The biogeography of polymicrobial infection
- PMID: 26714431
- PMCID: PMC5116812
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro.2015.8
The biogeography of polymicrobial infection
Abstract
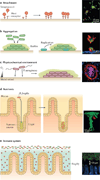
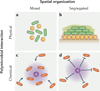
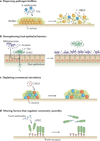
Microbial communities are spatially organized in both the environment and the human body. Although patterns exhibited by these communities are described by microbial biogeography, this discipline has previously only considered large-scale, global patterns. By contrast, the fine-scale positioning of a pathogen within an infection site can greatly alter its virulence potential. In this Review, we highlight the importance of considering spatial positioning in the study of polymicrobial infections and discuss targeting biogeography as a therapeutic strategy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Growth on Cystic Fibrosis Airway Epithelial Cells Is Enhanced during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Coinfection.mSphere. 2018 Aug 15;3(4):e00341-18. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00341-18. mSphere. 2018. PMID: 30111629 Free PMC article.
-
Biofilm models of polymicrobial infection.Future Microbiol. 2015;10(12):1997-2015. doi: 10.2217/fmb.15.109. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Future Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26592098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymicrobial biofilms by diabetic foot clinical isolates.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2016 Jan;61(1):35-43. doi: 10.1007/s12223-015-0401-3. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2016. PMID: 26104539
-
Polymicrobial community-acquired pneumonia: An emerging entity.Respirology. 2016 Jan;21(1):65-75. doi: 10.1111/resp.12663. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Respirology. 2016. PMID: 26494527 Review.
-
Polymicrobial-Host Interactions during Infection.J Mol Biol. 2016 Aug 28;428(17):3355-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 8. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27170548 Review.
Cited by
-
ddRFC: A scalable multiplexed droplet digital nucleic acid amplification test platform.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Nov 1;167:112499. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112499. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32846271 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Production of Hydrogen Cyanide Leads to Airborne Control of Staphylococcus aureus Growth in Biofilm and In Vivo Lung Environments.mBio. 2022 Oct 26;13(5):e0215422. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02154-22. Epub 2022 Sep 21. mBio. 2022. PMID: 36129311 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial interactions impact stress tolerance in a model oral community.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Oct 3;12(10):e0100524. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01005-24. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 39269155 Free PMC article.
-
Autolysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Mutant Is Suppressed by Staphylococcus aureus through Iron-Dependent Metabolism.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 28;34(4):795-803. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2312.12028. Epub 2024 Feb 2. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38303126 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotics Drive Expansion of Rare Pathogens in a Chronic Infection Microbiome Model.mSphere. 2022 Oct 26;7(5):e0031822. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00318-22. Epub 2022 Aug 16. mSphere. 2022. PMID: 35972133 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P. Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004;2:95–108. - PubMed
-
- Kaufmann SH, Schaible UE. 100th anniversary of Robert Koch’s Nobel Prize for the discovery of the tubercle bacillus. Trends Microbiol. 2005;13:469–475. - PubMed
-
- Smith H. The role of microbial interactions in infectious disease. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 1982;297:551–561. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

