Novel and conserved miRNAs in the halophyte Suaeda maritima identified by deep sequencing and computational predictions using the ESTs of two mangrove plants
- PMID: 26714456
- PMCID: PMC4696257
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-015-0682-3
Novel and conserved miRNAs in the halophyte Suaeda maritima identified by deep sequencing and computational predictions using the ESTs of two mangrove plants
Abstract
Background: Although miRNAs are reportedly involved in the salt stress tolerance of plants, miRNA profiling in plants has largely remained restricted to glycophytes, including certain crop species that do not exhibit any tolerance to salinity. Hence, this manuscript describes the results from the miRNA profiling of the halophyte Suaeda maritima, which is used worldwide to study salt tolerance in plants.
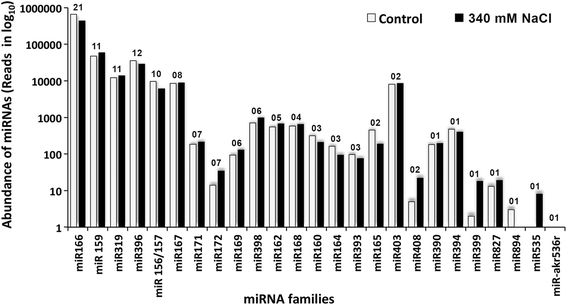
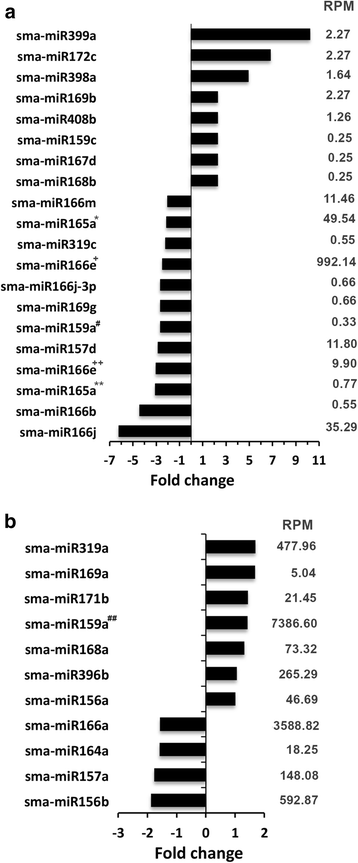
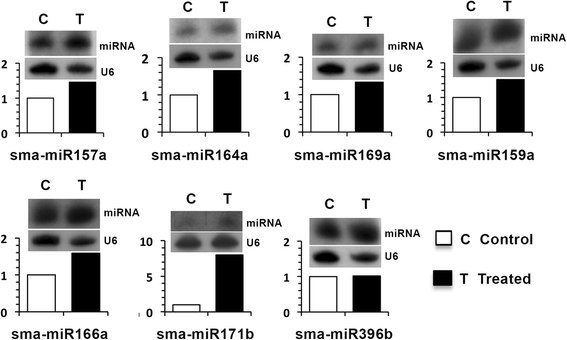
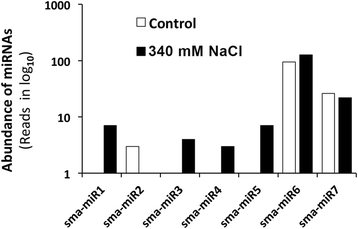
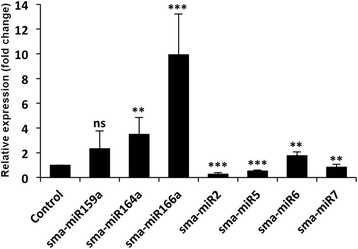
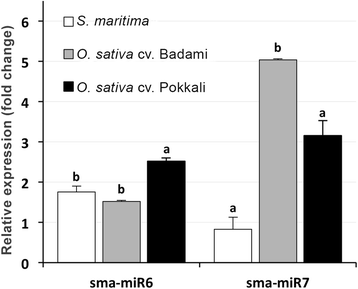
Results: A total of 134 conserved miRNAs were identified from unique sRNA reads, with 126 identified using miRBase 21.0 and an additional eight identified using the Plant Non-coding RNA Database. The presence of the precursors of seven conserved miRNAs was validated in S. maritima. In addition, 13 novel miRNAs were predicted using the ESTs of two mangrove plants, Rhizophora mangle and Heritiera littoralis, and the precursors of seven miRNAs were found in S. maritima. Most of the miRNAs considered for characterization were responsive to NaCl application, indicating their importance in the regulation of metabolic activities in plants exposed to salinity. An expression study of the novel miRNAs in plants of diverse ecological and taxonomic groups revealed that two of the miRNAs, sma-miR6 and sma-miR7, were also expressed in Oryza sativa, whereas another two, sma-miR2 and sma-miR5, were only expressed in plants growing under the influence of seawater, similar to S. maritima.
