Sonic hedgehog inhibitors prevent colitis-associated cancer via orchestrated mechanisms of IL-6/gp130 inhibition, 15-PGDH induction, Bcl-2 abrogation, and tumorsphere inhibition
- PMID: 26716648
- PMCID: PMC4884946
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6765
Sonic hedgehog inhibitors prevent colitis-associated cancer via orchestrated mechanisms of IL-6/gp130 inhibition, 15-PGDH induction, Bcl-2 abrogation, and tumorsphere inhibition
Abstract
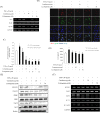
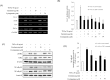
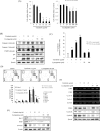
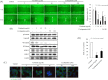
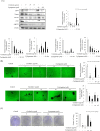
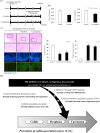
Sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling is essential in normal development of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, whereas aberrantly activated SHH is implicated in GI cancers because it facilitates carcinogenesis by redirecting stem cells. Since colitis-associated cancer (CAC) is associated with inflammatory bowel diseases, in which SHH and IL-6 signaling, inflammation propagation, and cancer stem cell (CSC) activation have been implicated, we hypothesized that SHH inhibitors may prevent CAC by blocking the above SHH-related carcinogenic pathways. In the intestinal epithelial cells IEC-6 and colon cancer cells HCT-116, IL-6 expression and its signaling were assessed with SHH inhibitors and levels of other inflammatory mediators, proliferation, apoptosis, tumorsphere formation, and tumorigenesis were also measured. CAC was induced in C57BL/6 mice by administration of azoxymethane followed by dextran sodium sulfate administration. SHH inhibitors were administered by oral gavage and the mice were sacrificed at 16 weeks. TNF-α-stimulated IEC-6 cells exhibited increased levels of proinflammatory cytokines and enzymes, whereas SHH inhibitors suppressed TNF-α-induced inflammatory signaling, especially IL-6/IL-6R/gp130 signaling. SHH inhibitors significantly induced apoptosis, inhibited cell proliferation, suppressed tumorsphere formation, and reduced stemness factors. In the mouse model, SHH inhibitors significantly reduced tumor incidence and multiplicity, decreased the expression of IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, STAT3, and NF-κB, and significantly induced apoptosis. In colosphere xenografts, SHH inhibitor significantly suppressed tumorigenesis by inhibiting tumorsphere formation. Taken together, our data suggest that administration of SHH inhibitors could be an effective strategy to prevent colitis-induced colorectal carcinogenesis, mainly by targeting IL-6 signaling, ablating CSCs, and suppressing oncogenic inflammation, achieving chemoquiescence ultimately.
Keywords: 15-PGDH; anti-inflammation; cancer stem cell; colitis associated cancer (CAC); sonic hedgehog (SHH).
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concerted actions of ameliorated colitis, aberrant crypt foci inhibition and 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase induction by sonic hedgehog inhibitor led to prevention of colitis-associated cancer.Int J Cancer. 2016 Mar 15;138(6):1482-93. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29892. Epub 2015 Oct 30. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26476372
-
Oroxylin A inhibits colitis-associated carcinogenesis through modulating the IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013 Aug;19(9):1990-2000. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0b013e318293c5e0. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013. PMID: 23823704
-
Chemopreventive Effects of Silibinin on Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Pathway.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Oct 25;2018:1562010. doi: 10.1155/2018/1562010. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30498394 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 trans-signaling and colonic cancer associated with inflammatory bowel disease.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(18):2095-103. doi: 10.2174/138161209788489140. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19519447 Review.
-
Cytokines in colitis associated cancer: potential drug targets?Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2008 Sep;7(3):187-94. doi: 10.2174/187152808785748137. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18782026 Review.
Cited by
-
Hedgehog/GLI signaling in tumor immunity - new therapeutic opportunities and clinical implications.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Dec 26;17(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0459-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31878932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear receptor coactivator SRC-1 promotes colorectal cancer progression through enhancing GLI2-mediated Hedgehog signaling.Oncogene. 2022 May;41(20):2846-2859. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02308-8. Epub 2022 Apr 13. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35418691
-
Biological characteristics of IL-6 and related intestinal diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Jan 1;17(1):204-219. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.51362. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390844 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemopreventive Strategies for Inflammation-Related Carcinogenesis: Current Status and Future Direction.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 19;18(4):867. doi: 10.3390/ijms18040867. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28422073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SMO Inhibition Modulates Cellular Plasticity and Invasiveness in Colorectal Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Feb 2;8:956. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00956. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29456503 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Feagins LA, Souza RF, Spechler SJ. Carcinogenesis in IBD: potential targets for the prevention of colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;6:297–305. - PubMed
-
- Danese S, Mantovani A. Inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal cancer: a paradigm of the Yin-Yang interplay between inflammation and cancer. Oncogene. 2010;29:3313–3323. - PubMed
-
- Choi J, Yoon SH, Kim JE, Rhee KH, Youn HS, Chung MH. Gene-specific oxidative DNA damage in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric mucosa. Int J Cancer. 2002;99:485–490. - PubMed
-
- Terzic J, Grivennikov S, Karin E, Karin M. Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:2101–2114. e2105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

