New Drugs from Marine Organisms in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 26712769
- PMCID: PMC4728502
- DOI: 10.3390/md14010005
New Drugs from Marine Organisms in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
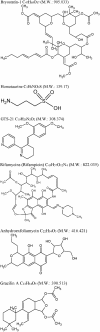
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder. Current approved drugs may only ameliorate symptoms in a restricted number of patients and for a restricted period of time. Currently, there is a translational research challenge into identifying the new effective drugs and their respective new therapeutic targets in AD and other neurodegenerative disorders. In this review, selected examples of marine-derived compounds in neurodegeneration, specifically in AD field are reported. The emphasis has been done on compounds and their possible relevant biological activities. The proposed drug development paradigm and current hypotheses should be accurately investigated in the future of AD therapy directions although taking into account successful examples of such approach represented by Cytarabine, Trabectedin, Eribulin and Ziconotide. We review a complexity of the translational research for such a development of new therapies for AD. Bryostatin is a prominent candidate for the therapy of AD and other types of dementia in humans.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; bryostatin; clinical/preclinical studies; marine drugs; mechanisms of activity; new drugs.
Figures
References
-
- World Alzheimer Report 2015. [(accessed on 3 September 2015)]. Available online: http://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2015.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical