Enzymatic Kinetic Resolution of 2-Piperidineethanol for the Enantioselective Targeted and Diversity Oriented Synthesis
- PMID: 26712740
- PMCID: PMC4730264
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17010017
Enzymatic Kinetic Resolution of 2-Piperidineethanol for the Enantioselective Targeted and Diversity Oriented Synthesis
Abstract
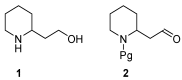
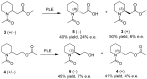
2-Piperidineethanol (1) and its corresponding N-protected aldehyde (2) were used for the synthesis of several natural and synthetic compounds. The existence of a stereocenter at position 2 of the piperidine skeleton and the presence of an easily-functionalized group, such as the alcohol, set 1 as a valuable starting material for enantioselective synthesis. Herein, are presented both synthetic and enzymatic methods for the resolution of the racemic 1, as well as an overview of synthesized natural products starting from the enantiopure 1.
Keywords: 2-piperidineethanol; alkaloid synthesis; enzymatic resolution; piperidine alkaloids.
Figures
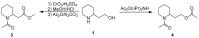
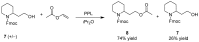










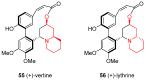
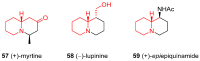
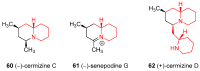
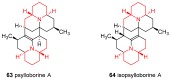


Similar articles
-
Total Synthesis of (-)-Anaferine: A Further Ramification in a Diversity-Oriented Approach.Molecules. 2020 Feb 27;25(5):1057. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051057. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32120931 Free PMC article.
-
Remote stereocenter discrimination in the enzymatic resolution of piperidine-2-ethanol. Short enantioselective synthesis of sedamine and allosedamine.J Org Chem. 2003 Nov 28;68(24):9525-7. doi: 10.1021/jo035215g. J Org Chem. 2003. PMID: 14629188
-
Alkaloid Synthesis Using Organocatalysts.Alkaloids Chem Biol. 2018;79:1-70. doi: 10.1016/bs.alkal.2017.12.001. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Alkaloids Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29455834 Review.
-
Enantioselective synthesis of cis- and trans-3,5-disubstituted piperidines. Synthesis of 20S- and 20R-dihydrocleavamine.Org Lett. 2003 Aug 21;5(17):3139-42. doi: 10.1021/ol035199+. Org Lett. 2003. PMID: 12917001
-
The 6π-azaelectrocyclization of azatrienes. Synthetic applications in natural products, bioactive heterocycles, and related fields.Nat Prod Rep. 2019 Feb 20;36(2):354-401. doi: 10.1039/c8np00014j. Nat Prod Rep. 2019. PMID: 30090891 Review.
Cited by
-
Total Synthesis of (-)-Anaferine: A Further Ramification in a Diversity-Oriented Approach.Molecules. 2020 Feb 27;25(5):1057. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051057. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32120931 Free PMC article.
-
Tensor-Based Integration of Time-Series Measurements Reveals Relationships Between Underlying Disease, Early Injury, and CD4+ Polarization in Liver Transplantation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 30:2025.05.29.655766. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.29.655766. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501716 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Simultaneous Enantiodivergent Synthesis of Diverse Lactones and Lactams via Sequential One-Pot Enzymatic Kinetic Resolution-Ring-Closing Metathesis Reactions.Molecules. 2022 Nov 9;27(22):7696. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227696. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freifelder M., Robinson R.M., Stone G.R. Hydrogenation of substituted pyridines with rhodium on carbon catalyst. J. Org. Chem. 1962;27:284–286. doi: 10.1021/jo01048a505. - DOI
-
- Paul S., Ghoshal A.K., Mandal B. Absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous solutions of 2-piperidineethanol: kinetics analysis. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009;48:1414–1419. doi: 10.1021/ie800723b. - DOI
-
- Zhang L., Fang Y. Cyclic Organosilicon Compounds as Electron Donors in Ziegler-Natta Catalyst Systems for Producing Propylene Polymer Having High Melt-Flowability. WO 2013063464. PCT Int. Appl. Patent. 2013 May 2;
-
- Krueger B.W., Sasse K., Hoever F.P., Nentwig G., Behrenz W. Preparation of α,ω-Amino Alcohols as Insect and Mite Repellents. EP 289842. Eur. Appl. Patent. 1988 Nov 9;
-
- He H., Zhao D., Zhu Y. Process for Preparation of Insect Repellent Icaridin. CN 102167681. Chinese Patent. 2011 Aug 31;
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

