Th17 cells reflect colon submucosal pathologic changes in active eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
- PMID: 26714881
- PMCID: PMC4696253
- DOI: 10.1186/s12865-015-0138-4
Th17 cells reflect colon submucosal pathologic changes in active eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Abstract
Background: Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) or eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EG), or both, with asthma precede the onset of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) in half of all EGPA patients. It is not known what determines whether patients with CEP or with EG following asthma will develop EGPA.
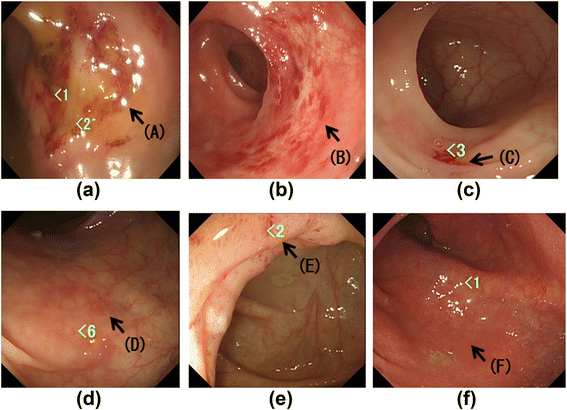
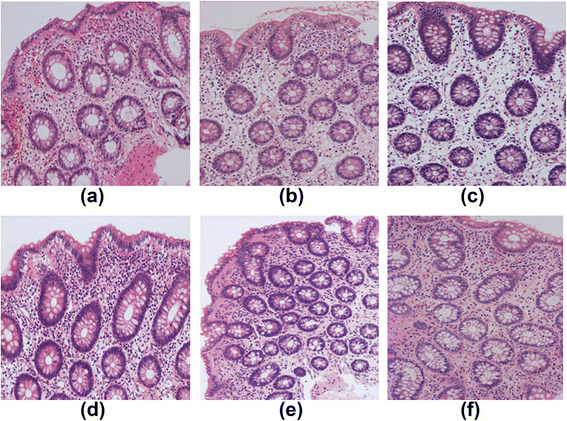
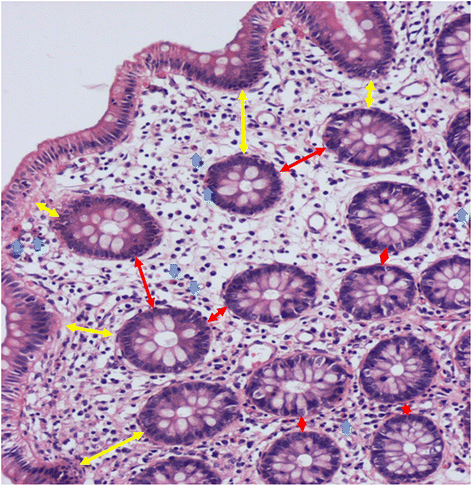
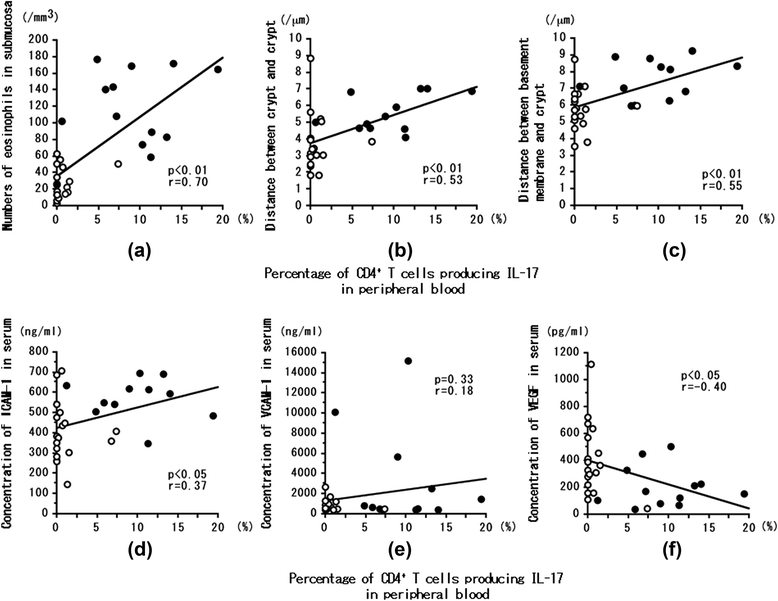
Methods: We studied 17 EGPA patients and 12 patients with CEP but without EGPA. We assayed serum ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and VEGF, and the percentage of peripheral blood CD4(+) T cells producing IL-17 (Th17 cells), at both onset and remission. We also examined the numbers of submucosal eosinophils and the basement membrane-to-crypt and crypt-to-crypt distance to evaluate edema in the colon submucosa at onset and remission in EGPA and at onset in CEP.
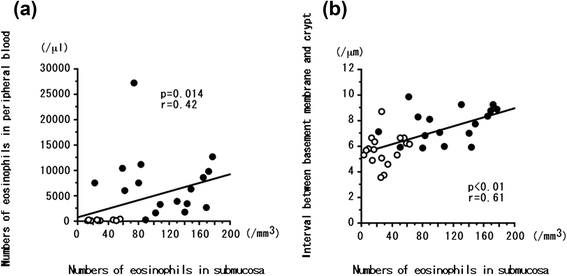
Results: Nine of 12 (75.0%) CEP patients had symptoms or endoscopic findings. Colonic submucosal eosinophil counts and edema in EGPA at onset were greater than at remission or in CEP at onset. Th17 cells (%) and serum ICAM-1 levels at onset were greater in EGPA than in CEP. In EGPA, peripheral blood Th17 cells (%) were significantly correlated with serum ICAM-1 level, colonic submucosal eosinophil count, and degree of edematous change; inversely correlated with serum VEGF level; but not correlated with VCAM-1 level.
Conclusions: Eosinophilia and colonic submucosal edematous change were greater in EGPA than in CEP. The mechanism of vasculitis in EGPA appears related to increases in serum Th17 cell numbers and ICAM-1 levels and decreases in VEGF levels.
Figures
References
-
- Lhote F, Guillevin L. Polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome. Clinical aspects and treatment. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1995;21:911–47. - PubMed
-
- Steinfeld S, Golstein M, De Vuyst P. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia (CEP) as a presenting feature of Churg-Strauss syndrome (CSS) Eur Respir J. 1994;7:2098. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

