Evaluation of the neurovascular bundle position at the palate with cone beam computed tomography: an observational study
- PMID: 26714787
- PMCID: PMC4696141
- DOI: 10.1186/s13005-015-0097-2
Evaluation of the neurovascular bundle position at the palate with cone beam computed tomography: an observational study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the neurovascular bundle (NVB) position with cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT).
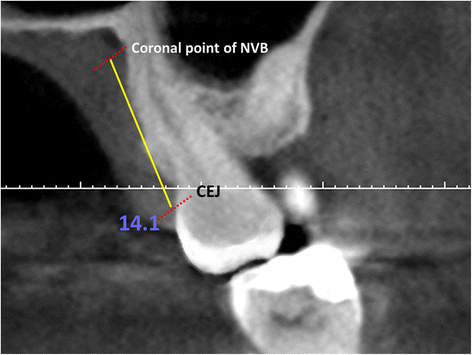
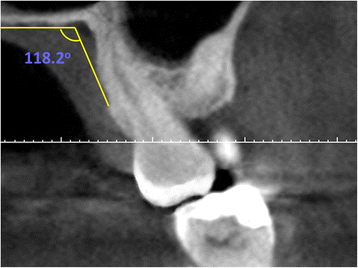
Methods: CBCT images of 345 patients were evaluated. The distance from the neurovascular bundle to the cemento-enamel junction (CEJ) was measured (DNB). The distance from mid-palatal suture to the alveolar crest was used to determine the palatal depth. Palatal junction angle (PA) was measured using the junction angle between the hard palate and alveolar crest. The relationships between the DNB and the palatal depth and between these two parameters and the PA were evaluated. Student's t-test was used to analyze the differences in DNB related to gender, and the correlation between the DNB while Pearson correlation analysis was used to determine the correlation between the DNB and age (p = 0.05). The relationship between the DNB and the palatal depth, and the relationship between these two parameters and the PA were also evaluated using Pearson correlation analysis.
Results: Except at the canine and first premolar areas the DNB was positively correlated with the palatal depth. No significant relationship between the PA and DNB or with PVD was observed. The highest DNB was 14 mm at the first molar, and the lowest was 10.8 mm at the canine.
Conclusions: Care is needed while rotating flap and harvesting the subepithelial connective tissue graft at the canine area because the neurovascular bundle passes approximately 11 mm apically to CEJ at the canine region.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Palatal mucosa thickness and palatal neurovascular bundle position evaluation by cone-beam computed tomography-retrospective study on relationships with palatal vault anatomy.PeerJ. 2021 Dec 20;9:e12699. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12699. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 35036169 Free PMC article.
-
Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of the soft tissue thickness and greater palatine foramen location in the palate.J Clin Periodontol. 2015 May;42(5):458-61. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12390. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Clin Periodontol. 2015. PMID: 25817728
-
Morphological characteristics of the palate according to mid-palatal suture maturational stage on cone-beam computed tomography images: A cross-sectional study.Int Orthod. 2025 Mar;23(1):100935. doi: 10.1016/j.ortho.2024.100935. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Int Orthod. 2025. PMID: 39454462
-
Palatal mucosal measurements in a Japanese population using cone-beam computed tomography.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2014 Jan-Feb;26(1):48-58. doi: 10.1111/jerd.12053. Epub 2013 Sep 5. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2014. PMID: 24548316
-
What Is the Safety Zone for Palatal Soft Tissue Graft Harvesting Based on the Locations of the Greater Palatine Artery and Foramen? A Systematic Review.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Feb;77(2):271.e1-271.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2018.10.002. Epub 2018 Oct 11. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 30395825
Cited by
-
Preliminary evaluation of near-infrared vein visualization technology in the screening of palatal blood vessels.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2018 Jan 1;23(1):e98-e104. doi: 10.4317/medoral.21996. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2018. PMID: 29274151 Free PMC article.
-
Palatal mucosa thickness and palatal neurovascular bundle position evaluation by cone-beam computed tomography-retrospective study on relationships with palatal vault anatomy.PeerJ. 2021 Dec 20;9:e12699. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12699. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 35036169 Free PMC article.
-
Radiological analysis of palatal arterial anatomy for periodontal surgery: insights from 3D-RA.Surg Radiol Anat. 2025 Aug 14;47(1):188. doi: 10.1007/s00276-025-03697-7. Surg Radiol Anat. 2025. PMID: 40813731
-
A novel clinical protocol for the greater palatine compression suture: A case report.J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018 Sep-Oct;22(5):456-458. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_140_18. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018. PMID: 30210198 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical variations of the greater palatine canal in cone-beam computed tomography.Surg Radiol Anat. 2017 Jul;39(7):717-723. doi: 10.1007/s00276-016-1791-x. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Surg Radiol Anat. 2017. PMID: 27933368
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources