Novel Heterotypic Rox Sites for Combinatorial Dre Recombination Strategies
- PMID: 26715092
- PMCID: PMC4777119
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.115.025841
Novel Heterotypic Rox Sites for Combinatorial Dre Recombination Strategies
Abstract
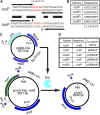
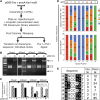
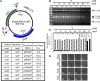
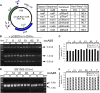
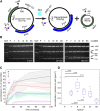
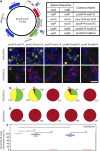
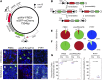
Site-specific recombinases (SSRs) such as Cre are widely used in gene targeting and genetic approaches for cell labeling and manipulation. They mediate DNA strand exchange between two DNA molecules at dedicated recognition sites. Precise understanding of the Cre recombination mechanism, including the role of individual base pairs in its loxP target site, guided the generation of mutant lox sites that specifically recombine with themselves but not with the wild type loxP. This has led to the development of a variety of combinatorial Cre-dependent genetic strategies, such as multicolor reporters, irreversible inversions, or recombination-mediated cassette exchange. Dre, a Cre-related phage integrase that recognizes roxP sites, does not cross-react with the Cre-loxP system, but has similar recombination efficiency. We have previously described intersectional genetic strategies combining Dre and Cre. We now report a mutagenesis screen aimed at identifying roxP base pairs critical for self-recognition. We describe several rox variant sites that are incompatible with roxP, but are able to efficiently recombine with themselves in either purified systems or bacterial and eukaryotic tissue culture systems. These newly identified rox sites are not recognized by Cre, thus enabling potential combinatorial strategies involving Cre, Dre, and target loci including multiple loxP and roxP variants.
Keywords: Cre recombination; Dre recombinase; gene targeting; site specific recombination.
Copyright © 2016 Chuang et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dre recombinase, like Cre, is a highly efficient site-specific recombinase in E. coli, mammalian cells and mice.Dis Model Mech. 2009 Sep-Oct;2(9-10):508-15. doi: 10.1242/dmm.003087. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Dis Model Mech. 2009. PMID: 19692579
-
Strategies for site-specific recombination with high efficiency and precise spatiotemporal resolution.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100509. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100509. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33676891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput screen identifying sequence and promiscuity characteristics of the loxP spacer region in Cre-mediated recombination.BMC Genomics. 2006 Apr 4;7:73. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-73. BMC Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16595017 Free PMC article.
-
TAILOR: transgene activation and inactivation using lox and rox in zebrafish.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 31;8(12):e85218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085218. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24391998 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding Flp-RMCE options: the potential of Recombinase Mediated Twin-Site Targeting (RMTT).Gene. 2014 Aug 10;546(2):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.06.002. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24905650 Review.
Cited by
-
iSeq 2.0: A Modular and Interchangeable Toolkit for Interaction Screening in Yeast.Cell Syst. 2019 Apr 24;8(4):338-344.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Apr 3. Cell Syst. 2019. PMID: 30954477 Free PMC article.
-
A knock-in allele of En1 expressing dre recombinase.Genesis. 2016 Aug;54(8):447-54. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22954. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Genesis. 2016. PMID: 27313055 Free PMC article.
-
A synaptic amplifier of hunger for regaining body weight in the hypothalamus.Cell Metab. 2023 May 2;35(5):770-785.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.03.002. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Cell Metab. 2023. PMID: 36965483 Free PMC article.
-
Novel methods for the generation of genetically engineered animal models.Bone. 2023 Feb;167:116612. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2022.116612. Epub 2022 Nov 13. Bone. 2023. PMID: 36379415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BATTLE: Genetically Engineered Strategies for Split-Tunable Allocation of Multiple Transgenes in the Nervous System.iScience. 2020 Jun 26;23(6):101248. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101248. Epub 2020 Jun 7. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32629613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anastassiadis K., Fu J., Patsch C., Hu S., Weidlich S., et al. , 2009. Dre recombinase, like Cre, is a highly efficient site-specific recombinase in E. coli, mammalian cells and mice. Dis. Model. Mech. 2: 508–515. - PubMed
-
- Birling M.-C., Gofflot F., Warot X., 2009. Site-specific recombinases for manipulation of the mouse genome. Methods Mol. Biol. 561: 245–263. - PubMed
-
- Bischof J., Basler K., 2008. Recombinases and their use in gene activation, gene inactivation, and transgenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 420: 175–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
