Increase of Th17 Cell Phenotype in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Chronic Allograft Dysfunction
- PMID: 26717145
- PMCID: PMC4696852
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145258
Increase of Th17 Cell Phenotype in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Chronic Allograft Dysfunction
Abstract
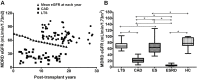
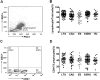
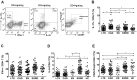
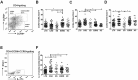
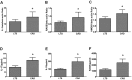
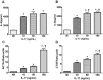
This study was performed to determine the association of Th17 cell phenotype with chronic allograft dysfunction in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs). We compared the expression of Th17 cell phenotype in KTRs with chronic allograft dysfunction group (CAD, n = 52) with four control groups (long-term stable KTRs (LTS, n = 67), early stable KTRs (ES, n = 28), end stage renal disease (ESRD, n = 45), and healthy control (HC, n = 26). We also performed in vitro study using human proximal renal tubular epithelial cell line (HPRTEpiC) to evaluate the effect of IL-17 on human renal tubular epithelial cells. The CAD group showed increased percentage of Th17 cells out of CD4+ T cells and also increased proportion of IL-17 producing cells out of effector memory T cells or out of CCR4+CCR6+/CD4+ T cells compared to the LTS group and other control groups. Also, the serum level of IL-17, IL-33, and RAGE, and the expression of IL-1beta, RAGE, and HMGB1 mRNA showed an increase in the CAD group compared to the LTS group. In vitro study revealed that IL-17 increased production of IL-6 and IL-8 and up-regulated profibrotic gene expression such as ACTA-2 and CTGF in HPRTEpiC in a dose-dependent manner, which suggests that IL-17 has a role in the development of renal tubular cell injury. The results of our study may suggest that increase of Th17 cell phenotype could be a marker for the chronic allograft injury; hence there is a need to develop diagnostic and therapeutic tools targeting the Th17 cells pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The immunomodulation role of Th17 and Treg in renal transplantation.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1113560. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1113560. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-33 levels are elevated in chronic allograft dysfunction of kidney transplant recipients and promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of human kidney (HK-2) cells.Gene. 2018 Feb 20;644:113-121. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Gene. 2018. PMID: 29122645
-
The imbalance between Tregs, Th17 cells and inflammatory cytokines among renal transplant recipients.BMC Immunol. 2015 Sep 23;16:56. doi: 10.1186/s12865-015-0118-8. BMC Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26400627 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of CD161+CD4+ T cells in the development of chronic antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplant recipients.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 16;13(7):e0200631. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200631. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30011312 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical significance of Th17 cells in kidney transplantation.Korean J Intern Med. 2018 Sep;33(5):860-866. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2018.095. Epub 2018 May 31. Korean J Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29843491 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium channel Orai1 promotes lymphocyte IL-17 expression and progressive kidney injury.J Clin Invest. 2019 Nov 1;129(11):4951-4961. doi: 10.1172/JCI126108. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 31415242 Free PMC article.
-
T cell-attracting CCL18 chemokine is a dominant rejection signal during limb transplantation.Cell Rep Med. 2022 Mar 15;3(3):100559. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100559. eCollection 2022 Mar 15. Cell Rep Med. 2022. PMID: 35492875 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Use of Tocilizumab and Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate the Development of an Anti-HLA-A2.1 Antibody in a Highly Sensitized Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 23;25(3):1378. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031378. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338657 Free PMC article.
-
The immunomodulation role of Th17 and Treg in renal transplantation.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1113560. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1113560. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of the Relationship Between Inflammation and Glomerular Filtration Rate.Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2023 Jan 19;10:20543581221132748. doi: 10.1177/20543581221132748. eCollection 2023. Can J Kidney Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 36700057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pearl JP, Parris J, Hale DA, Hoffmann SC, Bernstein WB, McCoy KL, et al. Immunocompetent T-cells with a memory-like phenotype are the dominant cell type following antibody-mediated T-cell depletion. Am J Transplant. 2005; 5: 465–474. - PubMed
-
- Trzonkowski P, Zilvetti M, Chapman S, Wieckiewicz J, Sutherland A, Friend P, et al. Homeostatic repopulation by CD28-CD8+ T cells in alemtuzumab-depleted kidney transplant recipients treated with reduced immunosuppression. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8: 338–347. 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.02078.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Louis S, Braudeau C, Giral M, Dupont A, Moizant F, Robillard N, et al. Contrasting CD25hiCD4+T cells/FOXP3 patterns in chronic rejection and operational drug-free tolerance. Transplantation. 2006; 81: 398–407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

