with young adults. Journal of Human Behavior in the Social Environment 2004;8(4):23‐43.
Mallett 2010 {published data only}
-
- Mallett KA, Ray AE, Turrisi R, Belden C, Bachrach RL, Larimer ME. Age of drinking onset as a moderator of the efficacy of parent‐based, brief motivational, and combined intervention approaches to reduce drinking and consequences among college students. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 2010;34(7):1154‐61. - PMC - PubMed
Maney 2002 {published data only}
-
- Maney DW, Mortensen S, Powell MP, Lozinska‐Lee M, Kennedy S, Moore B. Alcohol‐free alternative activities for university students: modeling associated drinking behavior. American Journal of Health Behavior 2002;33(4):225‐33.
Martens 2007 {published data only}
-
- Matthew PM, Ciminib MD, Barrb AR, Riverob EM, Vellis PA, Desemonec GA, et al. Implementing a screening and brief intervention for high‐risk drinking in university‐based health and mental health care settings: reductions in alcohol use and correlates of success. Addictive Behaviors 2007;32(11):2563‐72. - PubMed
Mastroleo 2010 {published data only}
McCambridge 2008a {published data only}
-
- McCambridge J, Day M. Randomized controlled trial of the effects of completing the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test questionnaire on self‐reported hazardous drinking. Addiction (Abingdon, England) 2008;103(2):241‐8. - PubMed
McCambridge 2008b {published data only}
-
- McCambridge J, Slym RL, Strang J. Randomized controlled trial of motivational interviewing compared with drug information and advice for early intervention among young cannabis users. Addiction (Abingdon, England) 2008;103(11):1809‐18. - PubMed
Moreira 2008 {published data only}
Murphy 2004 {published data only}
-
- Murphy JG, Benson TA, Vuchinich RE, et al. A comparison of personalized feedback for college student drinkers delivered with and without a motivational interview. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2004;65:200‐3. - PubMed
Murphy 2005 {published data only}
-
- Murphy JG, Colby SM, Correia CJ, Vuchinich RE. Using behavioral theories of choice to predict drinking outcomes following a brief intervention. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology 2005;13(2):93–101. - PubMed
Murphy 2012 {published data only}
Nye 1997 {published data only}
-
- Nye EC, Agostinelli G, Smith JE. Enhancing alcohol problem recognition: a self‐regulation model for the effects of self‐focusing and normative information. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 1997;60(5):685‐93. - PubMed
Prince 2010 {published data only}
Ragsdale 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ragsdale FR, Gronli TD, Batool N, Haight N, Mehaffey A, McMahon EC, et al. Effect of Red Bull energy drink on cardiovascular and renal function. Amino Acids 2010;38(4):1193‐200. - PubMed
Reilly 2008 {published data only}
-
- Reilly DW, Wood MD. A randomized test of a small‐group interactive social norms intervention. Journal of American College Health 2008;57(1):53‐60. - PubMed
Saitz 2007 {published data only}
-
- Saitz R, Palfai TP, Freedner N, Winter MR, Macdonald A, LU J, et al. Screening and brief intervention online for college students: the iHealth study. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2007;42:28‐36. - PubMed
Schulenberg 2001 {published data only}
-
- Schulenberg J, Maggs JL, Long SW, Sher KJ, Gotham HJ, Baer JS, et al. The problem of college drinking: insights from a developmental perspective. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2001;25(3):473‐7. - PubMed
Scribner 2011 {published data only}
Segal 2009 {published data only}
-
- Segal DS, Stockwell T. Low alcohol alternatives: a promising strategy for reducing alcohol related harm. International Journal of Drug Policy 2009;20(2):183‐7. - PubMed
Smith 2004 {published data only}
-
- Smith BH. A randomized study of a peer‐led, small group social norming intervention designed to reduce drinking among college students. Journal of Alcohol & Drug Education 2004;47(3):67‐75.
Spijkerman 2010 {published data only}
Ståhlbrandt 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ståhlbrandt H, Johnsson KO, Berglund M. Two‐year outcome of alcohol interventions in Swedish university halls of residence: a cluster randomized trial of a brief skills training program, twelve‐step‐influenced intervention, and controls. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research 2007;31(3):458‐66. - PubMed
Stamper 2004 {published data only}
-
- Stamper GA, Smith BH, Gant R, Bogle KE. Replicated findings of an evaluation of a brief intervention designed to prevent high‐risk drinking among first‐year college students: implications for social norming theory. Journal of Alcohol and Drug Education 2004;48(2):53.
