Technique modifications for septodermoplasty: an illustrative case
- PMID: 26714786
- PMCID: PMC4696144
- DOI: 10.1186/s40463-015-0112-4
Technique modifications for septodermoplasty: an illustrative case
Abstract
Background: Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant disease that results in telangiectasia of the sinonasal tract, gastro-intestinal tract as well as possible arteriovenous malformations of the lung, liver and brain. One of the most common disease manifestations of HHT is epistaxis. Severe recurrent epistaxis necessitating iron therapy and blood transfusion is often managed with septodermoplasty. Its initial description was as an open surgical technique requiring nasal packing.
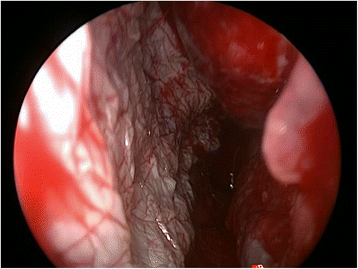
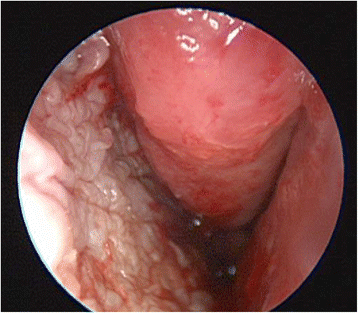
Case presentation: We describe a modified approach to septodermoplasty done completely endoscopically and without nasal packing for a patient with severe epistaxis due to HHT.
Conclusion: The described technique modifications for the presented case allowed for same day discharge following surgery, complete take of the skin graft and resultant epistaxis control that ended thepatient's transfusion dependency. The merits of these modifications should be further evaluated in a clinical trial.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Free-flap reconstruction for the management of life-threatening hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017 Oct;44(5):607-611. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2017. PMID: 27616747
-
A modified technique for septodermoplasty in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Laryngoscope. 2014 Jan;124(1):67-9. doi: 10.1002/lary.24303. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Laryngoscope. 2014. PMID: 23832829 No abstract available.
-
The effect of treatment for epistaxis secondary to hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Am J Rhinol. 2005 Jan-Feb;19(1):75-8. Am J Rhinol. 2005. PMID: 15794079
-
Treatment of Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia-Related Epistaxis.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2016 Jun;49(3):639-54. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2016.02.010. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2016. PMID: 27267016 Review.
-
Endoscopic cryotherapy for the treatment of epistaxis due to hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.J Craniofac Surg. 2014;25(2):e120-2. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000000453. J Craniofac Surg. 2014. PMID: 24469376 Review.
References
-
- Weber F. Multiple hereditary developmental angiomata (telangiectases) of the skin and mucous membranes associated with recurring hemorrhages. Lancet. 1907;2(4377):160–2.
-
- Hj R. Épistaxis répétées chez un sujet porteur de petits angiomes cutanés et muqueux. Gazette des Hopitaux Civils et Militaires. 1896;135:1322–23.
-
- Osler W. On a family form of recurring epistaxis, associated with multiple telangiectases of the skin and mucous membranes. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1901;12:333–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

