An epigenetic gateway to brain tumor cell identity
- PMID: 26713744
- PMCID: PMC5568053
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.4190
An epigenetic gateway to brain tumor cell identity
Abstract
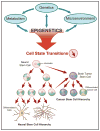
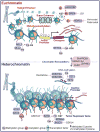
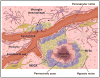
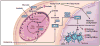
Precise targeting of genetic lesions alone has been insufficient to extend brain tumor patient survival. Brain cancer cells are diverse in their genetic, metabolic and microenvironmental compositions, accounting for their phenotypic heterogeneity and disparate responses to therapy. These factors converge at the level of the epigenome, representing a unified node that can be disrupted by pharmacologic inhibition. Aberrant epigenomes define many childhood and adult brain cancers, as demonstrated by widespread changes to DNA methylation patterns, redistribution of histone marks and disruption of chromatin structure. In this Review, we describe the convergence of genetic, metabolic and microenvironmental factors on mechanisms of epigenetic deregulation in brain cancer. We discuss how aberrant epigenetic pathways identified in brain tumors affect cell identity, cell state and neoplastic transformation, as well as addressing the potential to exploit these alterations as new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of brain cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 CA169117/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA159859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R01 CA159859/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA154130/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148699/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA148699/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087913/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA183510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA171652/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS089272/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197718/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA189647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154130/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