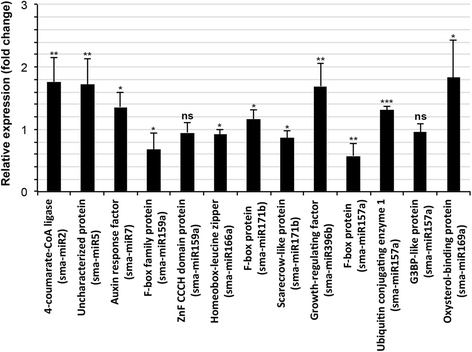
Conclusion: The distribution of conserved miRNAs among only 25 families indicated the possibility of identifying a greater number of miRNAs with increase in knowledge of the genomes of more halophytes. The expression of two novel miRNAs, sma-miR2 and sma-miR5, only in plants growing under the influence of seawater suggested their metabolic regulatory roles specific to saline environments, and such behavior might be mediated by alterations in the expression of certain genes, modifications of proteins leading to changes in their activity and production of secondary metabolites as revealed by the miRNA target predictions. Moreover, the auxin responsive factor targeted by sma-miR7 could also be involved in salt tolerance because the target is conserved between species. This study also indicated that the transcriptome of one species can be successfully used to computationally predict the miRNAs in other species, especially those that have similar metabolism, even if they are taxonomically separated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Computational prediction and experimental validation of a novel miRNA in Suaeda maritima, a halophyte.Genet Mol Res. 2016 Jan 22;15(1). doi: 10.4238/gmr.15017527. Genet Mol Res. 2016. PMID: 26909919
-
Transcriptome assembly, profiling and differential gene expression analysis of the halophyte Suaeda fruticosa provides insights into salt tolerance.BMC Genomics. 2015 May 6;16(1):353. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1553-x. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25943316 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput deep sequencing reveals that microRNAs play important roles in salt tolerance of euhalophyte Salicornia europaea.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Feb 26;15:63. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0451-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25848810 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the regulation of plant salt-stress tolerance by miRNA.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):5041-5055. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07179-6. Epub 2022 Apr 5. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35381964 Review.
-
Evaluation of Halophyte Biopotential as an Unused Natural Resource: The Case of Lobularia maritima.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 28;12(11):1583. doi: 10.3390/biom12111583. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36358933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and expression analysis of miRNAs and elucidation of their role in salt tolerance in rice varieties susceptible and tolerant to salinity.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 15;15(4):e0230958. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230958. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32294092 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of conserved orthologs and miRNAs for understanding their role in salt tolerance mechanism of Sesuvium portulacastrum L.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Nov;50(11):9731-9738. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08892-6. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37819497
-
Plant small RNAs: the essential epigenetic regulators of gene expression for salt-stress responses and tolerance.Plant Cell Rep. 2018 Jan;37(1):61-75. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2210-4. Epub 2017 Sep 26. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 28951953 Review.
-
Identification of Small RNAs Associated with Salt Stress in Chrysanthemums through High-Throughput Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 23;14(3):561. doi: 10.3390/genes14030561. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980835 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering leaf rust responsive miRNAs in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using high-throughput sequencing and prediction of their targets through degradome analysis.Planta. 2017 Jan;245(1):161-182. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2600-9. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Planta. 2017. PMID: 27699487
References
-
- Samuels M, Fire A, Sharp PA. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:14419–14427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

