Low-Dose Versus Standard-Dose Tissue Plasminogen Activator in Acute Ischemic Stroke in Asian Populations: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26717400
- PMCID: PMC5291641
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000002412
Low-Dose Versus Standard-Dose Tissue Plasminogen Activator in Acute Ischemic Stroke in Asian Populations: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
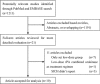
Recent studies have investigated the most efficacious dose of intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (IV-tPA) for acute ischemic stroke (AIS) patients. There remains no definitive consensus concerning the superior efficacious IV-tPA dose (standard- vs. low-dose), prompting us to perform a meta-analysis comparing the efficacy and safety profile of standard- versus low-dose IV-tPA.We identified relevant studies pertaining to the specific aim of our meta-analysis by searching PubMed and EMBASE (January 1990-September 2015) Either a fixed- or random-effects model was employed (dependent upon data heterogeneity) to analyze the efficacy and safety outcome.Ten cohort studies involving 4389 sum patients were included in the meta-analysis. By using the random-effects model, the meta-analysis indicated no statistically significant difference in favorable functional outcome (modified Rankin scale 0-1) at 3 months (heterogeneity: χ = 17.45, P = 0.04, I = 48%; OR: 0.88 [95% CI: 0.71-1.11]; P = 0.28) and incidence of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (SICH) (heterogeneity: χ = 14.41, P = 0.11, I = 38%; OR: 1.19 [95% CI: 0.76 to 1.87]; P = 0.45) between the standard- and low-dose groups. The fixed-effects model demonstrated no significant difference in mortality within 3 months (heterogeneity: χ = 6.73, P = 0.57, I = 0%; OR: 0.91 [95% CI: 0.73-1.12]; P = 0.37) between the standard- and low-dose groups.Low-dose IV-tPA is comparable to standard-dose IV-tPA in both efficacy (favorable functional outcome) and safety (SICH and mortality). Confirmation of these findings through randomized trials is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Low- versus Standard-Dose Intravenous Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator for Acute Ischemic Stroke: An Updated Meta-Analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Apr;27(4):988-997. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29224744 Review.
-
Standard-dose intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator for stroke is better than low doses.Stroke. 2014 Aug;45(8):2354-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.005989. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Stroke. 2014. PMID: 25013020
-
Low-dose tissue plasminogen activator and standard-dose tissue plasminogen activator in acute ischemic stroke in Asian populations: a review.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;36(3):161-6. doi: 10.1159/000354162. Epub 2013 Oct 12. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013. PMID: 24135524 Review.
-
Current status of intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in Asia.Int J Stroke. 2011 Dec;6(6):523-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1747-4949.2011.00671.x. Int J Stroke. 2011. PMID: 22111797 Review.
-
Intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in Asia.Expert Rev Neurother. 2012 Feb;12(2):209-17. doi: 10.1586/ern.11.148. Expert Rev Neurother. 2012. PMID: 22288676 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of chronic kidney disease on prognosis in acute stroke: unraveling the pathophysiology and clinical complexity for optimal management.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025 Feb;29(2):149-172. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02556-w. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39627467 Review.
-
Low versus standard dose intravenous alteplase in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke in Egyptian patients.Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2021 Apr;26(2):179-185. doi: 10.17712/nsj.2021.2.20200148. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2021. PMID: 33814371 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of low dose alteplase for intravenous thrombolysis in Asian stroke patients: a meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 22;7(1):16076. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16355-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29167555 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of Glycoprotein IIb-IIIa Inhibitors Used in Stroke-Related Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020 Jan-Dec;26:1076029620942594. doi: 10.1177/1076029620942594. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 32727211 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Dose vs Standard-Dose Alteplase for Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: Secondary Analysis of the ENCHANTED Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Neurol. 2017 Nov 1;74(11):1328-1335. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.2286. JAMA Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28973174 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med 1995; 333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Mori E, Minematsu K, Nakagawara J, et al. Effects of 0.6 mg/kg intravenous alteplase on vascular and clinical outcomes in middle cerebral artery occlusion: Japan Alteplase Clinical Trial II (J-ACT II). Stroke 2010; 41:461–465. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawara J, Minematsu K, Okada Y, et al. Thrombolysis with 0.6 mg/kg intravenous alteplase for acute ischemic stroke in routine clinical practice: the Japan post-Marketing Alteplase Registration Study (J-MARS). Stroke 2010; 41:1984–1989. - PubMed
-
- Toyoda K, Koga M, Naganuma M, et al. Routine use of intravenous low-dose recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in Japanese patients: general outcomes and prognostic factors from the SAMURAI register. Stroke 2009; 40:3591–3595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

