Ecology-driven stereotypes override race stereotypes
- PMID: 26712013
- PMCID: PMC4720338
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1519401113
Ecology-driven stereotypes override race stereotypes
Abstract
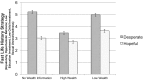
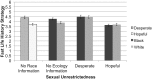
Why do race stereotypes take the forms they do? Life history theory posits that features of the ecology shape individuals' behavior. Harsh and unpredictable ("desperate") ecologies induce fast strategy behaviors such as impulsivity, whereas resource-sufficient and predictable ("hopeful") ecologies induce slow strategy behaviors such as future focus. We suggest that individuals possess a lay understanding of ecology's influence on behavior, resulting in ecology-driven stereotypes. Importantly, because race is confounded with ecology in the United States, we propose that Americans' stereotypes about racial groups actually reflect stereotypes about these groups' presumed home ecologies. Study 1 demonstrates that individuals hold ecology stereotypes, stereotyping people from desperate ecologies as possessing faster life history strategies than people from hopeful ecologies. Studies 2-4 rule out alternative explanations for those findings. Study 5, which independently manipulates race and ecology information, demonstrates that when provided with information about a person's race (but not ecology), individuals' inferences about blacks track stereotypes of people from desperate ecologies, and individuals' inferences about whites track stereotypes of people from hopeful ecologies. However, when provided with information about both the race and ecology of others, individuals' inferences reflect the targets' ecology rather than their race: black and white targets from desperate ecologies are stereotyped as equally fast life history strategists, whereas black and white targets from hopeful ecologies are stereotyped as equally slow life history strategists. These findings suggest that the content of several predominant race stereotypes may not reflect race, per se, but rather inferences about how one's ecology influences behavior.
Keywords: affordance management; ecology; life history theory; race stereotypes; stereotype content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Katz D, Braly K. Racial stereotypes in one hundred college students. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1933;28(3):280–290.
-
- Devine PG, Elliot AJ. Are racial stereotypes really fading? Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 1995;21(11):1139–1150.
-
- Madon S, et al. Ethic and national stereotypes: The Princeton trilogy revisited and revised. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. 2001;27(8):996–1010.
-
- Sng O, Williams KEG, Neuberg SL. Evolutionary approaches to stereotyping and prejudice. In: Sibley CG, Barlow FK, editors. Cambridge Handbook of the Psychology of Prejudice. Cambridge Univ Press; Cambridge, UK: 2015. in press.
-
- Gibson JJ. The Ecological Approach to Visual Perception. Houghton, Mifflin and Company; Boston, MA: 1979.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

