Developmental dysplasia of the hip: What has changed in the last 20 years?
- PMID: 26716085
- PMCID: PMC4686436
- DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i11.886
Developmental dysplasia of the hip: What has changed in the last 20 years?
Abstract
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) describes the spectrum of structural abnormalities that involve the growing hip. Early diagnosis and treatment is critical to provide the best possible functional outcome. Persistence of hip dysplasia into adolescence and adulthood may result in abnormal gait, decreased strength and increased rate of degenerative hip and knee joint disease. Despite efforts to recognize and treat all cases of DDH soon after birth, diagnosis is delayed in some children, and outcomes deteriorate with increasing delay of presentation. Different screening programs for DDH were implicated. The suspicion is raised based on a physical examination soon after birth. Radiography and ultrasonography are used to confirm the diagnosis. The role of other imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance imaging, is still undetermined; however, extensive research is underway on this subject. Treatment depends on the age of the patient and the reducibility of the hip joint. At an early age and up to 6 mo, the main treatment is an abduction brace like the Pavlik harness. If this fails, closed reduction and spica casting is usually done. After the age of 18 mo, treatment usually consists of open reduction and hip reconstruction surgery. Various treatment protocols have been proposed. We summarize the current practice for detection and treatment of DDH, emphasizing updates in screening and treatment during the last two decades.
Keywords: Children; Developmental dysplasia; Developmental dysplasia of the hip; Hip; Infant; Newborn.
Figures
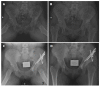
References
-
- Guille JT, Pizzutillo PD, MacEwen GD. Development dysplasia of the hip from birth to six months. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2000;8:232–242. - PubMed
-
- Klisic PJ. Congenital dislocation of the hip--a misleading term: brief report. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71:136. - PubMed
-
- Aronsson DD, Goldberg MJ, Kling TF, Roy DR. Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatrics. 1994;94:201–208. - PubMed
-
- Vitale MG, Skaggs DL. Developmental dysplasia of the hip from six months to four years of age. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2001;9:401–411. - PubMed
-
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Clinical practice guideline: early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Committee on Quality Improvement, Subcommittee on Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. American Academy of Pediatrics. Pediatrics. 2000;105:896–905. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

