Effects of vitamin C treatment on collar-induced intimal thickening
- PMID: 26719672
- PMCID: PMC4687616
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S97020
Effects of vitamin C treatment on collar-induced intimal thickening
Abstract
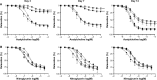
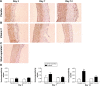
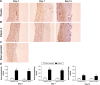
Vitamin C has efficient antioxidant properties and is involved in important physiological processes such as collagen synthesis. As such, vitamin C deficiency leads to serious complications, including vascular diseases. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of vitamin C treatment on collar-induced intimal thickening. Rabbits were fed a normocholesterolemic diet and a non-occlusive silicon collar was placed around the left carotid artery for 3, 7, and 14 days. The rabbits were treated with or without vitamin C (150 mg/kg/day). Collar-induced intimal thickening became apparent at day 7. The effect of the collar on intimal thickening was more prominent at day 14. Vitamin C treatment significantly inhibited collar-induced intimal thickening at day 14. The placement of the collar around the carotid artery decreased maximum contractile responses against contractile agents (KCl, phenylephrine, 5-hydroxytryptamine). The effect of the collar on contractile responses was enhanced as days elapsed. Decreased contractile responses of collared carotid arteries normalized at day 14 in the vitamin C treatment group. Vitamin C treatment also restored sensitivity to phenylephrine. The collar also significantly decreased acetylcholine-induced relaxations at day 3 and day 7. Acetylcholine-induced relaxations normalized in collared-arteries in the placebo group at day 14. Vitamin C treatment significantly increased acetylcholine-induced relaxations of both normal and collared carotid arteries at day 14. MMP-9 expression increased in collared arteries at day 3 and day 7 but did not change at day 14. MMP-2 expression increased in collared arteries at day 14. However, vitamin C treatment reduced collar-stimulated expression of MMP-2 at day 14. These findings indicate that vitamin C may have potentially beneficial effects on the early stages of atherosclerosis. Furthermore these results, for the first time, may indicate that vitamin C can also normalize decreased contractile response through perivascular collar placement.
Keywords: MMP; collar; intimal thickening; rabbit carotid artery; vascular reactivity; vitamin C.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of nicardipine on collar-induced intimal thickening and vascular reactivity in the rabbit.J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999 Apr;51(4):441-7. doi: 10.1211/0022357991772493. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10385217
-
Effect of verapamil on intimal thickening and vascular reactivity in the collared carotid artery of the rabbit.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;118(7):1681-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15592.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8842432 Free PMC article.
-
Dexamethasone influences intimal thickening and vascular reactivity in the rabbit collared carotid artery.Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Dec 29;294(2-3):753-61. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00635-4. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8750742
-
Effects of treatment with FK409, a nitric oxide donor, on collar-induced intimal thickening and vascular reactivity.Eur J Pharmacol. 1999 Jun 11;374(1):33-9. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00236-8. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10422638
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein enhances intimal thickening and alters vascular reactivity.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1999;61(1):19-36; discussion 36-8. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 1999. PMID: 10379196 Review.
References
-
- Newby AC. Dual role of matrix metalloproteinases (matrixins) in intimal thickening and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. Physiol Rev. 2005;85(1):1–31. - PubMed
-
- Booth RF, Martin JF, Honey AC, Hassall DG, Beesley JE, Moncada S. Rapid development of atherosclerotic lesions in the rabbit carotid artery induced by perivascular manipulation. Atherosclerosis. 1989;76(2–3):257–268. - PubMed
-
- De Meyer GR, Van Put DJ, Kockx MM, et al. Possible mechanisms of collar-induced intimal thickening. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(10):1924–1930. - PubMed
-
- Kockx MM, De Meyer GR, Jacob WA, Bult H, Herman AG. Triphasic sequence of neointimal formation in the cuffed carotid artery of the rabbit. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992;12(12):1447–1457. - PubMed
-
- Bellosta S, Baetta R, Canavesi M, et al. Raloxifene inhibits matrix metalloproteinases expression and activity in macrophages and smooth muscle cells. Pharmacol Res. 2007;56(2):160–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

