Reversible cerebral and brain stem dysfunction in n: Hexane neuropathy
- PMID: 26713026
- PMCID: PMC4683893
- DOI: 10.4103/0972-2327.160088
Reversible cerebral and brain stem dysfunction in n: Hexane neuropathy
Abstract
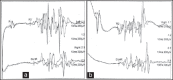
A 18-year-old male, screen printer by profession developed sensory motor polyneuropathy, change in his behavior, bilateral 6(th) and 7(th) cranial nerve palsies, down beat nystagmus and cerebellar dysarthria. He had bilaterally prolonged P100 latency; left: 137 ms; right: 144 ms. P 37 was not recordable on either side while N 20 was normal. The inter latency difference between Ipsilateral R2 and Contralateral R2 was 6.15 ms, on the left side and normal on the right side. In the follow-up, there was normalization of the blink reflex study, improvement in P100 latency [left: 114 ms; right: 120 ms.] but worsening of peripheral nerve conductions. The sequential clinical recovery was of the behavioral dysfunction, down beat nystagmus, 6(th) nerve, 7(th) nerve involvement and ataxia, in that order. Sural nerve biopsy showed loss of large diameter myelinated fibers.
Keywords: 6th and 7th nerve palsy; blink reflex; central nervous system involvement; down beat nystagmus; n- Hexane neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
N-hexane neuropathy in screen printers.Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2007 May-Jun;47(3):145-52. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17557647
-
The role of blink reflex R1 latency as an electrophysiological marker in diabetic distal symmetrical polyneuropathy.Clin Neurophysiol. 2020 Jan;131(1):34-39. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2019.09.022. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Clin Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 31751837
-
[Medial medullary infarction: report of three patients presented with central vestibular dysfunction without limb and lingual weakness].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1999 Oct;39(10):1059-63. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1999. PMID: 10655770 Review. Japanese.
-
Blink reflex, H-reflex and nerve-conduction alterations in leprosy patients.Lepr Rev. 2006 Jun;77(2):114-20. Lepr Rev. 2006. PMID: 16895067
-
Hemiplegic peripheral neuropathy accompanied with multiple cranial nerve palsy.Clin Pract. 2012 Mar 30;2(2):e40. doi: 10.4081/cp.2012.e40. eCollection 2012 Mar 30. Clin Pract. 2012. PMID: 24765439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
2,5-Hexanedione Affects Ovarian Granulosa Cells in Swine by Regulating the CDKN1A Gene: A Transcriptome Analysis.Vet Sci. 2023 Mar 7;10(3):201. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10030201. Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36977240 Free PMC article.
-
Proapoptotic effects of 2,5‑hexanedione on pheochromocytoma cells via oxidative injury.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Oct;20(4):3249-3255. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10546. Epub 2019 Aug 1. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31432125 Free PMC article.
-
Hair pyrrole adducts serve as biomarkers for peripheral nerve impairment induced by 2,5-hexanedione and n-hexane in rats.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 31;13(12):e0209939. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209939. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30596762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH. Ultrastructural studies of the dying-back process, IV. Differential vulnerability of PNS and CNS fibres in experimental central-peripheral distal axonopathies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1977;36:300–20. - PubMed
-
- Schaumburg HH, Spencer PS. Degeneration in central and peripheral nervous systems produced by pure n-hexane: An experimental study. Brain. 1976;99:183–92. - PubMed
-
- Korobkin R, Asbury AK, Summer AJ, Nielsen SL. Glue-sniffing neuropathy. Arch Neurol. 1975;32:158–62. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