Steffian 1999 {published data only}
-
- Steffian G. Correction of normative misperceptions: an alcohol abuse prevention program. Journal of Drug Education 1999;29(2):115‐38. - PubMed
Sugarman 2009 {published data only}
Tevyaw 2007 {published data only}
Thombs 2002 {published data only}
-
- Thombs DL, Hamilton MJ. Effects of a social norm feedback campaign on the drinking norms and behavior of division I student‐athletes. Journal of Drug Education 2002;32(3):227‐44. - PubMed
Tollison 2008 {published data only}
Trocker 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Trocker MT. Alcohol abuse prevention among fraternity men: addressing individual perceptions and moderating group culture determinants of high‐risk drinking. Dissertation, University of Illinois at Urbana‐Champaign, USA 2004.
Turner 2008 {published data only}
-
- Turner J, Perkins HW, Bauerle J. Declining negative consequences related to alcohol misuse among students exposed to a social norms marketing intervention on a college campus. Journal of American College Health 2008;57(1):85‐94. - PubMed
Vernig 2009 {published data only}
-
- Vernig PM, Orsillo SM. Psychophysiological and self‐reported emotional responding in alcohol‐dependent college students: the impact of brief acceptance/mindfulness instruction. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy 2009;38(3):174‐83. - PubMed
Walker 2002 {published data only}
-
- Walker K. Report on a social norm intervention at a south Australian university. Health Promotion Journal of Australia 2002;13(3):211‐3.
Walters 2009b {published data only}
Werch 2008 {published data only}
Werch 2010 {published data only}
White 2006 {published data only}
-
- White HR, Morgan TJ, Pugh LA, et al. Evaluating two brief substance‐use interventions for mandated college students. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2006;67(2):309‐17. - PubMed
White 2007 {published data only}
-
- White HR, Mun EY, Pugh L, Morgan TJ. Long‐term effects of brief substance use interventions for mandated college students: sleeper effects of an in‐person personal feedback intervention. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2007;31(8):1380‐91. - PubMed
White 2008 {published data only}
Wild 2007 {published data only}
-
- Wild TC, Cunningham JA, Roberts AB. Controlled study of brief personalized assessment‐feedback for drinkers interested in self‐help. Addiction 2007;102(2):241‐50. - PubMed
Young 2010 {published data only}
-
- Young C, Mayson T. The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Scale (AUDIT) normative scores for a multiracial sample of Rhodes University residence students. Journal of Child & Adolescent Mental Health 2010;22(1):15‐23. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Croom 2009 {published data only}
-
- Croom K, Lewis D, Marchell T, Lesser ML, Reyna VF, Kubicki‐Bedford L, et al. Impact of an online alcohol education course on behavior and harm for incoming first‐year college students: short‐term evaluation of a randomized trial. Journal of the American College Health Association 2009;57(4):445‐54. - PubMed
Whiteside 2010 {published data only}
-
- Whiteside U. A brief personalized feedback intervention integrating a motivational interviewing therapeutic style and dialectical behavioral therapy skills for depressed or anxious heavy drinking young adults. PhD dissertation, University of Washington, USA.
Additional references
Anderson 2006
-
- Anderson P, Baumberg B. Alcohol in Europe a public health perspective. Institute of Alcohol Studies. available from http://www.ias.org.uk/uploads/alcohol_europe.pdf, accessed December 2015 2006.
Berkowitz 2005
-
- Berkowitz AD. An overview of the social norms approach. In: Lederman LC, Stewart LP editor(s). Changing the Culture of College Drinking: A Socially Situated Health Communication Campaign. Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press, 2005.
Bewick 2008b
-
- Bewick MB, Trusler B, Barkham M, Hill JA, Cahill J, Mulhern B. The effectiveness of web‐based interventions designed to decrease alcohol consumption—A systematic review. Preventive Medicine 2008;47(1):17‐26. - PubMed
Carey 2004
-
- Carey KB, Neal DJ, Collins SE. A psychometric analysis of the self‐regulation questionnaire. Addictive Behaviors 2004;29(2):253‐60. - PubMed
Carey 2007
Carter 2010
CONSORT 2010
-
- CONSORT. Consolidated standards of reporting trials. Library for health research reporting, 2010. http://www.equator‐network.org/resource‐centre/library‐of‐health‐research‐reporting/ (accessed 16 July 2010).
Dawson 2004
-
- Dawson DA, Grant BF, Stinson FS, Chou PS. Another look at heavy episodic drinking and alcohol use among college and non college youth. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2004;65:477‐89. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Egger 1997
Fager 2004
-
- Fager J, Mazurek MB. The effectiveness of intervention studies to decrease alcohol use in college undergraduate students: an integrative analysis. Worldviews on Evidence‐Based Nursing 2004;1(2):102‐19. - PubMed
Fewtrell 2008
-
- Fewtrell MS, Kennedy K, Singhal A, Martin RM, Ness A, Hadders‐Algra M, et al. How much loss to follow‐up is acceptable in long‐term randomised trials and prospective studies?. Archives of Disease in Childhood 2008;93(6):458‐61. - PubMed
Foxcroft 2014a
-
- Foxcroft DR. Can prevention classification be improved by considering the function of prevention?. Prevention Science 2014;15(6):818‐22. - PubMed
Foxcroft 2014b
-
- Foxcroft DR. "Form ever follows function. This is the law”. A prevention taxonomy based on a functional typology. Addiciones 2014;26(1):10‐14. - PubMed
Foxcroft 2016
-
- Foxcroft DR, Coombes LC, Wood S, Allen D, Almeida‐Santimano NML, Moreira TM. Motivational interviewing for alcohol misuse in young adults. Cochrane review (in press). - PubMed
GRADE 2004
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:383‐94. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated September 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. www.cochrane‐handbook.org 2011.
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hingson 2005
-
- Hingson R, Heeren T, Winter M, Wechsler H. Magnitude of alcohol‐related mortality and morbidity among U.S. college students ages 18‐24: changes from 1998 to 2001. Annual Review of Public Health 2005;26:259‐79. - PubMed
Hrobjartsson 2014
Huh 2015
Karam 2007
-
- Karam K, Kypri K, Salamoun M. Alcohol use among college students: an international perspective. Current Opinion in Psychiatry 2007;20:213‐21. - PubMed
Kypri 2002
-
- Kypri K, Langley JD, McGee R, Saunders JB, Williams S. High prevalence, persistent hazardous drinking among New Zealand tertiary students. Alcohol & Alcoholism 2002;37(5):457‐64. - PubMed
Lewis 2006
Mcalaney 2007
-
- McAlaney J, McMahon J. Normative beliefs, misperceptions and heavy episodic drinking in a British student sample. Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs 2007;68(3):385‐92. - PubMed
NIAAA 2015
-
- NIAAA (National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism). College Drinking. Factsheet October 2015;http://pubs.niaaa.nih.gov/publications/CollegeFactSheet/CollegeFactSheet... November 2015).
O' Malley 2002
-
- O'Malley P, Johnston L. Epidemiology of alcohol and other drug use among American college students. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2002;Suppl 14:23‐39. - PubMed
Perkins 1996
-
- Perkins HW, Wechsler H. Variation in perceived college drinking norms and its impact on alcohol abuse: a nationwide study. Journal of Drug Issues 1996;26(4):961‐74.
Perkins 2003
-
- Perkins HW, editor. The Social Norms Approach to Preventing School and College Age Substance Abuse: A Handbook for Educators, Counselors, and Clinicians. First Edition. San Francisco: Jossey‐Bass, 2003.
Perkins 2007
-
- Perkins W. Misperceptions of peer drinking norms in Canada: another look at the "reign of error" and its consequences among college students. Addictive Behaviors 2007;32(11):2645‐56. - PubMed
Petrosino 2005
-
- Petrosino A, Soydan H. The impact of program developers as evaluators on criminal recidivism: results from meta‐analyses of experimental and quasi‐experimental research. Journal of Experimental Criminology 2005;1(4):435‐450.
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Schunemann 2006
-
- Schünemann HJ, Jaeschke R, Cook D, Bria W, El‐Solh A, Ernst A, et al. An official ATS statement: grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in ATS guidelines and recommendations. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006;174:605‐14. - PubMed
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors), Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Tanner‐Smith 2015
Underwood 2000
-
- Underwood B, Fox K. A survey of alcohol and drug use among UK based dental undergraduates. British Dental Journal 2000;18:314‐7. - PubMed
Walters 2004
Wechsler 1994
-
- Wechsler H, Davenport A, Dowdall G, Moeykins B, Castillo S. Health and behavioral consequences of binge drinking in college: a national survey of students at 140 campuses. JAMA 1994;272(21):1672‐7. - PubMed
World Health Organization 2011
-
- World Health Organization. Global status report on alcohol and health. http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/global_alcohol_report/ms... [accessed 29th May 2014].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

