The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Adaptor Protein Skp1 Is Glycosylated by an Evolutionarily Conserved Pathway That Regulates Protist Growth and Development
- PMID: 26719340
- PMCID: PMC4813455
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.703751
The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Adaptor Protein Skp1 Is Glycosylated by an Evolutionarily Conserved Pathway That Regulates Protist Growth and Development
Abstract
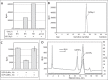
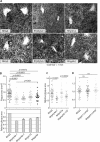
Toxoplasma gondii is a protist parasite of warm-blooded animals that causes disease by proliferating intracellularly in muscle and the central nervous system. Previous studies showed that a prolyl 4-hydroxylase related to animal HIFα prolyl hydroxylases is required for optimal parasite proliferation, especially at low O2. We also observed that Pro-154 of Skp1, a subunit of the Skp1/Cullin-1/F-box protein (SCF)-class of E3-ubiquitin ligases, is a natural substrate of this enzyme. In an unrelated protist, Dictyostelium discoideum, Skp1 hydroxyproline is modified by five sugars via the action of three glycosyltransferases, Gnt1, PgtA, and AgtA, which are required for optimal O2-dependent development. We show here that TgSkp1 hydroxyproline is modified by a similar pentasaccharide, based on mass spectrometry, and that assembly of the first three sugars is dependent on Toxoplasma homologs of Gnt1 and PgtA. Reconstitution of the glycosyltransferase reactions in extracts with radioactive sugar nucleotide substrates and appropriate Skp1 glycoforms, followed by chromatographic analysis of acid hydrolysates of the reaction products, confirmed the predicted sugar identities as GlcNAc, Gal, and Fuc. Disruptions of gnt1 or pgtA resulted in decreased parasite growth. Off target effects were excluded based on restoration of the normal glycan chain and growth upon genetic complementation. By analogy to Dictyostelium Skp1, the mechanism may involve regulation of assembly of the SCF complex. Understanding the mechanism of Toxoplasma Skp1 glycosylation is expected to help develop it as a drug target for control of the pathogen, as the glycosyltransferases are absent from mammalian hosts.
Keywords: E3 ubiquitin ligase; SCF-complex; Skp1; Toxoplasma gondii; cytoplasmic glycosylation; glycobiology; glycosyltransferase; parasitology.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Characterization of a cytoplasmic glucosyltransferase that extends the core trisaccharide of the Toxoplasma Skp1 E3 ubiquitin ligase subunit.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 10;292(45):18644-18659. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.809301. Epub 2017 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28928220 Free PMC article.
-
A terminal α3-galactose modification regulates an E3 ubiquitin ligase subunit in Toxoplasma gondii.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jul 3;295(27):9223-9243. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013792. Epub 2020 May 15. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32414843 Free PMC article.
-
O2 sensing-associated glycosylation exposes the F-box-combining site of the Dictyostelium Skp1 subunit in E3 ubiquitin ligases.J Biol Chem. 2017 Nov 17;292(46):18897-18915. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.809160. Epub 2017 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28928219 Free PMC article.
-
A cytoplasmic prolyl hydroxylation and glycosylation pathway modifies Skp1 and regulates O2-dependent development in Dictyostelium.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Feb;1800(2):160-71. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.11.006. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19914348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary and functional implications of the complex glycosylation of Skp1, a cytoplasmic/nuclear glycoprotein associated with polyubiquitination.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003 Feb;60(2):229-40. doi: 10.1007/s000180300018. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 12678488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of SCFTIR1/AFBs E3 ligase assembly by S-nitrosylation of Arabidopsis SKP1-like1 impacts on auxin signaling.Redox Biol. 2018 Sep;18:200-210. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Redox Biol. 2018. PMID: 30031268 Free PMC article.
-
Succinylated Wheat Germ Agglutinin Colocalizes with the Toxoplasma gondii Cyst Wall Glycoprotein CST1.mSphere. 2020 Mar 4;5(2):e00031-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00031-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32132158 Free PMC article.
-
The Toxoplasma oxygen-sensing protein, TgPhyA, is required for resistance to interferon gamma-mediated nutritional immunity in mice.PLoS Biol. 2024 Jun 10;22(6):e3002690. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002690. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 38857298 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen-dependent regulation of F-box proteins in Toxoplasma gondii is mediated by Skp1 glycosylation.J Biol Chem. 2024 Nov;300(11):107801. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107801. Epub 2024 Sep 21. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39307307 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma F-box protein 1 is required for daughter cell scaffold function during parasite replication.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jul 26;15(7):e1007946. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007946. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31348812 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pereira-Chioccola V. L., Vidal J. E., and Su C. (2009) Toxoplasma gondii infection and cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients. Future Microbiol. 4, 1363–1379 - PubMed
-
- Luft B. J., and Remington J. S. (1992) Toxoplasmic encephalitis in AIDS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 15, 211–222 - PubMed
-
- Lambert H., and Barragan A. (2010) Modelling parasite dissemination: host cell subversion and immune evasion by Toxoplasma gondii. Cell. Microbiol. 12, 292–300 - PubMed
-
- Xu Y., Brown K. M., Wang Z. A., van der Wel H., Teygong C., Zhang D., Blader I. J., and West C. M. (2012) The Skp1 protein from Toxoplasma is modified by a cytoplasmic prolyl 4-hydroxylase associated with oxygen sensing in the social amoeba Dictyostelium. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 25098–25110 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

