Maternal Geophagy of Calabash Chalk on Foetal Cerebral Cortex Histomorphology
- PMID: 26715904
- PMCID: PMC4683845
Maternal Geophagy of Calabash Chalk on Foetal Cerebral Cortex Histomorphology
Abstract
Background: Calabash chalk, a kaolin-base substance is a common geophagic material mostly consumed by pregnant women. This study investigated its effect on the histomorphology of the foetal cerebral cortex.
Methods: Twelve gestating Wistar rats were divided equally into groups 1 and 2. On pregnancy day seven (PD7), group 2 animals were administered 200 mg/kg body weight of calabash chalk suspension, while group 1 animals served as the control and received 1 ml of distilled water, by oral gavages and for 14 days (PD7-PD20). On PD21, the dams were sacrificed, and the foetuses removed, examined for gross malformations, weighed and culled to two foetuses per mother. Their whole brains were excised, weighed and preserved using 10% buffered formalin, and routinely processed by haematoxylin and eosin, and Luxol fast blue methods.
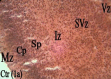
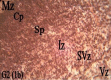
Results: The foetuses showed no morphological change, but their mean body weights was higher (p=0.0001). Histomorphological sections of the cerebral cortex showed hypertrophy and hyperplasia of cells in all the cortical layers, with less demonstrated Nissl and higher (p=0.001) cellular population compared with the control group.
Conclusion: Calabash chalk cause body weight increase and histomorphological changes in the cerebral cortex of foetuses.
Keywords: body weight; cerebral cortex; chalk; maternal; morphology; rats.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of calabash chalk on the histomorphology of the gastro-oesophageal tract of growing wistar rats.Malays J Med Sci. 2012 Jan;19(1):30-5. Malays J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22977372 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational Toxicity of Calabash Chalk (Nzu) in Wistar Rats.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2018 Oct-Dec;8(4):249-252. doi: 10.4103/ijabmr.IJABMR_412_17. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2018. PMID: 30598913 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of calabash chalk effect on femur bone morphometry and mineralization in young wistar rats: A pilot study.Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2012 Jul;2(2):107-10. doi: 10.4103/2229-516X.106352. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2012. PMID: 23776822 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of androstenedione (CAS No. 63-05-8) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies).Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010 Sep;(560):1, 7-31,33-171 passim. Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 2010. PMID: 21037592 Review.
-
Review of the nature of some geophagic materials and their potential health effects on pregnant women: some examples from Africa.Environ Geochem Health. 2019 Dec;41(6):2949-2975. doi: 10.1007/s10653-019-00288-5. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Environ Geochem Health. 2019. PMID: 30977022 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of prenatal calabash chalk geophagy on the developing brain of Wistar rats.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024 Mar 14;16:443-454. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2024.03.007. eCollection 2024 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38544793 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of "edible clay" (takere) suspension on serum lipid profiles and atherogenic indices of normal Wistar rats.Food Sci Nutr. 2019 Feb 6;7(3):977-986. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.910. eCollection 2019 Mar. Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30918640 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical analysis of calabash chalk and its effect on locomotor activities and behavior in Swiss albino mice.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 15;9(3):e14463. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14463. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36994387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abrahams PW, Follansbee MH, Hunt A, Smith B, Wragg J. Iron nutrition and possible lead toxicity: an appraisal of geophagy undertaken by pregnant women of UK Asian communities. Appl Geochem. 2006;21:98–108. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.09.015 .
-
- Henry J, Kwong AM. Why is geophagy treated like dirt? Deviant Behav. 2003;24:353–371. doi: 10.1080/713840222 .
-
- London (GB): Food Standards Agency; 2002. [cited 2012 May 12]. Agency warns of the dangers of traditional remedy for morning sickness. [Internet] Available from: http://tna.europarchive.org/20110116113217/http://www.food.gov.uk/news/p... .
-
- Dean JR, Deary ME, Gbefa BK, Scott WC. Characterisation and analysis of persistent organic pollutants and major, minor and trace elements in Calabash chalk. Chemosphere. 2004;57(1):21–25. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.05.023 . - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
