MAP1LC3B overexpression protects against Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type-1-induced defective autophagy in vitro
- PMID: 26719147
- PMCID: PMC4888554
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00213.2015
MAP1LC3B overexpression protects against Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type-1-induced defective autophagy in vitro
Abstract
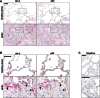
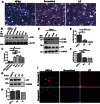
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder, and some patients with HPS develop pulmonary fibrosis, known as HPS-associated interstitial pneumonia (HPSIP). We have previously reported that HPSIP is associated with severe surfactant accumulation, lysosomal stress, and alveolar epithelial cell type II (AECII) apoptosis. Here, we hypothesized that defective autophagy might result in excessive lysosomal stress in HPSIP. Key autophagy proteins, including LC3B lipidation and p62, were increased in HPS1/2 mice lungs. Electron microscopy demonstrated a preferable binding of LC3B to the interior of lamellar bodies in the AECII of HPS1/2 mice, whereas in wild-type mice it was present on the limiting membrane in addition to the interior of the lamellar bodies. Similar observations were noted in human HPS1 lung sections. In vitro knockdown of HPS1 revealed increased LC3B lipidation and p62 accumulation, associated with an increase in proapoptotic caspases. Overexpression of LC3B decreased the HPS1 knockdown-induced p62 accumulation, whereas rapamycin treatment did not show the same effect. We conclude that loss of HPS1 protein results in impaired autophagy that is restored by exogenous LC3B and that defective autophagy might therefore play a critical role in the development and progression of HPSIP.
Keywords: Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome; Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome-associated interstitial pneumonia; alveolar epithelial cells; apoptosis; autophagy; lung fibrosis.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




References
-
- Anderson PD, Huizing M, Claassen DA, White J, Gahl WA. Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 4 (HPS-4): clinical and molecular characteristics. Hum Genet 113: 10–17, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Anikster Y, Huizing M, White J, Shevchenko YO, Fitzpatrick DL, Touchman JW, Compton JG, Bale SJ, Swank RT, Gahl WA, Toro JR. Mutation of a new gene causes a unique form of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome in a genetic isolate of central Puerto Rico. Nat Genet 28: 376–380, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Araya J, Kojima J, Takasaka N, Ito S, Fujii S, Hara H, Yanagisawa H, Kobayashi K, Tsurushige C, Kawaishi M, Kamiya N, Hirano J, Odaka M, Morikawa T, Nishimura SL, Kawabata Y, Hano H, Nakayama K, Kuwano K. Insufficient autophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 304: L56–L69, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Blommaart EF, Luiken JJ, Meijer AJ. Autophagic proteolysis: control and specificity. Histochem J 29: 365–385, 1997. - PubMed
-
- Boissy RE, Zhao Y, Gahl WA. Altered protein localization in melanocytes from Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome: support for the role of the HPS gene product in intracellular trafficking. Lab Invest 78: 1037–1048, 1998. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

