Cadmium Induces Apoptosis in Freshwater Crab Sinopotamon henanense through Activating Calcium Signal Transduction Pathway
- PMID: 26714174
- PMCID: PMC4694652
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144392
Cadmium Induces Apoptosis in Freshwater Crab Sinopotamon henanense through Activating Calcium Signal Transduction Pathway
Abstract
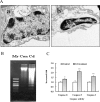
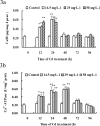
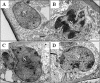
Calcium ion (Ca2+) is one of the key intracellular signals, which is implicated in the regulation of cell functions such as impregnation, cell proliferation, differentiation and death. Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic environmental pollutant that can disturb cell functions and even lead to cell death. Recently, we have found that Cd induced apoptosis in gill cells of the freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense via caspase activation. In the present study, we further investigated the role of calcium signaling in the Cd-induced apoptosis in the animals. Our data showed that Cd triggered gill cell apoptosis which is evidenced by apoptotic DNA fragmentation, activations of caspases-3, -8 and -9 and the presence of apoptotic morphological features. Moreover, Cd elevated the intracellular concentration of Ca2+, the protein concentration of calmodulin (CaM) and the activity of Ca2+-ATPase in the gill cells of the crabs. Pretreatment of the animals with ethylene glycol-bis-(b-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid (EGTA), Ca2+ chelator, inhibited Cd-induced activation of caspases-3, -8 and -9 as well as blocked the Cd-triggered apoptotic DNA fragmentation. The apoptotic morphological features were no longer observed in gill cells pretreated with the Ca2+ signaling inhibitors before Cd treatment. Our results indicate that Cd evokes gill cell apoptosis through activating Ca2+-CaM signaling transduction pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Cadmium induces hydrogen peroxide production and initiates hydrogen peroxide-dependent apoptosis in the gill of freshwater crab, Sinopotamon henanense.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012 Nov;156(3-4):195-201. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 Jun 9. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22692000
-
Sublethal Cd-induced cellular damage and metabolic changes in the freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014 Feb;21(3):1738-1745. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-2068-0. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014. PMID: 23975712
-
Effects of cadmium alone and in combination with low molecular weight chitosan on metallothionein, glutathione-S-transferase, acid phosphatase, and ATPase of freshwater crab Sinopotamon yangtsekiense.Environ Toxicol. 2014 Mar;29(3):298-309. doi: 10.1002/tox.21758. Epub 2012 Feb 13. Environ Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 22331632
-
Cadmium induces ultrastructural changes in the hepatopancreas of the freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense.Micron. 2013 Apr;47:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2013.01.002. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Micron. 2013. PMID: 23402952
-
Interplay of calcium and cadmium in mediating cadmium toxicity.Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Mar 25;211:54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.01.007. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Chem Biol Interact. 2014. PMID: 24463198 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of cadmium on oxidative stress and cell apoptosis in Drosophila melanogaster larvae.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 19;12(1):4762. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08758-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35307728 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis reveals GA induced apoptosis in HCT116 human colon cancer cells through calcium and p53 signal pathways.RSC Adv. 2018 Apr 3;8(22):12449-12458. doi: 10.1039/c8ra00260f. eCollection 2018 Mar 26. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35539409 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium Exposure: Mechanisms and Pathways of Toxicity and Implications for Human Health.Toxics. 2024 May 26;12(6):388. doi: 10.3390/toxics12060388. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 38922068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cadmium-Related Effects on Cellular Immunity Comprises Altered Metabolism in Earthworm Coelomocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 17;21(2):599. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020599. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31963425 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xuan RJ, Wu H, Li YJ, Wang JX, Wang L. Sublethal Cd-induced cellular damage and metabolic changes in the freshwater crab Sinopotamon henanense. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014; 21: 1738–1745. - PubMed
-
- Proskuryakov SY, Konoplyannikov AG, Gabaib VL. Necrosis: a specific form of programmed cell death? Experimental Cell Reasearch 2003; 283: 1–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

