Structural and functional analysis of RopB: a major virulence regulator in Streptococcus pyogenes
- PMID: 26714274
- PMCID: PMC4794775
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.13294
Structural and functional analysis of RopB: a major virulence regulator in Streptococcus pyogenes
Abstract
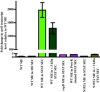
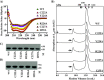
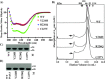
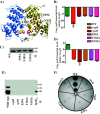
Group A Streptococcus (GAS) is an exclusive human pathogen that causes significant disease burden. Global regulator RopB of GAS controls the expression of several major virulence factors including secreted protease SpeB during high cell density. However, the molecular mechanism for RopB-dependent speB expression remains unclear. To understand the mechanism of transcription activation by RopB, we determined the crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of RopB. RopB-CTD has the TPR motif, a signature motif involved in protein-peptide interactions and shares significant structural homology with the quorum sensing RRNPP family regulators. Characterization of the high cell density-specific cell-free growth medium demonstrated the presence of a low molecular weight proteinaceous secreted factor that upregulates RopB-dependent speB expression. Together, these results suggest that RopB and its cognate peptide signals constitute an intercellular signalling machinery that controls the virulence gene expression in concert with population density. Structure-guided mutational analyses of RopB dimer interface demonstrated that single alanine substitutions at this critical interface significantly altered RopB-dependent speB expression and attenuated GAS virulence. Results presented here suggested that a properly aligned RopB dimer interface is important for GAS pathogenesis and highlighted the dimerization interactions as a plausible therapeutic target for the development of novel antimicrobials.
© 2015 The Authors. Molecular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Leaderless secreted peptide signaling molecule alters global gene expression and increases virulence of a human bacterial pathogen.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 3;114(40):E8498-E8507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705972114. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28923955 Free PMC article.
-
An amino-terminal signal peptide of Vfr protein negatively influences RopB-dependent SpeB expression and attenuates virulence in Streptococcus pyogenes.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Dec;82(6):1481-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07902.x. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 22040048 Free PMC article.
-
Endopeptidase PepO Regulates the SpeB Cysteine Protease and Is Essential for the Virulence of Invasive M1T1 Streptococcus pyogenes.J Bacteriol. 2018 Mar 26;200(8):e00654-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00654-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 29378883 Free PMC article.
-
From transcription to activation: how group A streptococcus, the flesh-eating pathogen, regulates SpeB cysteine protease production.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Aug;81(3):588-601. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07709.x. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21707787 Review.
-
Virulence factor regulation and regulatory networks in Streptococcus pyogenes and their impact on pathogen-host interactions.Trends Microbiol. 2003 May;11(5):224-32. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(03)00098-2. Trends Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12781526 Review.
Cited by
-
The leaderless communication peptide (LCP) class of quorum-sensing peptides is broadly distributed among Firmicutes.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 23;14(1):5947. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41719-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37741855 Free PMC article.
-
Leaderless secreted peptide signaling molecule alters global gene expression and increases virulence of a human bacterial pathogen.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Oct 3;114(40):E8498-E8507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705972114. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28923955 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental pH and peptide signaling control virulence of Streptococcus pyogenes via a quorum-sensing pathway.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 13;10(1):2586. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10556-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31197146 Free PMC article.
-
RstA Is a Major Regulator of Clostridioides difficile Toxin Production and Motility.mBio. 2019 Mar 12;10(2):e01991-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01991-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30862746 Free PMC article.
-
In silico characterisation of stand-alone response regulators of Streptococcus pyogenes.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 19;15(10):e0240834. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240834. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33075055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjorck, L. , Akesson, P. , Bohus, M. , Trojnar, J. , Abrahamson, M. , Olafsson, I. , and Grubb, A. (1989) Bacterial growth blocked by a synthetic peptide based on the structure of a human proteinase inhibitor. Nature 337: 385–386. - PubMed
-
- Carroll, R.K. , and Musser, J.M. (2011) From transcription to activation: how group A Streptococcus, the flesh‐eating pathogen, regulates SpeB cysteine protease production. Mol Microbiol 81: 588–601. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

